The Power of Visualization: Understanding and Utilizing Highlight Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Visualization: Understanding and Utilizing Highlight Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visualization: Understanding and Utilizing Highlight Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Visualization: Understanding and Utilizing Highlight Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Visualization: Understanding and Utilizing Highlight Maps
- 3.1 What is a Highlight Map?
- 3.2 The Importance of Highlight Maps
- 3.3 Applications of Highlight Maps
- 3.4 FAQs about Highlight Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Creating Effective Highlight Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Power of Visualization: Understanding and Utilizing Highlight Maps
In the realm of data analysis and visualization, the ability to effectively communicate insights and patterns is paramount. While traditional methods like charts and graphs often provide valuable information, they may struggle to capture the nuances and complexities of multifaceted datasets. This is where highlight maps come into play, offering a powerful tool for visually representing data and revealing hidden relationships.
What is a Highlight Map?
A highlight map, also known as a heatmap, is a visual representation of data where values are depicted using a color gradient. Areas with higher values are typically represented by warmer colors, while lower values are shown in cooler tones. This color-coded representation allows for quick and intuitive identification of areas of interest, trends, and outliers within the data.
The Importance of Highlight Maps
Highlight maps offer numerous advantages over traditional data representations, making them a valuable tool across various fields:
1. Enhanced Data Exploration:
Highlight maps provide a clear and concise way to explore large datasets, enabling users to quickly identify areas of interest, potential anomalies, and patterns that might be missed with other methods. This visual representation allows for a more intuitive understanding of the data’s distribution and relationships.
2. Improved Data Communication:
Highlight maps excel in communicating complex data to diverse audiences. Their visual nature simplifies the interpretation of information, making it accessible to individuals with varying levels of technical expertise. This visual clarity facilitates effective communication of insights and fosters better collaboration.
3. Identification of Trends and Outliers:
The color gradient used in highlight maps effectively highlights areas with high and low values, enabling the identification of trends and outliers. This feature is particularly useful for identifying potential risks, opportunities, and areas requiring further investigation.
4. Data Comparison and Analysis:
Highlight maps can be used to compare different datasets or variables, allowing for side-by-side analysis and identification of similarities, differences, and potential correlations. This comparative approach facilitates a deeper understanding of the data’s relationships and interdependencies.
5. Data-Driven Decision-Making:
By providing a clear and concise visual representation of data, highlight maps empower informed decision-making. They enable users to quickly grasp critical information, identify potential risks and opportunities, and make data-driven decisions with greater confidence.
Applications of Highlight Maps
The versatility of highlight maps makes them applicable across various domains, including:
1. Business Analytics:
- Sales and Marketing: Identifying high-performing sales regions, understanding customer demographics, and optimizing marketing campaigns.
- Financial Analysis: Detecting financial irregularities, analyzing stock market trends, and identifying investment opportunities.
- Operations Management: Optimizing supply chain logistics, identifying production bottlenecks, and improving operational efficiency.
2. Healthcare:
- Medical Imaging: Identifying areas of interest in medical scans, aiding in disease diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Epidemiology: Visualizing disease outbreaks and identifying high-risk areas, informing public health interventions.
- Clinical Research: Analyzing patient data to identify treatment effectiveness and potential side effects.
3. Environmental Studies:
- Climate Change: Visualizing temperature anomalies, identifying areas affected by climate change, and informing mitigation strategies.
- Pollution Monitoring: Mapping pollution levels, identifying sources of contamination, and informing environmental regulations.
- Natural Resource Management: Monitoring forest cover, identifying areas with high biodiversity, and informing conservation efforts.
4. Social Sciences:
- Urban Planning: Identifying areas with high crime rates, analyzing population density, and informing urban development projects.
- Political Science: Mapping voting patterns, understanding political trends, and analyzing electoral outcomes.
- Sociology: Visualizing social inequalities, identifying areas with high poverty rates, and informing social policy interventions.
FAQs about Highlight Maps
1. What types of data can be represented using highlight maps?
Highlight maps can represent various types of data, including numerical, categorical, and spatial data. They are particularly effective for visualizing data with a continuous range of values, such as temperature, sales figures, or population density.
2. How are highlight maps created?
Highlight maps are typically created using specialized software or tools like Excel, Tableau, or R. These tools allow users to import data, select appropriate color gradients, and customize the visualization to meet their specific needs.
3. What are the limitations of highlight maps?
While powerful, highlight maps have limitations. They may not be suitable for representing highly complex datasets with multiple variables or for visualizing data with discrete values. Additionally, the choice of color gradient can influence data interpretation, and it is crucial to use appropriate color schemes to avoid misrepresentation.
4. How can I ensure the accuracy and clarity of highlight maps?
To ensure the accuracy and clarity of highlight maps, it is important to select an appropriate color gradient, clearly label the axes and legend, and use consistent scales. Additionally, consider using interactive features like tooltips to provide more detailed information on hover.
Tips for Creating Effective Highlight Maps
1. Choose an appropriate color gradient: Select a color scheme that effectively represents the data range and ensures clarity and visual appeal. Consider using warm colors for higher values and cool colors for lower values.
2. Label axes and legend: Clearly label the axes and legend to provide context and facilitate data interpretation. Use concise and informative labels that are easy to understand.
3. Use consistent scales: Ensure that the color scale remains consistent across different highlight maps to facilitate comparison and analysis. This ensures that the same color represents the same value across different visualizations.
4. Consider using interactive features: Incorporate features like tooltips, zoom capabilities, and filtering options to enhance data exploration and provide more detailed insights.
5. Focus on clarity and simplicity: Aim for a clear and concise visualization that effectively communicates the key insights without overwhelming the viewer with unnecessary detail.
Conclusion
Highlight maps offer a powerful and versatile tool for visualizing data, revealing hidden patterns, and facilitating informed decision-making. Their ability to represent complex data in a clear and intuitive manner makes them invaluable across various fields, from business analytics to healthcare and environmental studies. By understanding the strengths and limitations of highlight maps and following best practices for their creation, users can leverage this powerful visualization technique to gain meaningful insights from their data and make data-driven decisions with greater confidence.

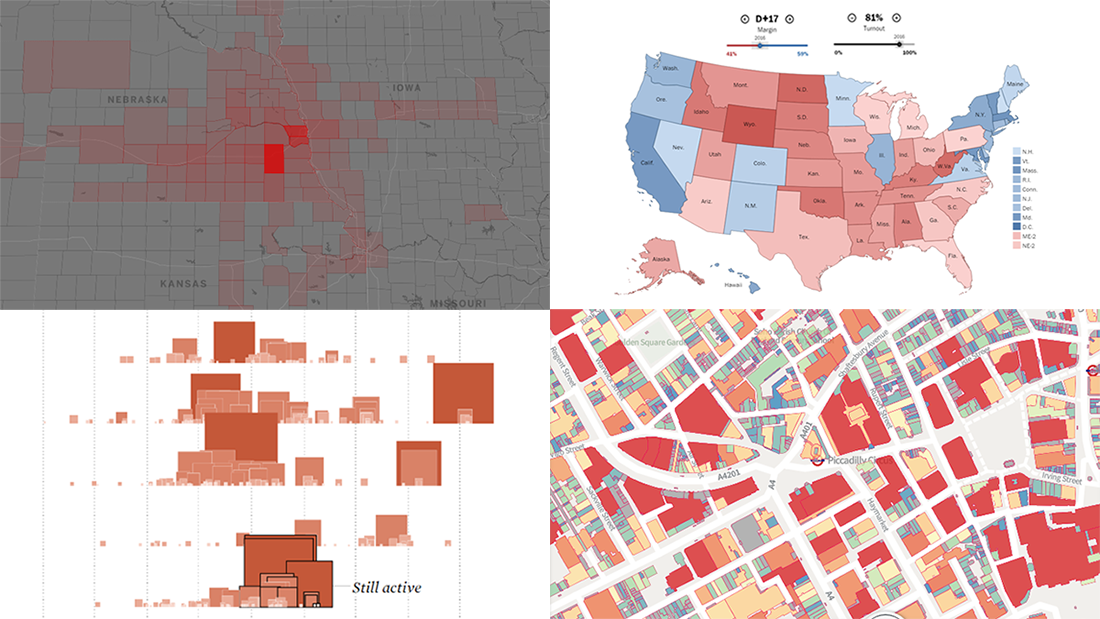
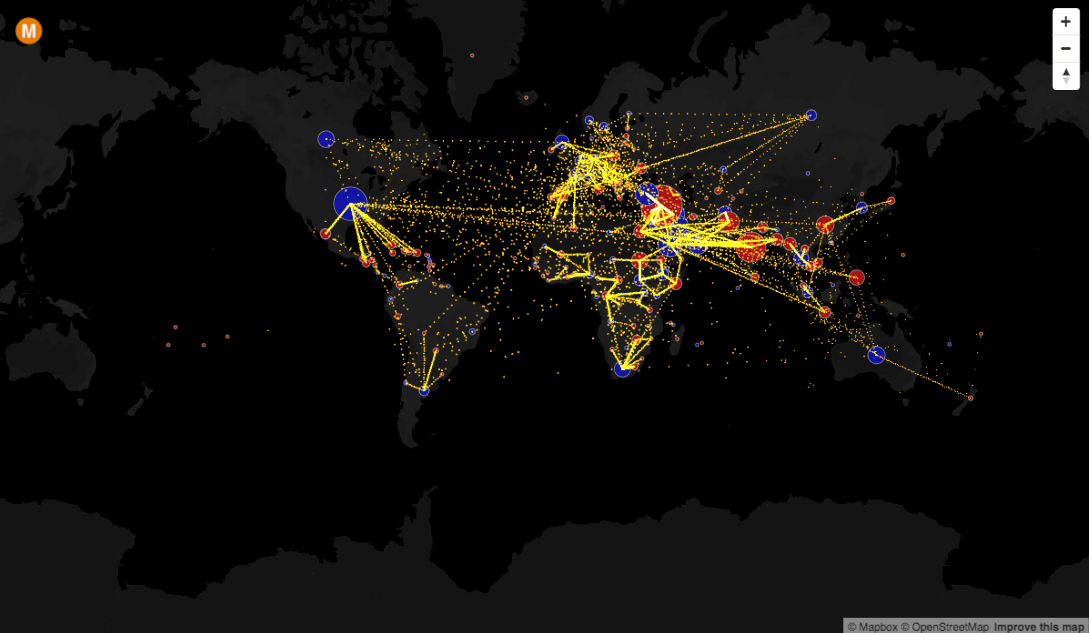




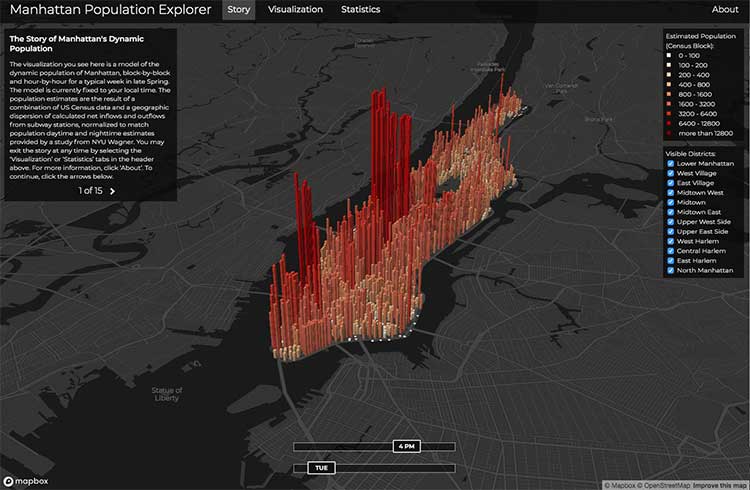
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visualization: Understanding and Utilizing Highlight Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!