Shechem: A Crossroads of History and Faith
Related Articles: Shechem: A Crossroads of History and Faith
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shechem: A Crossroads of History and Faith. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shechem: A Crossroads of History and Faith
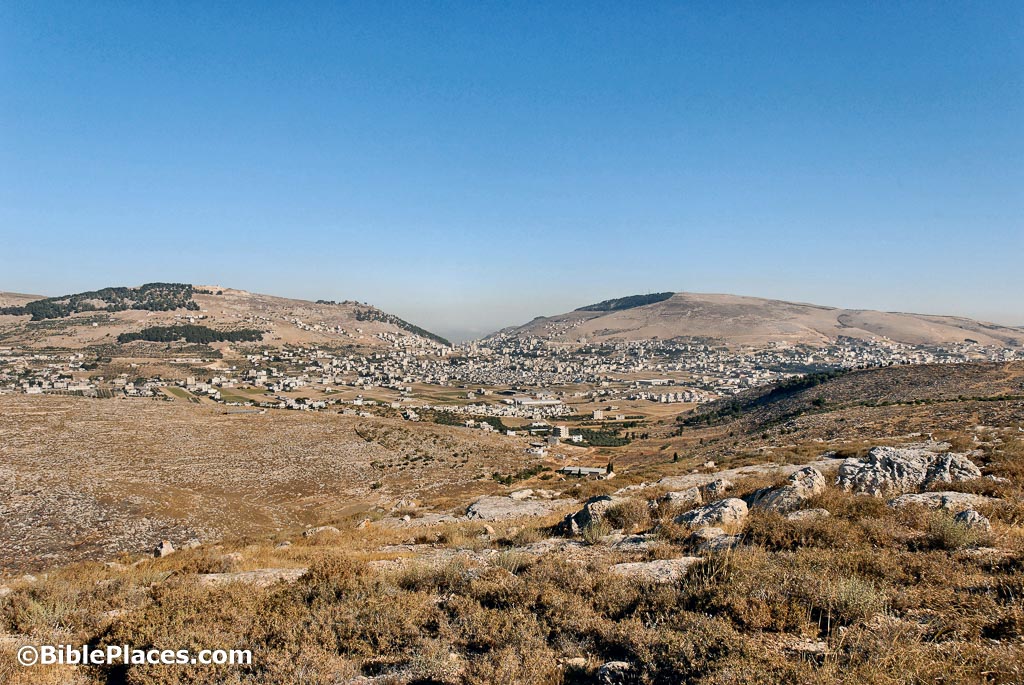

Shechem, a city steeped in history and religious significance, holds a prominent place in the narratives of both the Bible and ancient Near Eastern history. Its strategic location at the crossroads of major trade routes and its fertile valley have made it a magnet for civilizations and cultures throughout the ages. This article will explore the historical and geographical significance of Shechem, examining its role in the development of ancient Israel, its connection to Abraham and Jacob, and its enduring presence in religious traditions.
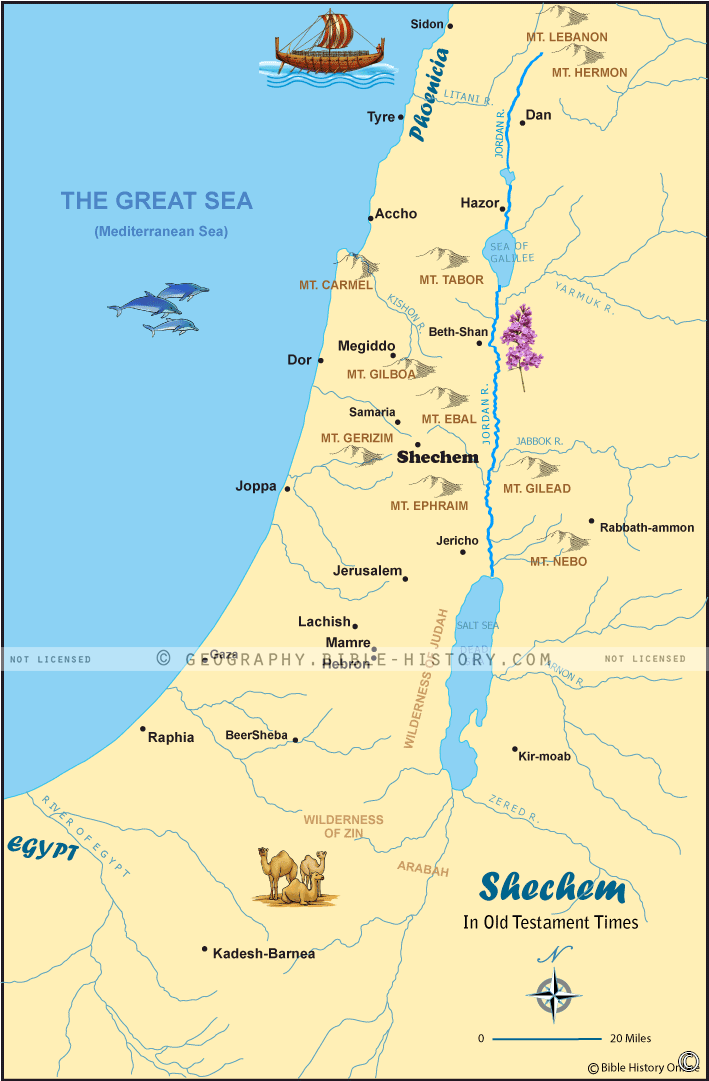
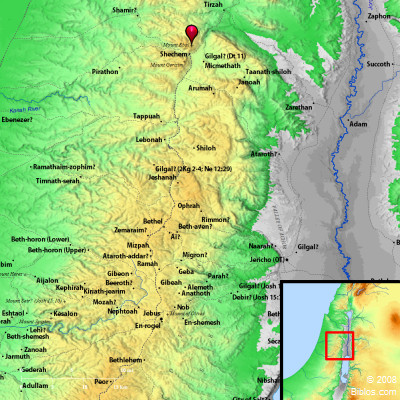
Geographical Context:
Located in the heart of the fertile Shechem Valley, a natural passageway between the Mediterranean coast and the Jordan Valley, Shechem’s strategic location has been a key factor in its importance. The valley, known as the "Valley of Blessings" in Hebrew, is blessed with rich soil and abundant water sources, making it ideal for agriculture. The city itself sits at the foot of Mount Gerizim, a prominent mountain revered by Samaritans, and Mount Ebal, another significant peak mentioned in the Bible.
The Ancient City of Shechem:
Archaeological evidence suggests that Shechem was inhabited as early as the Chalcolithic period (4500-3300 BCE). Its strategic location made it a natural hub for trade and communication, attracting various cultures and civilizations throughout its history. The city was fortified and controlled by the Canaanite city-state of Shechem, and its importance is evident in its mention in Egyptian texts from the 19th Dynasty (1292-1186 BCE).
Shechem in the Biblical Narrative:
Shechem plays a pivotal role in the biblical narrative, particularly in the story of Jacob and his descendants. The city is first mentioned in connection with Abraham, who built an altar there (Genesis 12:6). Jacob, fleeing from his brother Esau, sought refuge in Shechem (Genesis 33:18). He later purchased land from the local inhabitants and established a permanent settlement there (Genesis 33:19).
Shechem’s importance in the development of ancient Israel is further highlighted in the story of Joshua. After the conquest of Canaan, Joshua gathered the Israelites at Shechem to renew their covenant with God (Joshua 24:1-28). This event cemented Shechem’s status as a central location for the Israelites, marking a significant turning point in their history.
The Samaritan Connection:
Shechem holds particular significance for the Samaritans, a religious group who trace their lineage back to the northern tribes of Israel. They consider Mount Gerizim to be the site of the true temple, rejecting the temple in Jerusalem. The Samaritan community in Shechem, while small, has maintained its traditions and beliefs for centuries, contributing to the city’s enduring religious significance.
The Legacy of Shechem:
Despite its historical and religious importance, Shechem has faced periods of decline and destruction. The city was conquered and destroyed by the Assyrians in 722 BCE, marking the end of the Northern Kingdom of Israel. It was later rebuilt and flourished under the Romans, but it eventually fell into decline again.
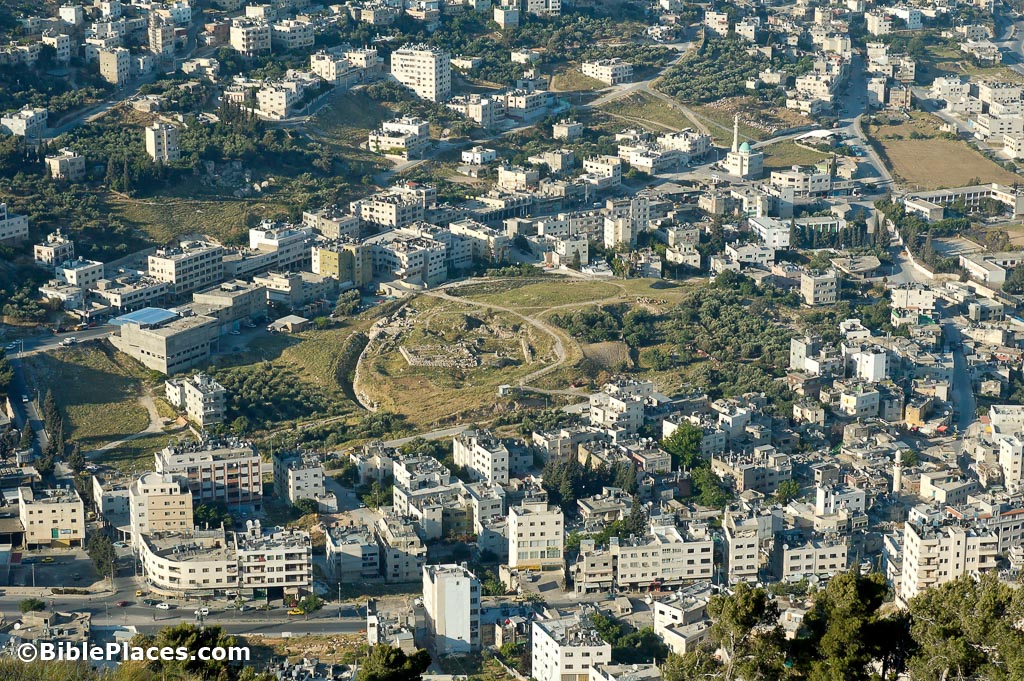
Today, the site of ancient Shechem is known as Nablus, a Palestinian city with a rich history and a diverse population. While the city no longer holds the same political and religious prominence as in ancient times, it remains a testament to the enduring legacy of Shechem, a place that has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the formation of nations, and the development of religious traditions.
FAQs about Shechem:
1. What is the significance of Shechem in the Bible?
Shechem plays a crucial role in the biblical narrative, serving as a key location for the stories of Abraham, Jacob, and Joshua. It is the site of Jacob’s encounter with God, the establishment of his family’s settlement, and the renewal of the covenant with God after the conquest of Canaan.
2. What is the relationship between Shechem and the Samaritans?
Shechem holds a special place in Samaritan religious tradition. They consider Mount Gerizim to be the site of the true temple, rejecting the temple in Jerusalem. The Samaritan community in Shechem has maintained its traditions and beliefs for centuries, contributing to the city’s enduring religious significance.
3. What is the current name of Shechem?
The site of ancient Shechem is currently known as Nablus, a Palestinian city located in the West Bank.
4. What are some of the key archaeological sites in Shechem/Nablus?
Key archaeological sites in Shechem/Nablus include the Jacob’s Well, the Tomb of Joseph, and the ruins of the ancient city, including the remains of a Canaanite temple and a Roman amphitheater.
5. What are some of the cultural and historical influences on Shechem?
Shechem has been influenced by various cultures and civilizations throughout its history, including the Canaanites, Israelites, Assyrians, Romans, and Ottomans. This diverse history is reflected in the city’s architecture, language, and traditions.
Tips for Visiting Shechem/Nablus:
- Plan your visit in advance: Research the best time to visit, consider the current political situation, and obtain any necessary travel documentation.
- Be respectful of local customs and traditions: Dress modestly, avoid public displays of affection, and be mindful of religious sensitivities.
- Learn some basic Arabic phrases: This will help you communicate with locals and enhance your experience.
- Visit the Jacob’s Well: This sacred well is a significant landmark for both Christians and Muslims.
- Explore the Old City: The Old City of Nablus is a maze of narrow streets and bustling markets, offering a glimpse into the city’s rich history and culture.
- Visit the Tomb of Joseph: This tomb, venerated by both Muslims and Christians, is a testament to the city’s enduring religious significance.
Conclusion:
Shechem, now known as Nablus, is a city steeped in history and faith, offering a glimpse into the ancient world and the enduring power of religion and tradition. Its strategic location, fertile valley, and rich history have made it a crossroads of cultures and civilizations, attracting traders, pilgrims, and conquerors throughout the ages. As a place of pilgrimage, a center of trade, and a site of religious significance, Shechem continues to hold a place of importance in the narratives of history, religion, and culture. Its legacy is a testament to the enduring power of place, faith, and the human spirit.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shechem: A Crossroads of History and Faith. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!