Unraveling Colorado’s Geological Tapestry: A Journey Through Time on a Map
Related Articles: Unraveling Colorado’s Geological Tapestry: A Journey Through Time on a Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling Colorado’s Geological Tapestry: A Journey Through Time on a Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling Colorado’s Geological Tapestry: A Journey Through Time on a Map
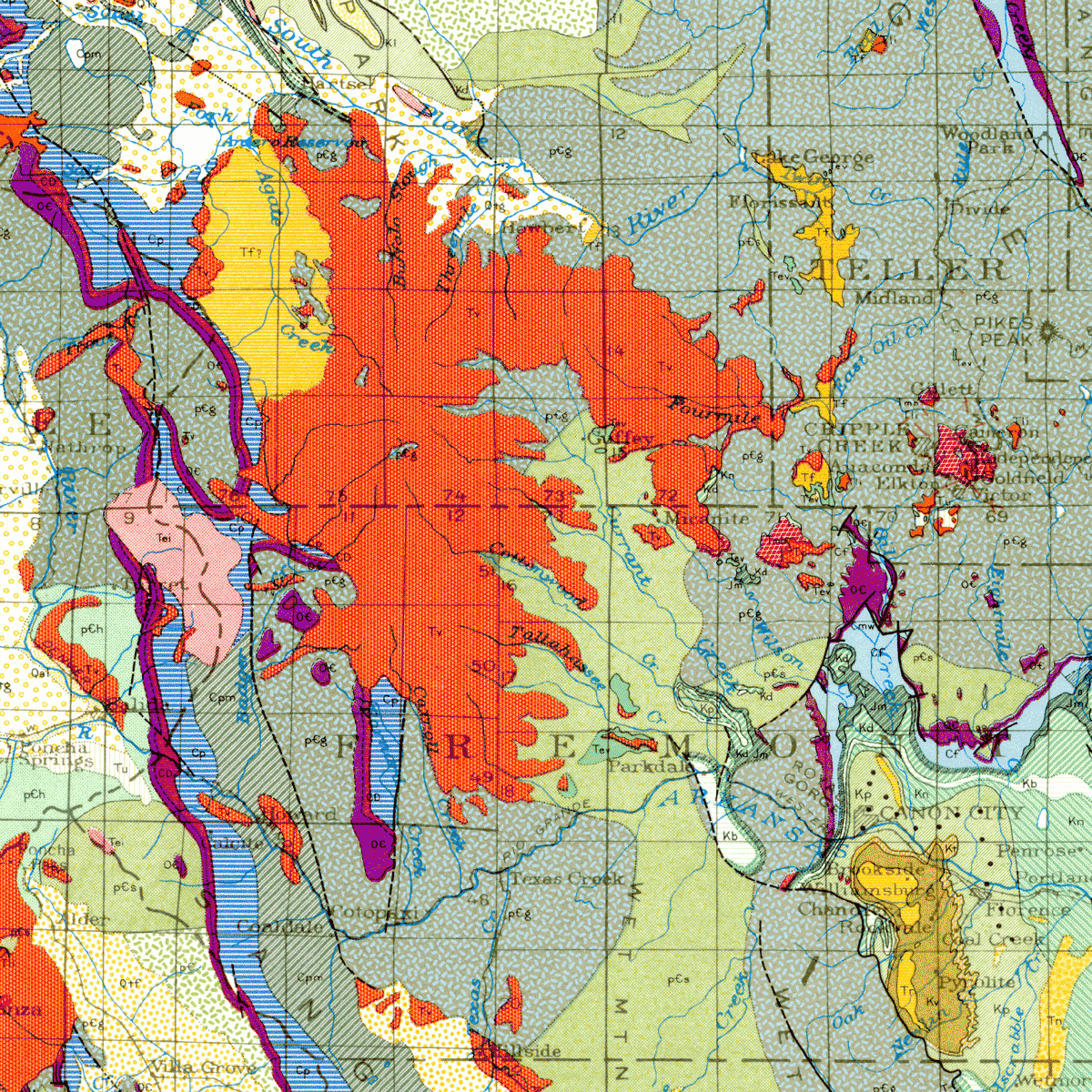
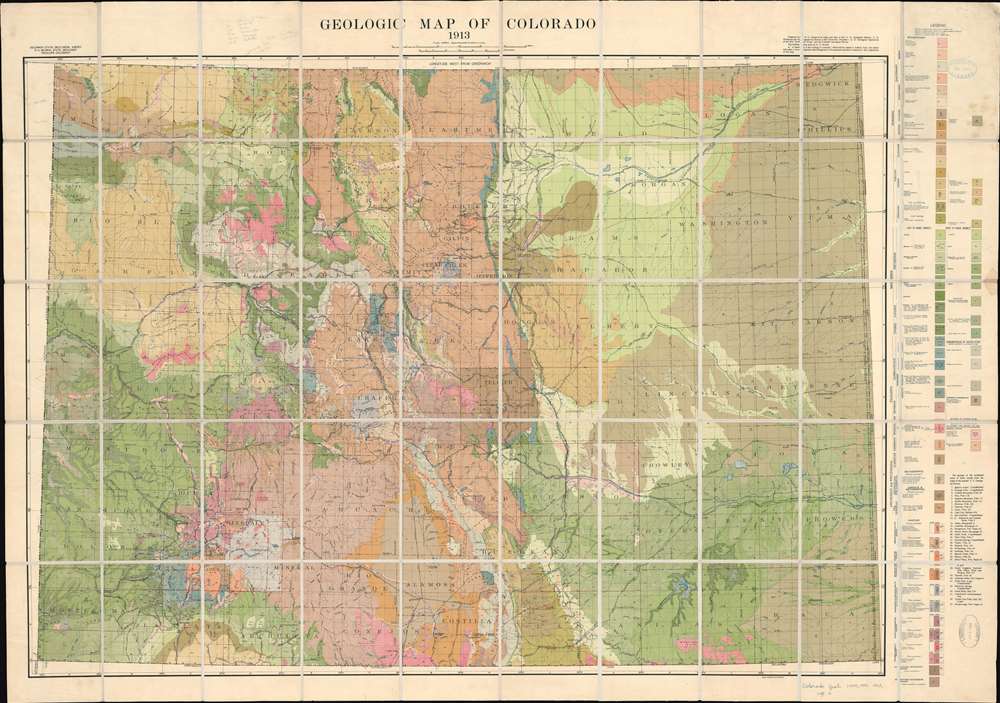
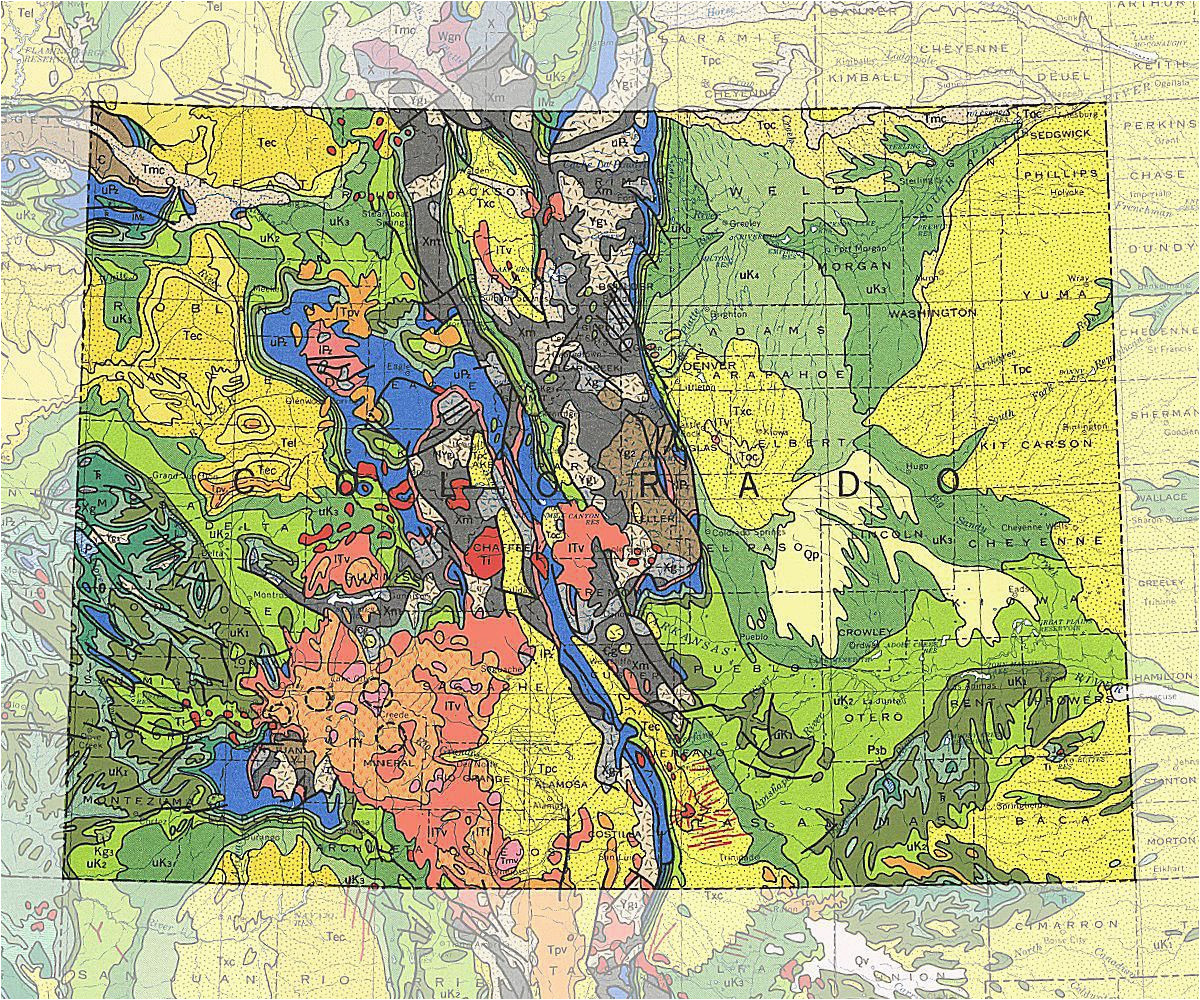
Colorado, a state renowned for its majestic mountains, rugged canyons, and diverse landscapes, is a testament to a complex and captivating geological history. This history is eloquently captured in the Colorado Geological Map, a visual representation of the state’s bedrock, its hidden stories, and its potential resources. This map, a product of extensive research and meticulous analysis, serves as a key to understanding the state’s past, present, and future.
The Colorado Geological Map: A Window into the Past
The map reveals the state’s intricate geological tapestry, showcasing the vast array of rock formations that span billions of years. These formations, like layers of a cake, provide a chronological record of Earth’s evolution, offering insights into ancient environments, tectonic shifts, and volcanic activity.
-
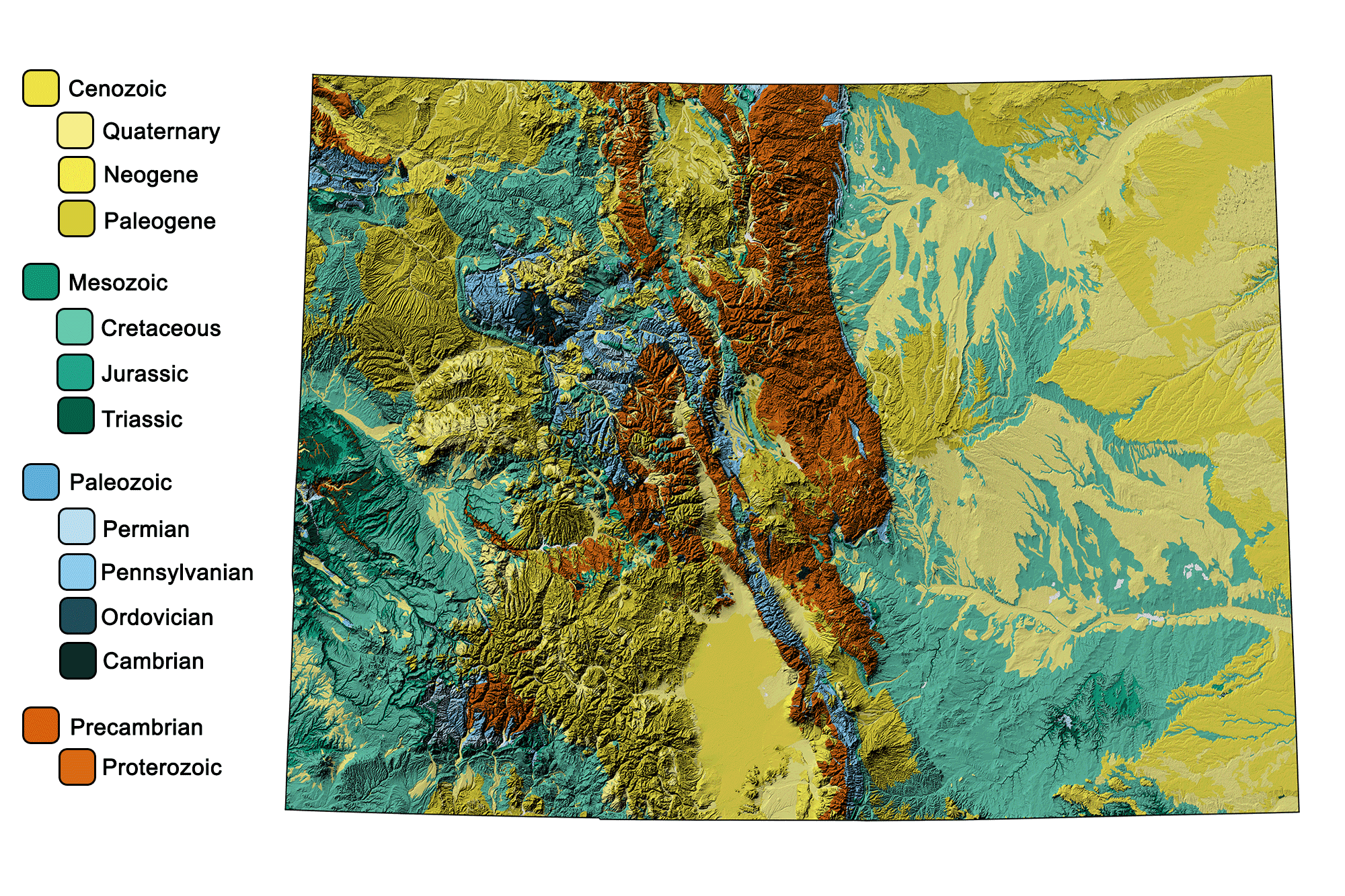
Precambrian Basement Rocks: The map’s foundation is comprised of Precambrian rocks, some of the oldest on Earth, dating back over 540 million years. These rocks, primarily metamorphic and igneous, were formed deep within the Earth’s crust and were later exposed through uplift and erosion. They form the base of the Colorado Rockies and represent the earliest chapters of the state’s geological narrative.
-
Paleozoic Era (540-252 million years ago): The map depicts the deposition of sedimentary rocks during this era, marking periods of shallow seas, extensive deserts, and ancient mountain ranges. These formations, rich in fossils, provide valuable insights into the evolution of life and ancient climates.
-
Mesozoic Era (252-66 million years ago): This era, known for the rise of dinosaurs, is represented by the deposition of sandstone, shale, and limestone, indicating a transition from marine to terrestrial environments. The iconic red rock formations of the Colorado Plateau, like the Garden of the Gods, originated during this period.
-
Cenozoic Era (66 million years ago to present): The map highlights the dramatic uplift of the Rocky Mountains during this era, a process that continues today. This uplift, driven by tectonic forces, resulted in the formation of the majestic peaks, deep canyons, and vast plains that characterize Colorado’s landscape.
The Colorado Geological Map: A Guide to Resources and Hazards
Beyond its historical significance, the geological map serves as a practical tool for resource management and hazard mitigation.
-
Mineral Resources: The map identifies areas rich in mineral deposits, ranging from precious metals like gold and silver to industrial minerals like limestone and gypsum. Understanding the geological context of these deposits is crucial for sustainable mining practices and economic development.
-
Energy Resources: The map reveals the distribution of fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, providing valuable information for energy exploration and development. It also highlights geothermal energy potential, offering alternative energy sources for the state.
-
Water Resources: The map helps identify aquifers, the underground reservoirs that store groundwater, a vital resource for Colorado’s water supply. It also reveals the geological factors influencing water flow and quality, aiding in water management and conservation efforts.
-
Natural Hazards: The map provides insights into potential geological hazards like landslides, earthquakes, and volcanic activity. This knowledge is essential for developing mitigation strategies and ensuring public safety.
FAQs about the Colorado Geological Map:
Q: What is the most recent geological event that shaped Colorado’s landscape?
A: The most recent significant geological event was the uplift of the Rocky Mountains, which began in the Cenozoic Era and continues today. This process, driven by tectonic forces, shaped the state’s iconic peaks, valleys, and canyons.
Q: How does the Colorado Geological Map help with water management?
A: The map reveals the location of aquifers, underground reservoirs that store groundwater. It also helps understand the flow paths and quality of groundwater, aiding in water resource management and conservation efforts.
Q: Can the map predict future geological events?
A: While the map provides insights into past events and current geological processes, it cannot predict future events with certainty. However, it helps identify areas prone to hazards like earthquakes and landslides, allowing for better mitigation strategies.
Tips for Using the Colorado Geological Map:
- Start with the basics: Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend and the various symbols representing different rock types and geological features.
- Explore specific areas: Use the map to investigate the geology of your region, focusing on local rock formations, mineral resources, and potential hazards.
- Connect with experts: Consult with geologists or other experts for further guidance and interpretation of the map’s information.
Conclusion:
The Colorado Geological Map is more than just a collection of lines and colors; it is a window into the state’s rich history, a guide to its resources, and a warning system for potential hazards. By understanding the geological processes that shaped Colorado, we can make informed decisions about resource management, environmental protection, and public safety. The map, a testament to the power of scientific inquiry, serves as a valuable tool for navigating the complexities of Colorado’s geological landscape and its future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling Colorado’s Geological Tapestry: A Journey Through Time on a Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!