Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Palestine: A Geographic and Historical Journey
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Palestine: A Geographic and Historical Journey
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Palestine: A Geographic and Historical Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Palestine: A Geographic and Historical Journey

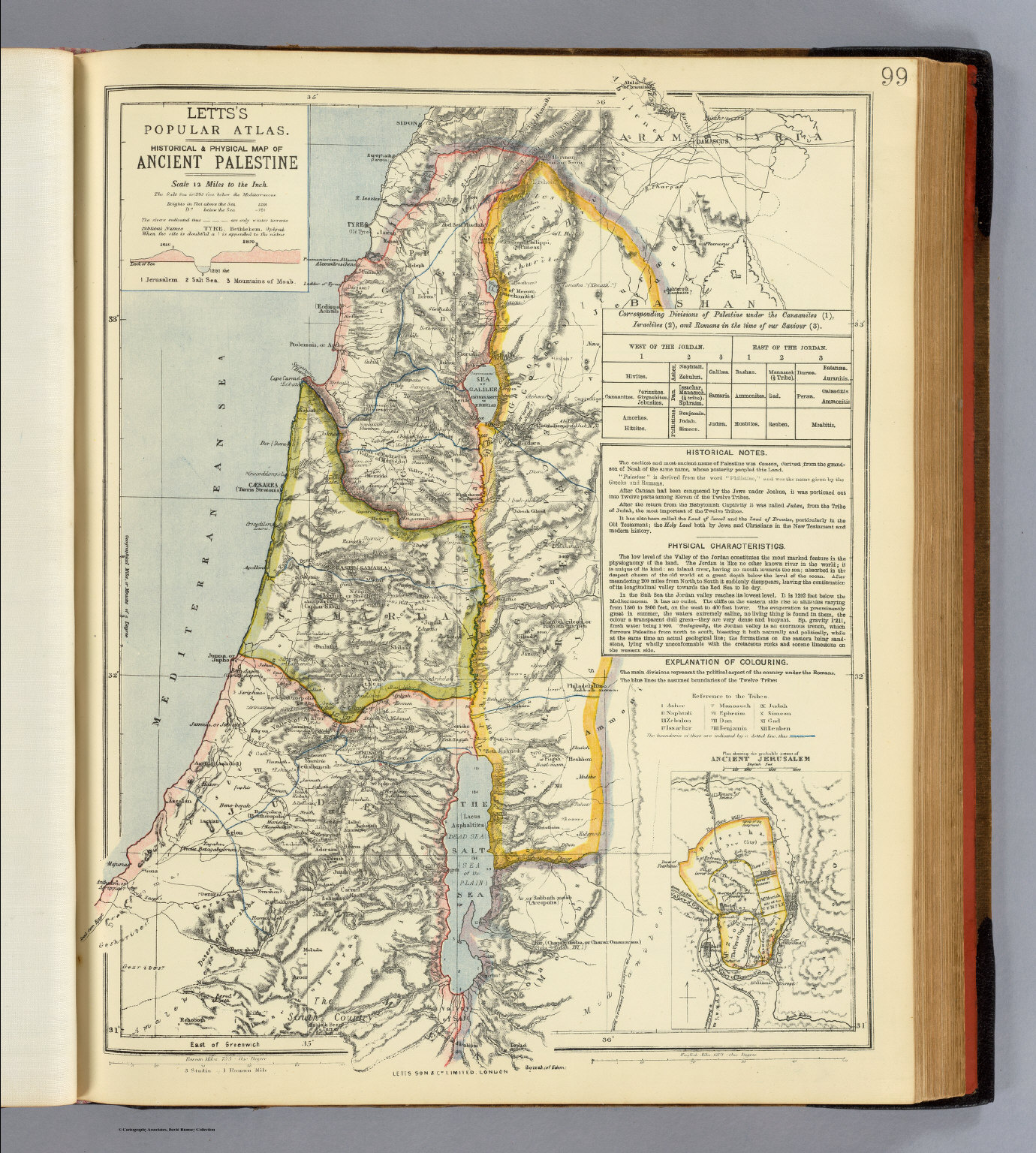
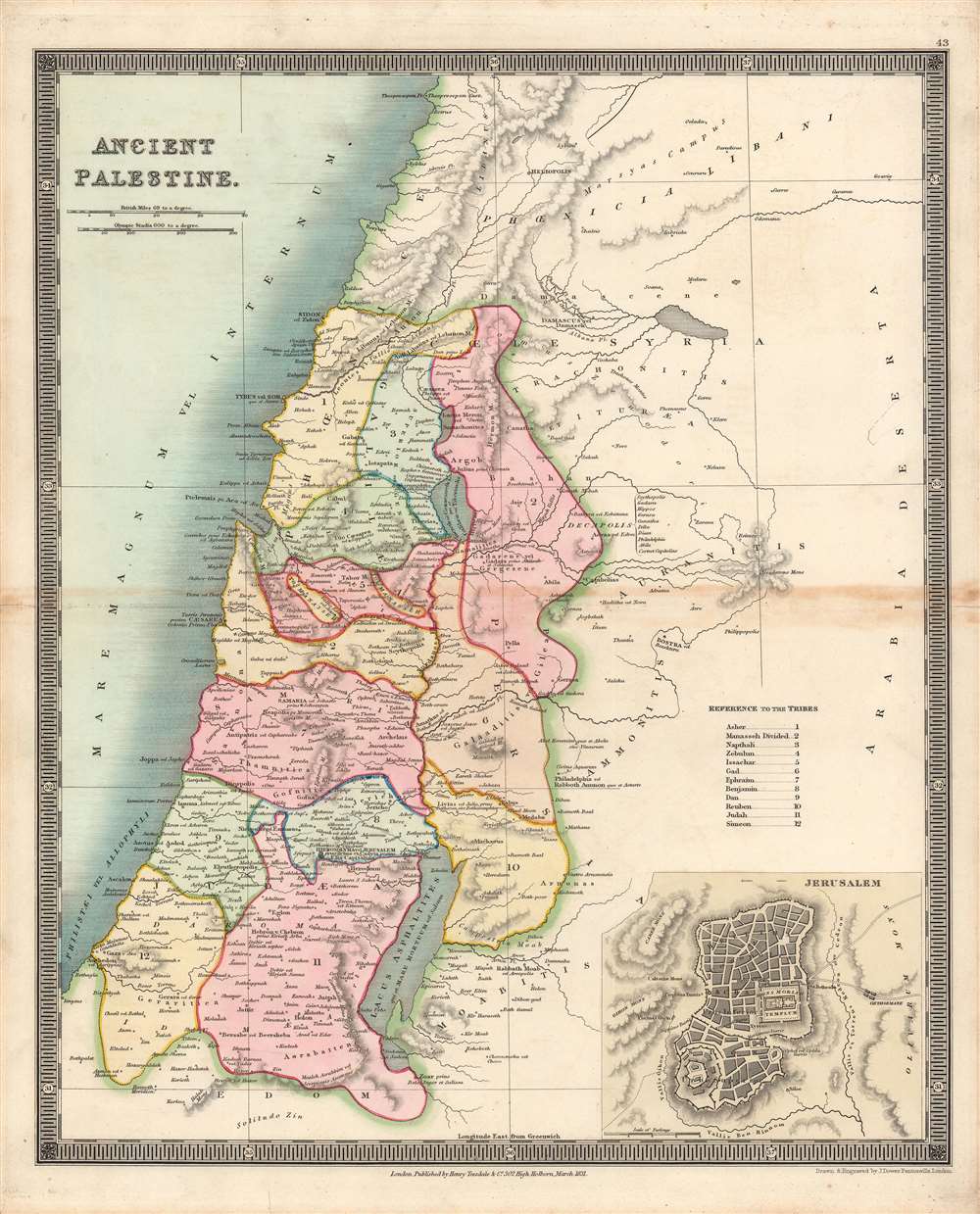
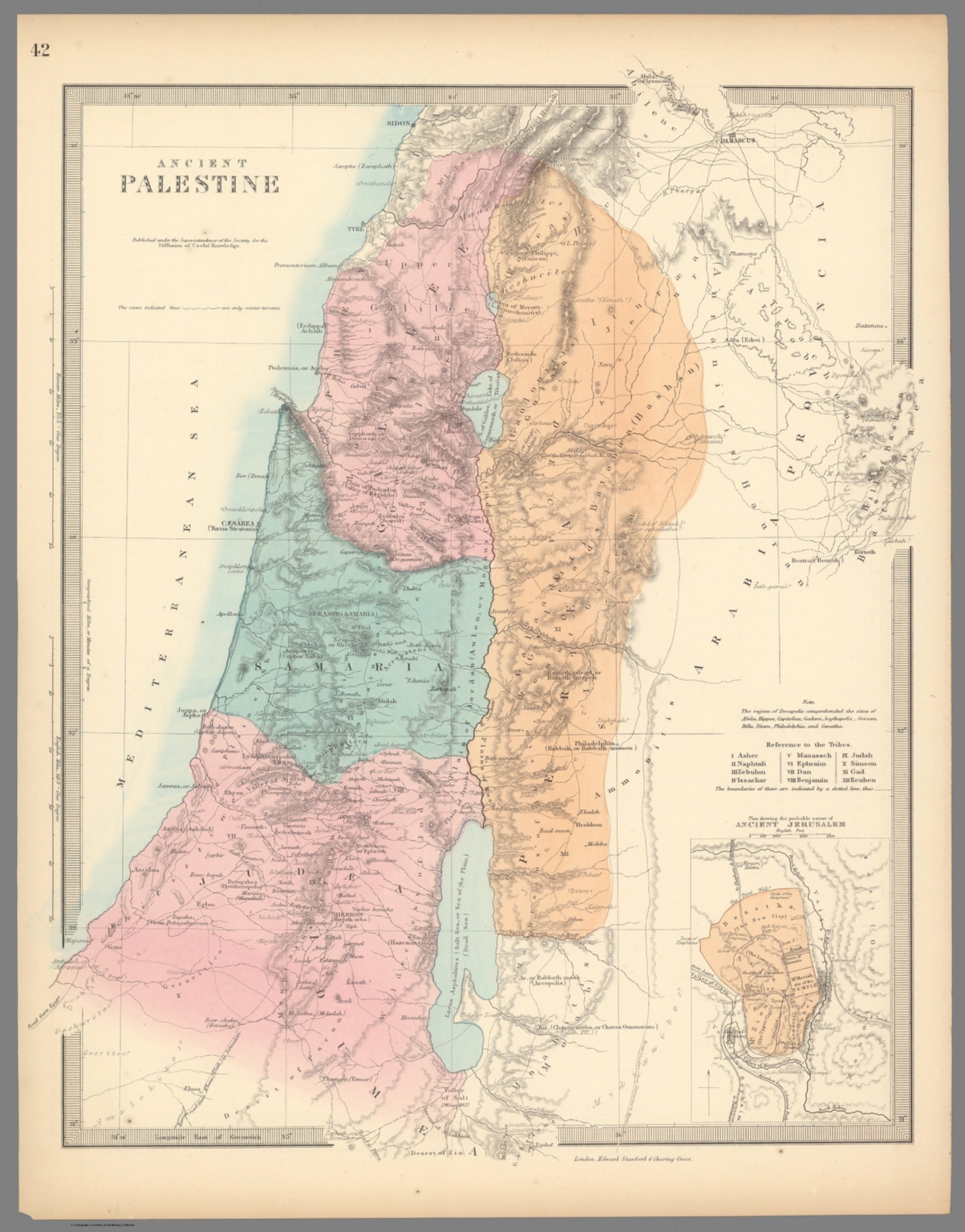
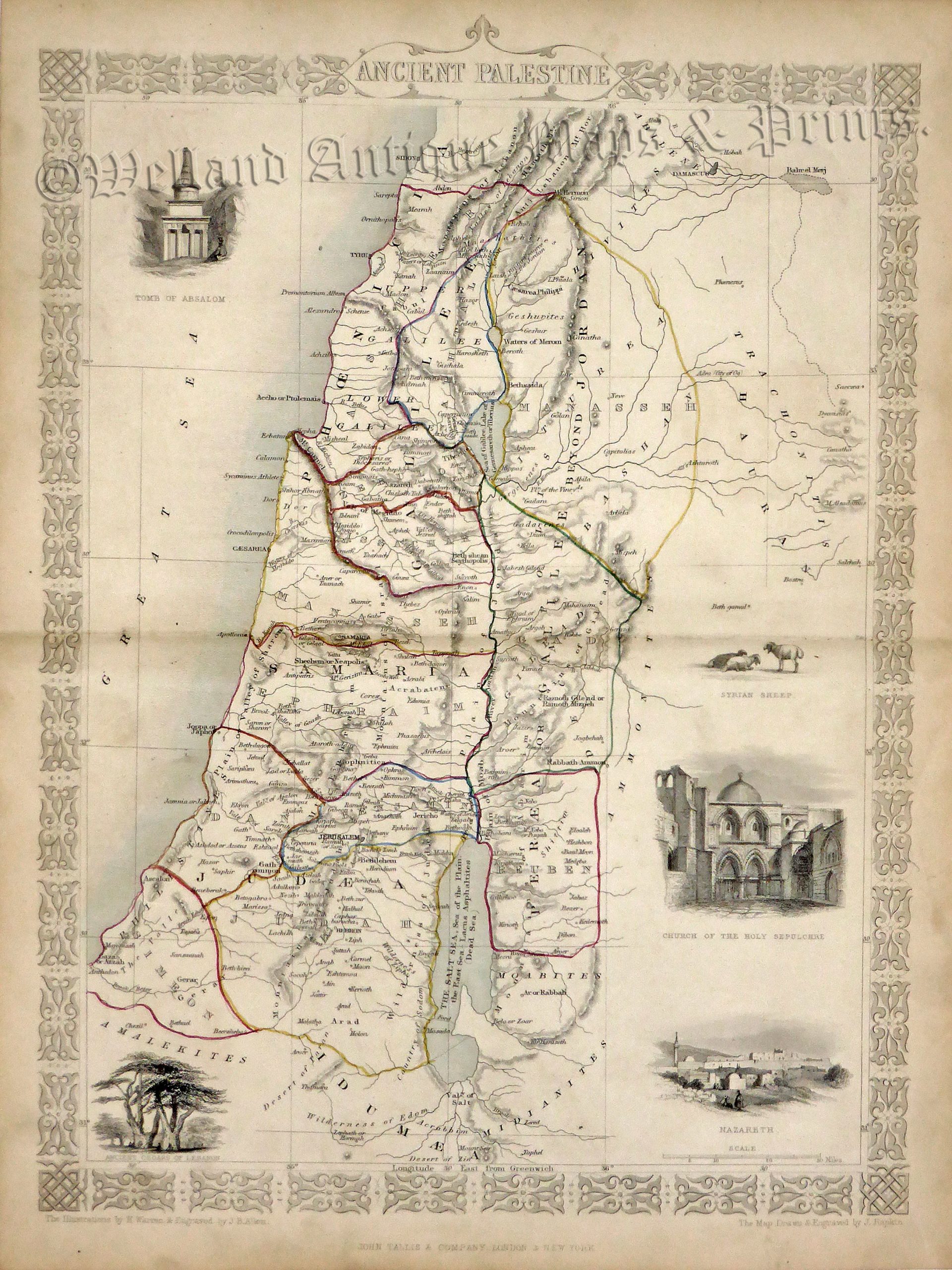
The land known as Palestine, a name that evokes a rich tapestry of history, religion, and culture, has captivated scholars and travelers for millennia. To understand this complex and vital region, a map becomes an indispensable tool, offering a visual key to its intricate geography and the dynamic forces that shaped its past. This article delves into the complexities of mapping ancient Palestine, examining its physical features, the ebb and flow of empires and cultures, and the enduring significance of its historical legacy.
The Land: A Crossroads of Civilizations
Ancient Palestine, situated at the eastern edge of the Mediterranean Sea, lies within a geographical crucible. Its landscape, a mosaic of rolling hills, fertile valleys, and arid deserts, provides a natural bridge between Africa, Asia, and Europe. This strategic location has made Palestine a crossroads of civilizations for centuries, with empires rising and falling, leaving their indelible marks on the land.
Mapping the Terrain: A Mosaic of Landscapes
A map of ancient Palestine reveals a diverse and dynamic terrain. To the west, the coastal plain, a narrow strip of land bordering the Mediterranean, offered access to trade routes and facilitated cultural exchange. The central highlands, a rugged plateau, provided natural defenses and served as a haven for independent kingdoms. To the east, the Jordan River Valley, a fertile rift valley, offered a vital water source and a corridor for trade and travel. The Transjordan, a plateau east of the Jordan River, provided a buffer zone between Palestine and the Arabian Desert.
Ancient Empires and the Shifting Sands of Time
The map of ancient Palestine reflects the ebb and flow of empires, each leaving its imprint on the land and its inhabitants. The Bronze Age witnessed the rise of powerful empires like the Egyptians, who controlled the region for centuries. The Iron Age saw the emergence of the Philistines, a seafaring people who settled along the coast, and the rise of the Israelite kingdom, which would eventually dominate the region.
The Roman Conquest and the Rise of Christianity
The Roman conquest of Palestine in 63 BCE marked a turning point in the region’s history. The Romans established a province called Judea, with Jerusalem as its capital. This period saw the rise of Christianity, which would profoundly shape the region’s future. The map of ancient Palestine during this era reflects the Roman presence, with roads, cities, and fortifications built to consolidate their control.
Byzantine Rule and the Spread of Christianity
After the fall of the Roman Empire, Palestine fell under the rule of the Byzantine Empire. This era, marked by the flourishing of Christianity, witnessed the construction of magnificent churches and monasteries, many of which still stand today. The map of ancient Palestine during this period showcases the Byzantine influence, with its focus on cities and religious centers.
The Islamic Conquest and the Rise of a New Era
The Islamic conquest of Palestine in the 7th century CE brought a new era to the region. The Umayyad Caliphate established Damascus as its capital, and Palestine became an integral part of the expanding Islamic world. The map of ancient Palestine during this period reflects the Islamic presence, with the construction of mosques and the development of new trade routes.
The Crusader Period and the Clash of Civilizations
The Crusades, a series of religious wars launched by European Christians to reclaim the Holy Land from Muslim rule, left their mark on Palestine. Crusader kingdoms were established in the region, and the map of ancient Palestine during this era showcases the strategic importance of key cities like Jerusalem, Acre, and Jaffa.
Ottoman Rule and the Legacy of the Past
Following the Crusades, Palestine came under the rule of the Ottoman Empire for centuries. The Ottomans maintained a relatively stable rule, allowing the region’s diverse communities to coexist. The map of ancient Palestine during this period reveals a complex mosaic of cultures, with a blend of Islamic, Christian, and Jewish traditions.
The Importance of Mapping Ancient Palestine
Mapping ancient Palestine offers a vital window into the region’s rich history and complex cultural tapestry. It allows us to:
- Visualize the Geography: Maps provide a visual representation of the land’s physical features, from its coastal plains to its rugged highlands, helping us understand the impact of geography on the region’s development.
- Trace the Rise and Fall of Empires: By mapping the boundaries of ancient empires and kingdoms, we can trace the ebb and flow of power, understanding how political forces shaped the region’s history.
- Explore the Cultural Mosaic: Maps reveal the distribution of different communities, religions, and languages, showcasing the diverse tapestry of cultures that have coexisted in Palestine.
- Understand the Significance of Key Sites: Maps highlight the locations of important cities, religious centers, and archaeological sites, providing a framework for understanding the region’s historical and religious significance.
FAQs About Mapping Ancient Palestine
Q: What are the challenges of mapping ancient Palestine?
A: Mapping ancient Palestine presents several challenges. Archaeological evidence is often fragmentary, making it difficult to reconstruct the exact boundaries of ancient kingdoms and cities. The region’s history is complex and dynamic, with shifting borders and overlapping empires, making it difficult to create a definitive map.
Q: How do maps help us understand the history of Palestine?
A: Maps provide a visual framework for understanding the region’s history. By tracing the boundaries of ancient empires, kingdoms, and settlements, we can visualize the flow of power, the spread of cultures, and the impact of historical events on the land.
Q: What are some of the most important sites to map in ancient Palestine?
A: Some of the most important sites to map in ancient Palestine include Jerusalem, with its holy sites for Judaism, Christianity, and Islam; Jericho, one of the oldest cities in the world; and the Dead Sea, a unique geographical feature with a rich history.
Tips for Understanding Maps of Ancient Palestine
- Pay attention to scale: Different maps use different scales, which can affect the level of detail provided.
- Look for key features: Identify important geographical features such as mountains, rivers, and coastal plains, as they played a significant role in shaping the region’s history.
- Consider the context: Maps should be viewed within the context of the historical period they represent, as boundaries and political structures changed over time.
Conclusion
Mapping ancient Palestine provides a vital tool for understanding the region’s complex history, its diverse cultural tapestry, and its enduring significance. The map serves as a visual guide, allowing us to trace the rise and fall of empires, the spread of religions, and the impact of historical events on the land. By studying maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the richness and complexity of ancient Palestine, a region that continues to hold a profound place in the world’s history and imagination.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Ancient Palestine: A Geographic and Historical Journey. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!