Unlocking the Secrets of Texas: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Oil Fields
Related Articles: Unlocking the Secrets of Texas: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Oil Fields
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Secrets of Texas: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Oil Fields. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Secrets of Texas: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Oil Fields

Texas, the Lone Star State, has long been synonymous with oil and gas production. Its vast reserves and strategic location have propelled the state to the forefront of the energy industry, shaping its economy and influencing global markets. Understanding the distribution of these resources is crucial for comprehending the state’s economic landscape, environmental considerations, and future energy prospects. This article delves into the intricacies of Texas’ oil fields, providing a comprehensive overview of their geography, history, and significance.
A Tapestry of Oil and Gas: Mapping the Resource Landscape
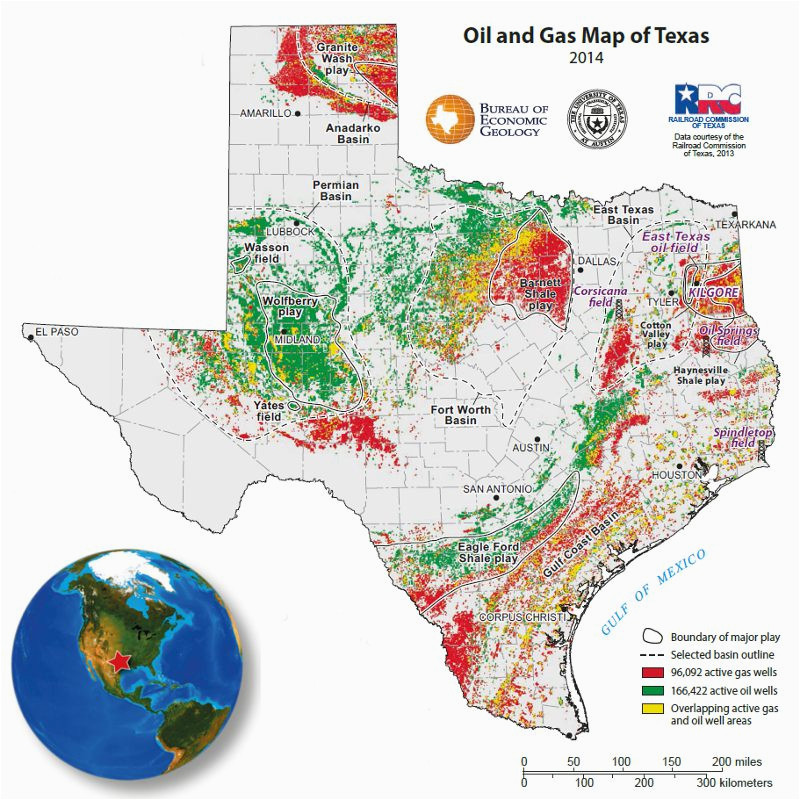
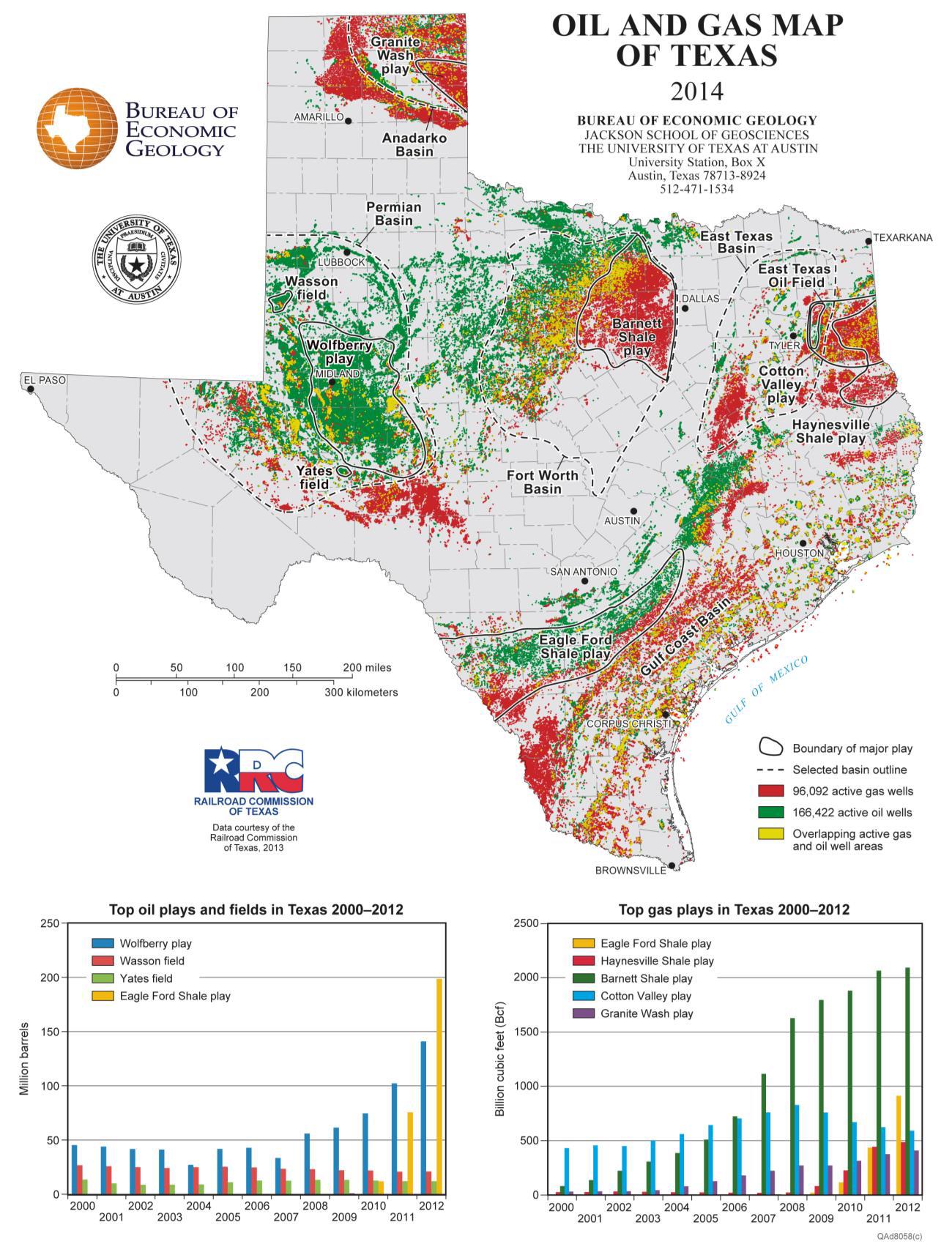
The Texas oil field map is a complex tapestry, woven with the threads of geological formations, historical discoveries, and ongoing exploration. It reveals a diverse landscape, with oil and gas deposits scattered across the state, from the Permian Basin in the west to the East Texas Basin in the east.
1. The Permian Basin: A Hub of Energy
The Permian Basin, spanning portions of West Texas and southeastern New Mexico, stands as the most prolific oil-producing region in the United States. Its vast reserves of shale oil, particularly in the Permian Basin’s Midland and Delaware Basins, have spurred a renaissance in oil production, contributing significantly to the recent surge in US energy independence. The region boasts a complex geological history, with layers of sedimentary rock deposited over millions of years, trapping hydrocarbons in their porous layers.
2. The Eagle Ford Shale: A Transformative Discovery
South Texas’ Eagle Ford Shale, discovered in the early 2000s, transformed the state’s energy landscape. This shale formation, stretching from the Rio Grande Valley to San Antonio, holds vast reserves of oil and natural gas, contributing to Texas’ position as a leading energy producer. The Eagle Ford Shale has fueled economic growth in the region, creating jobs and boosting local economies.
3. The East Texas Basin: A Legacy of Oil Production
The East Texas Basin, located in the eastern portion of the state, holds historical significance in Texas’ oil production. Its discovery in 1930 triggered the "East Texas Oil Boom," ushering in a new era of oil exploration and development. While production has declined since its peak, the East Texas Basin remains a significant source of oil and gas, contributing to the state’s energy portfolio.
4. Other Notable Fields: A Diverse Landscape
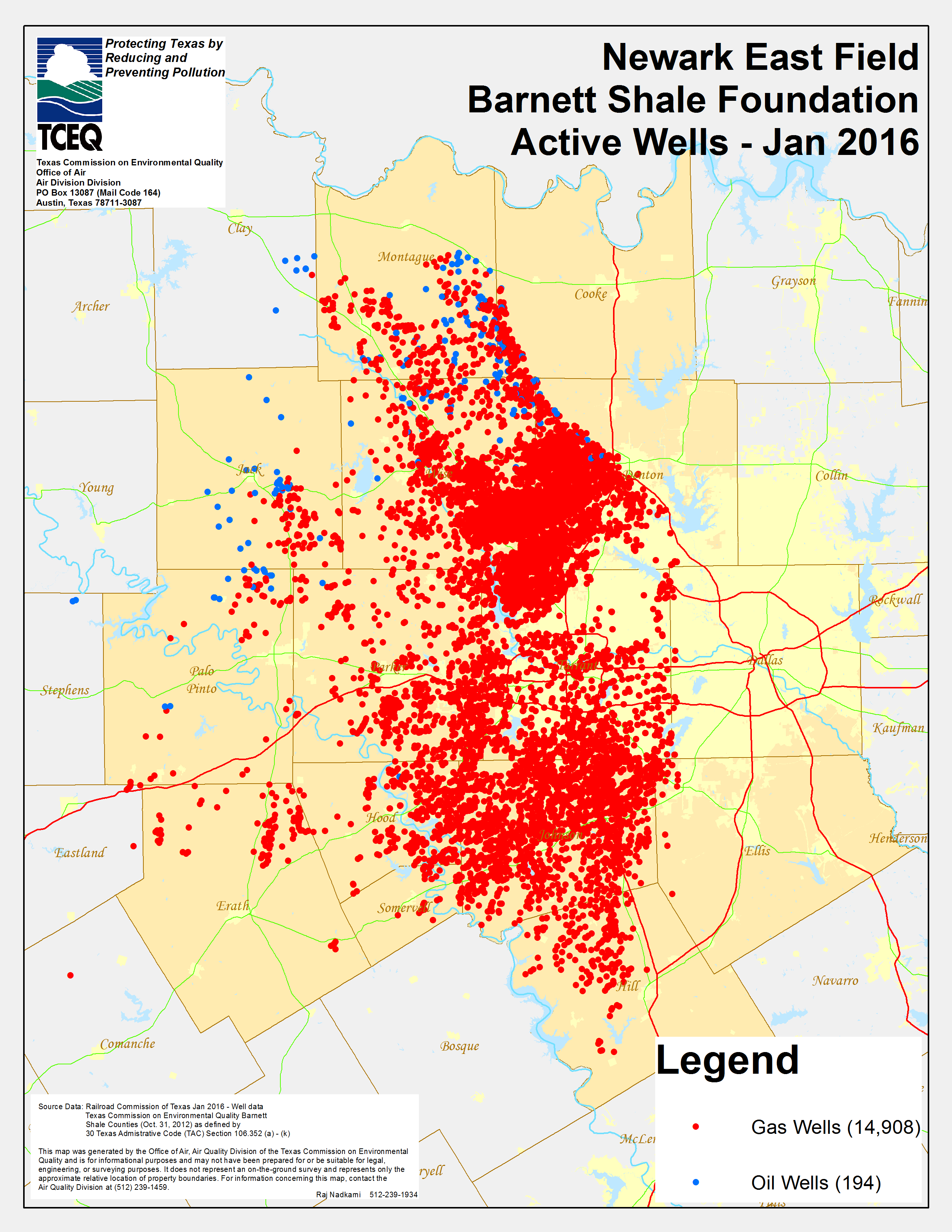
Beyond these major formations, Texas boasts numerous other oil and gas fields, each with its own unique characteristics and history. These include the Barnett Shale in North Texas, known for its natural gas production, and the Austin Chalk, which has yielded significant oil and gas resources. The diversity of these fields highlights the vastness and complexity of Texas’ oil and gas reserves.
The Evolution of Oil and Gas Production in Texas: From Discovery to Innovation
Texas’ oil and gas industry has evolved significantly over the past century, driven by technological advancements, changing market dynamics, and environmental considerations.
1. The Early Days: The Wildcatters and the Boom Years
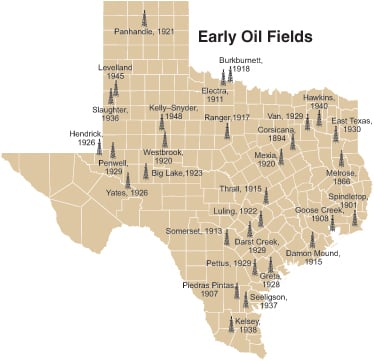
The early 20th century witnessed a wave of exploration and discovery, fueled by the pioneering spirit of "wildcatters" who ventured into uncharted territories. The discovery of the Spindletop oil field in 1901 marked a watershed moment, catapulting Texas into the center of the global oil industry. The following decades saw a flurry of discoveries, with the East Texas Oil Boom of the 1930s solidifying Texas’ position as a major oil producer.
2. The Era of Technological Innovation: The Rise of Hydraulic Fracturing
The development of hydraulic fracturing (fracking) in the late 20th century revolutionized oil and gas production, particularly in shale formations. This technique, involving injecting pressurized fluids into rock formations to release trapped hydrocarbons, unlocked vast new reserves, leading to a surge in production in the Permian Basin and Eagle Ford Shale.
3. The Quest for Sustainability: Balancing Energy Needs and Environmental Concerns
As the world grapples with climate change, the Texas oil and gas industry is facing increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices. This has led to advancements in technologies like carbon capture and storage, as well as efforts to reduce methane emissions. The industry is also exploring alternative energy sources, such as renewable energy and biofuels, to diversify its energy portfolio.
The Importance of the Texas Oil Field Map: Unveiling the Economic and Environmental Significance
The Texas oil field map serves as a vital tool for understanding the state’s energy landscape, highlighting its economic and environmental significance.
1. Economic Powerhouse: Fueling the Texas Economy
Texas’ oil and gas industry is a major driver of the state’s economy, generating billions of dollars in revenue and supporting hundreds of thousands of jobs. The industry directly contributes to employment in various sectors, including exploration, production, refining, transportation, and distribution. It also indirectly supports numerous other businesses through supply chains and related industries.
2. Global Energy Player: Shaping International Markets
Texas’ oil and gas production plays a significant role in global energy markets. The state’s vast reserves and production capacity contribute to US energy independence and influence global oil prices. The growth of the Permian Basin, in particular, has significantly boosted US oil production, making the country a leading exporter of crude oil.
3. Environmental Considerations: Navigating the Challenges of Resource Extraction
The extraction of oil and gas resources comes with environmental challenges, including potential air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and greenhouse gas emissions. The Texas oil field map helps policymakers and industry stakeholders understand the potential environmental impacts of oil and gas operations, facilitating informed decision-making and promoting sustainable practices.
FAQs about the Texas Oil Field Map
1. What is the most significant oil field in Texas?
The Permian Basin, spanning portions of West Texas and southeastern New Mexico, is the most prolific oil-producing region in the United States.
2. What is the difference between oil and natural gas?
Oil and natural gas are both fossil fuels formed from the remains of ancient organisms. Oil is a liquid hydrocarbon, while natural gas is a gaseous hydrocarbon.
3. What are the environmental concerns associated with oil and gas extraction?
Oil and gas extraction can lead to air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and greenhouse gas emissions.
4. How is the Texas oil and gas industry responding to environmental concerns?
The industry is adopting sustainable practices, including carbon capture and storage, methane emission reduction, and exploring alternative energy sources.
5. What is the future of the Texas oil and gas industry?
The industry is expected to continue playing a significant role in the state’s economy, with ongoing exploration and production in existing and new fields. However, the industry is also facing pressure to adapt to a changing energy landscape, with increasing demand for renewable energy and a focus on sustainability.
Tips for Understanding the Texas Oil Field Map
1. Explore Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including government websites, industry reports, and academic publications, provide detailed information about Texas oil and gas fields.
2. Consult with Experts: Engage with experts in the oil and gas industry, such as geologists, engineers, and economists, to gain insights into the complexities of the state’s energy landscape.
3. Attend Industry Events: Participate in industry conferences and workshops to stay abreast of the latest developments in oil and gas exploration, production, and environmental management.
4. Visit Oil and Gas Facilities: Take tours of oil and gas facilities to gain firsthand understanding of the operations involved in resource extraction and processing.
5. Stay Informed about Regulations: Familiarize yourself with state and federal regulations governing oil and gas production, including environmental protection measures and safety protocols.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Energy and a Future of Innovation
The Texas oil field map is a testament to the state’s rich energy history and its ongoing role in shaping the global energy landscape. It highlights the economic and environmental significance of oil and gas production, while also revealing the complexities and challenges associated with resource extraction. As Texas continues to navigate the evolving energy landscape, the oil field map will continue to provide valuable insights into the state’s energy future, guiding decision-making and promoting sustainable development.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Secrets of Texas: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Oil Fields. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!