Unraveling the Secrets of Ancient India: A Journey Through the Oldest Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Secrets of Ancient India: A Journey Through the Oldest Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Secrets of Ancient India: A Journey Through the Oldest Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Secrets of Ancient India: A Journey Through the Oldest Maps

The allure of ancient maps lies in their ability to transport us through time, revealing the world as it was perceived centuries ago. While the concept of mapping dates back millennia, pinpointing the "oldest map of India" requires careful consideration. This article delves into the fascinating history of Indian cartography, examining the earliest known representations of the subcontinent and exploring their significance in understanding ancient knowledge and societal structures.
Early Representations: Beyond the Realm of Maps
Before delving into specific maps, it’s crucial to acknowledge that the earliest representations of India were not necessarily maps in the modern sense. Ancient civilizations, particularly the Indus Valley Civilization (c. 3300-1300 BCE), employed various forms of spatial representation.
- Stone Seals: These small, engraved objects, found in abundance at Indus Valley sites, often depicted animals, geometric patterns, and even rudimentary representations of settlements. While not maps in the conventional sense, they offer glimpses into the spatial awareness and symbolic language of the Indus people.
- Pottery Designs: Pottery fragments unearthed from ancient Indian sites sometimes feature geometric patterns or stylized representations of landscapes. These designs, while not precise maps, provide clues about the understanding of space and the environment in ancient India.
- Literary References: Ancient Indian texts like the Rig Veda (c. 1500 BCE) contain descriptions of geographical features, rivers, and settlements. These literary references, while not visual representations, provide valuable insights into the geographical knowledge of the time.
The Dawn of Cartography: The Ancient Greek and Roman Influence
The emergence of recognizable maps in India can be traced back to the influence of Greek and Roman cartographers. Alexander the Great’s conquests in the 4th century BCE brought Greek cartographic knowledge to the Indian subcontinent. This influence is evident in the works of Greek geographers like Strabo (c. 64 BCE – c. 24 CE) and Ptolemy (c. 90 – c. 168 CE), whose writings and maps included detailed descriptions of India’s geography and its diverse regions.
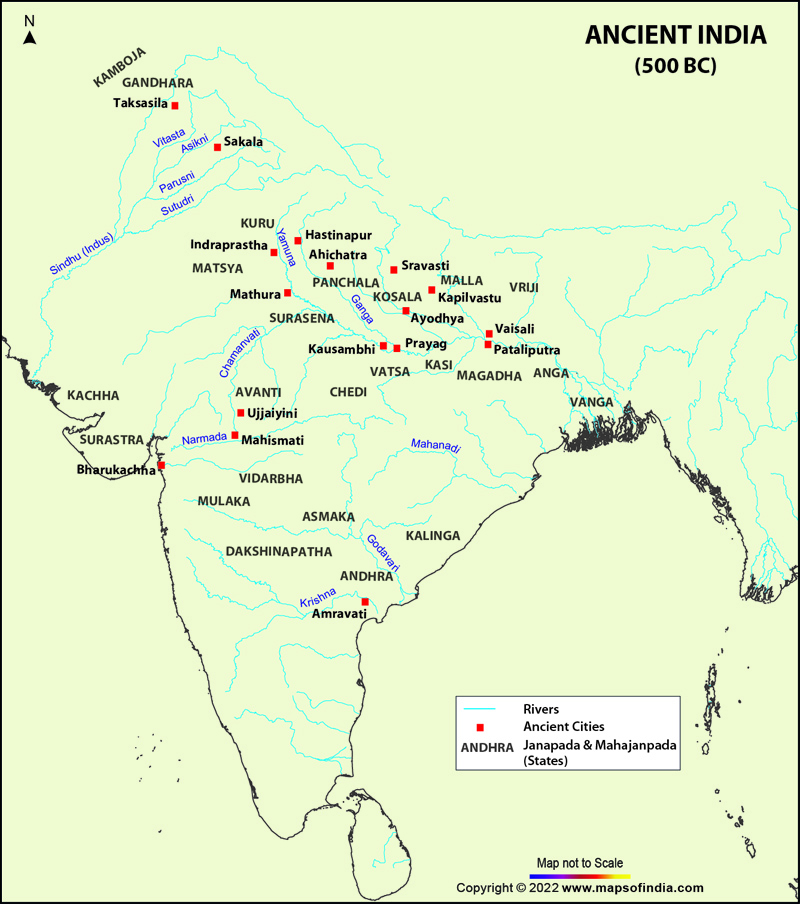
The Earliest Known Maps: A Glimpse into Ancient India
- The "Behistun Inscription" (c. 520 BCE): This inscription, carved into a cliff face in Persia, is a multilingual record of the victories of Darius I, the Achaemenid King. It includes a depiction of India, referred to as "Hindush," which is considered one of the earliest known visual representations of the subcontinent.
- The "Ptolemy’s World Map" (c. 150 CE): Ptolemy’s influential map, based on a combination of Greek and Roman sources, included a detailed representation of India. It showcased the subcontinent’s major rivers, cities, and geographical features, marking a significant step in the development of Indian cartography.
- The "Buddhist Cave Paintings" (c. 1st Century BCE – 1st Century CE): Cave paintings found at various Buddhist sites in India, particularly in Ajanta and Ellora, often depict scenes of daily life and religious narratives. Some of these paintings include representations of landscapes and geographical features, offering a glimpse into the spatial awareness of the time.
The Rise of Indian Cartography: Mapping the Land and the Cosmos
Over the centuries, Indian cartography evolved beyond mere representations of geographical features. Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain scriptures, as well as astronomical texts, incorporated intricate maps of the cosmos and the universe.
- The "Jyotish Shastra" (c. 4th Century BCE – 1st Century CE): This ancient Indian astronomical treatise, based on Vedic knowledge, contained detailed descriptions of the celestial bodies, their movements, and their influence on Earth. These descriptions implicitly included maps of the cosmos, demonstrating the advanced understanding of celestial mechanics in ancient India.
- The "Surya Siddhanta" (c. 4th Century CE): This astronomical text, considered a cornerstone of Indian astronomy, contained detailed information about the Earth, the planets, and the solar system. It included a spherical model of the Earth, suggesting a sophisticated understanding of its shape and its place in the cosmos.
The Significance of Early Indian Maps: Unveiling the Past
The oldest maps of India, despite their rudimentary nature, hold immense historical and cultural significance. They provide invaluable insights into:
- Geographical Knowledge: Early maps reveal the extent of geographical knowledge in ancient India, showcasing the understanding of major rivers, mountains, and cities.
- Trade and Communication Networks: Maps often depicted trade routes and settlements, offering insights into the flow of goods and people across the subcontinent.
- Cultural and Religious Beliefs: Maps often incorporated religious symbols and motifs, reflecting the cultural and religious beliefs of the time.
- Social and Political Structures: Maps sometimes depicted political boundaries and important settlements, providing glimpses into the social and political structures of ancient India.
FAQs Regarding the Oldest Map of India:
1. What is the earliest known visual representation of India?
The "Behistun Inscription" (c. 520 BCE) is considered one of the earliest known visual representations of India.
2. What is the significance of Ptolemy’s map of India?
Ptolemy’s map, based on Greek and Roman sources, provided a detailed representation of India’s geography, marking a significant step in the development of Indian cartography.
3. Did ancient Indians have a sophisticated understanding of astronomy?
Yes, ancient Indian texts like the "Jyotish Shastra" and the "Surya Siddhanta" demonstrate a sophisticated understanding of astronomy, incorporating intricate maps of the cosmos and the universe.
4. What are the key insights provided by the oldest maps of India?
The oldest maps provide insights into ancient geographical knowledge, trade routes, cultural beliefs, and social and political structures.
5. What are some of the challenges in studying ancient Indian maps?
The study of ancient Indian maps faces challenges like the limited availability of original sources, the need for specialized knowledge in deciphering ancient languages and scripts, and the interpretation of symbolic representations.
Tips for Studying Ancient Indian Maps:
- Consult Scholarly Sources: Refer to academic journals, books, and online resources specializing in ancient Indian history and cartography.
- Learn About Ancient Indian Scripts and Languages: Understanding the languages and scripts used in ancient India is crucial for interpreting maps and inscriptions.
- Pay Attention to Context: Consider the historical, cultural, and religious context in which a map was created to understand its significance.
- Compare and Contrast Maps: Compare different maps from various periods to identify changes in geographical knowledge, cultural beliefs, and societal structures.
Conclusion:
The quest for the oldest map of India is a journey into the heart of ancient knowledge. While definitive answers may be elusive, the exploration of early representations of the subcontinent unveils a fascinating tapestry of geographical awareness, cultural beliefs, and societal structures. By studying these ancient maps, we gain a deeper understanding of India’s rich history and its enduring legacy. The pursuit of knowledge through the lens of ancient maps continues to illuminate the path towards a more complete and nuanced understanding of the past.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Secrets of Ancient India: A Journey Through the Oldest Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!