Unveiling the Tapestry of Sinai: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Sinai: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Sinai: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of Sinai: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
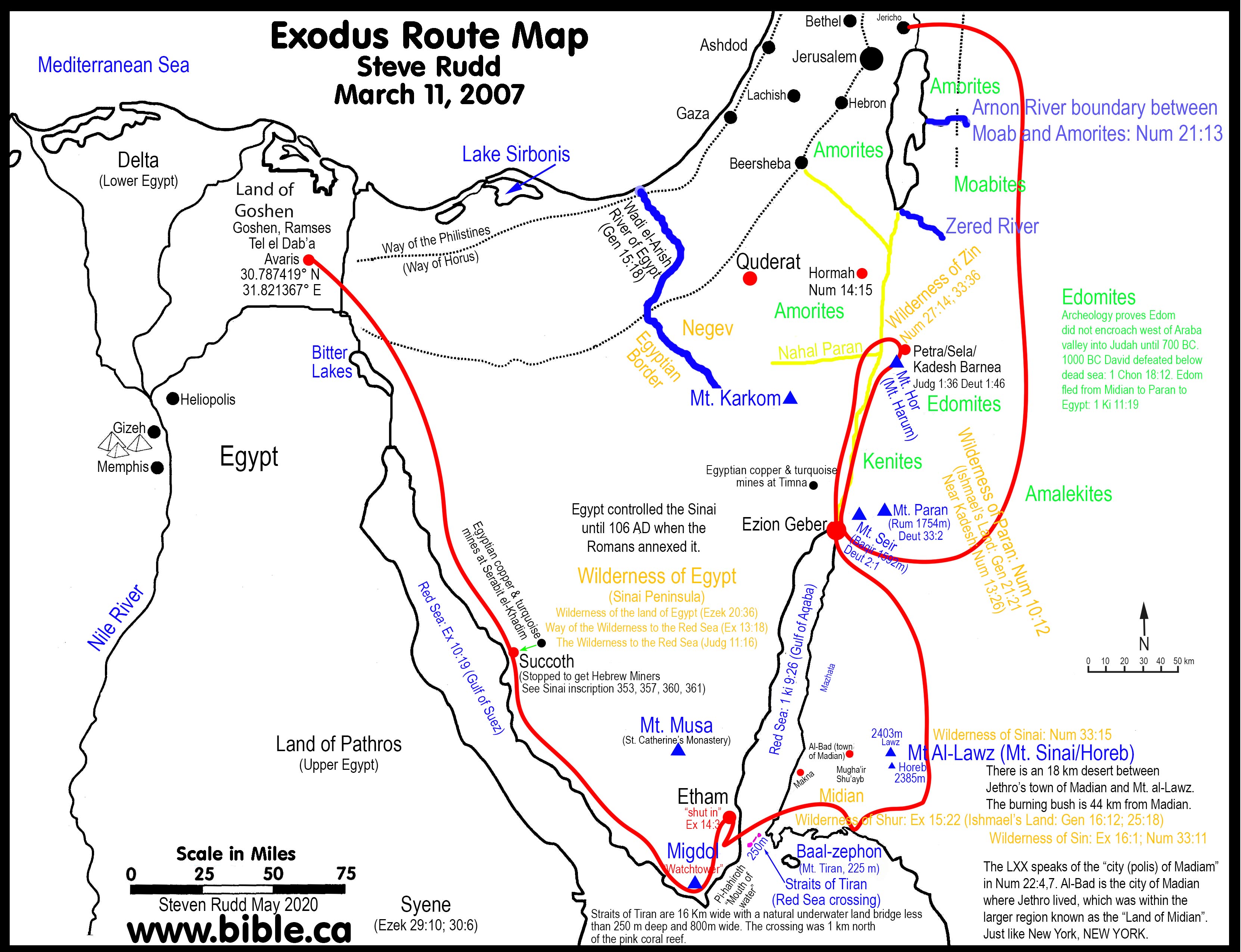
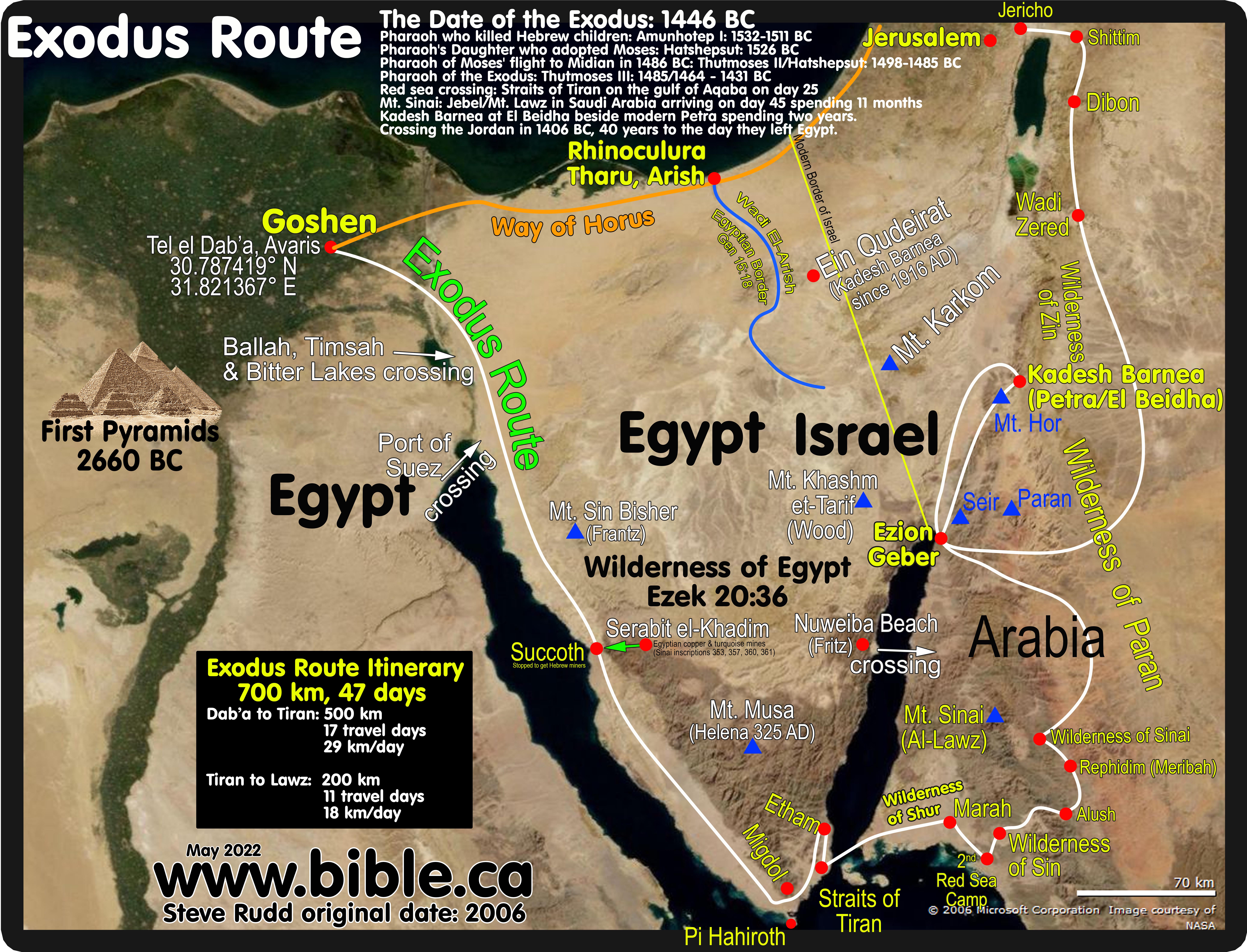
The Sinai Peninsula, a triangular landmass nestled between the northeastern corner of Africa and the southwestern tip of Asia, holds a unique position in both geography and history. Its arid landscape, sculpted by wind and time, bears witness to millennia of human activity, from ancient civilizations to modern-day encounters. This article delves into the complexities of the Sinai map, highlighting its geographical features, historical significance, and contemporary relevance.
A Land of Contrasts: Unveiling the Geographical Tapestry
The Sinai Peninsula, bordered by Egypt to the west, Israel and the Gaza Strip to the north, and the Red Sea to the east, is a microcosm of contrasting landscapes. Its diverse terrain, ranging from the towering peaks of Mount Sinai (Jabal Musa) to the sun-drenched shores of the Red Sea, offers a captivating spectrum of natural beauty.
Mountains and Valleys: The peninsula’s dominant feature is the rugged Sinai Mountains, a continuation of the Arabian Shield. These mountains, reaching heights of over 2,600 meters, are a testament to the region’s geological history, characterized by volcanic activity and tectonic shifts. The central Sinai Mountains, with their dramatic peaks and deep canyons, offer breathtaking views and serve as a haven for diverse flora and fauna.
Desert Landscapes: The majority of the Sinai Peninsula is covered by vast, arid deserts, sculpted by wind and sand. The eastern desert, bordering the Red Sea, is a harsh yet captivating landscape, characterized by towering cliffs, shimmering sand dunes, and the occasional oasis. The western desert, stretching towards the Nile Valley, presents a more subdued landscape, dotted with rocky plateaus and ancient wadis (dry riverbeds).
Coastal Delights: The Red Sea coastline, framing the eastern edge of the peninsula, is a paradise for divers and snorkelers. Its crystal-clear waters teem with vibrant coral reefs, teeming with diverse marine life. The coastal areas also offer a glimpse into the history of ancient trade routes, with remnants of ports and shipwrecks whispering tales of bygone eras.
A Crossroads of Civilizations: Historical Significance
Sinai’s geographical position has made it a pivotal crossroads throughout history, connecting Africa, Asia, and Europe. The peninsula has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the passage of nomadic tribes, and the development of religious traditions.
Ancient Kingdoms and Trade Routes: The Sinai Peninsula played a crucial role in the ancient world, serving as a bridge between Egypt and the Levant. The turquoise mines of Serabit el-Khadim, dating back to the Old Kingdom, provided valuable resources to the pharaohs. The ancient Egyptians established a network of trade routes through the peninsula, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas.
The Exodus and the Birth of Monotheism: The biblical story of the Exodus, which recounts the Israelites’ journey from Egyptian slavery to the Promised Land, is deeply intertwined with the Sinai Peninsula. Mount Sinai, believed to be the site of God’s revelation of the Ten Commandments, holds immense religious significance for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
The Rise and Fall of Empires: The Sinai Peninsula witnessed the rise of various empires, including the Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman empires. Each left its mark on the landscape, with remnants of fortifications, temples, and monasteries echoing their presence. The region also played a strategic role in the Crusades, with numerous battles fought for control of the peninsula.
Contemporary Challenges and Opportunities
The Sinai Peninsula today faces a complex set of challenges and opportunities. Its unique geography and historical legacy present both opportunities for economic development and challenges in terms of security and environmental sustainability.
Tourism and Economic Development: The Sinai Peninsula’s natural beauty and historical significance have made it a popular tourist destination. Tourism, particularly in the coastal areas, has become a significant source of income for the region. However, sustainable tourism practices and infrastructure development remain crucial for the long-term economic prosperity of the peninsula.
Security and Stability: The Sinai Peninsula has been the site of various security challenges, including terrorist activities and political unrest. The region’s proximity to conflict zones in the Middle East and its porous borders pose significant challenges to security and stability.
Environmental Sustainability: The Sinai Peninsula’s arid environment is particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. The region’s limited water resources, fragile ecosystems, and potential for desertification require careful management and conservation efforts.
FAQs about the Sinai Map
What are the major geographical features of the Sinai Peninsula?
The Sinai Peninsula is characterized by its rugged mountains, vast deserts, and coastal areas. The central Sinai Mountains, with peaks exceeding 2,600 meters, dominate the landscape. The eastern desert, bordering the Red Sea, features towering cliffs and sand dunes, while the western desert is a more subdued landscape with rocky plateaus and wadis. The Red Sea coastline offers a paradise for divers and snorkelers, with vibrant coral reefs and diverse marine life.
What is the historical significance of the Sinai Peninsula?
The Sinai Peninsula has been a crossroads of civilizations for millennia. It played a crucial role in ancient trade routes connecting Egypt and the Levant. The biblical story of the Exodus and Mount Sinai’s significance to Judaism, Christianity, and Islam have shaped the region’s history. The peninsula witnessed the rise and fall of empires, including the Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman empires.
What are the major challenges facing the Sinai Peninsula today?
The Sinai Peninsula faces challenges related to security, environmental sustainability, and economic development. The region is susceptible to terrorist activities and political unrest due to its proximity to conflict zones and porous borders. Environmental challenges include limited water resources, fragile ecosystems, and the potential for desertification. Sustainable tourism practices and infrastructure development are crucial for the region’s economic prosperity.
What are the potential opportunities for the Sinai Peninsula’s future?
The Sinai Peninsula’s natural beauty, historical significance, and strategic location offer potential opportunities for economic development. Tourism, particularly in the coastal areas, can be a significant source of income. The region’s strategic location can facilitate trade and investment. However, addressing security challenges, promoting sustainable development, and fostering regional cooperation are crucial for realizing these opportunities.
Tips for Exploring the Sinai Peninsula
Plan your trip: Research different destinations and activities based on your interests. Consider the best time of year to visit, taking into account weather conditions and potential crowds.
Respect the local culture: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, particularly when visiting religious sites. Dress modestly and avoid public displays of affection.
Stay hydrated: The Sinai Peninsula is a desert region, so it is essential to stay hydrated. Carry plenty of water, especially when hiking or exploring remote areas.
Be aware of security risks: Stay informed about current security conditions and follow official safety guidelines. Avoid traveling to areas with high security risks.
Protect the environment: Be mindful of your impact on the environment. Pack out all trash, avoid disturbing wildlife, and respect the fragile desert ecosystem.
Conclusion
The Sinai Peninsula, a land of contrasts and historical significance, continues to hold a unique position in the modern world. Its geographic features, historical legacy, and contemporary challenges and opportunities offer a captivating tapestry of human experience. Understanding the Sinai map, with its intricate interplay of geography, history, and contemporary issues, provides valuable insights into a region that continues to shape the world around it. By embracing responsible tourism, promoting sustainable development, and fostering regional cooperation, the Sinai Peninsula can unlock its potential and contribute to a brighter future for its people and the world.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Sinai: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
