Navigating West Africa: A Geographical and Cultural Journey
Related Articles: Navigating West Africa: A Geographical and Cultural Journey
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating West Africa: A Geographical and Cultural Journey. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating West Africa: A Geographical and Cultural Journey

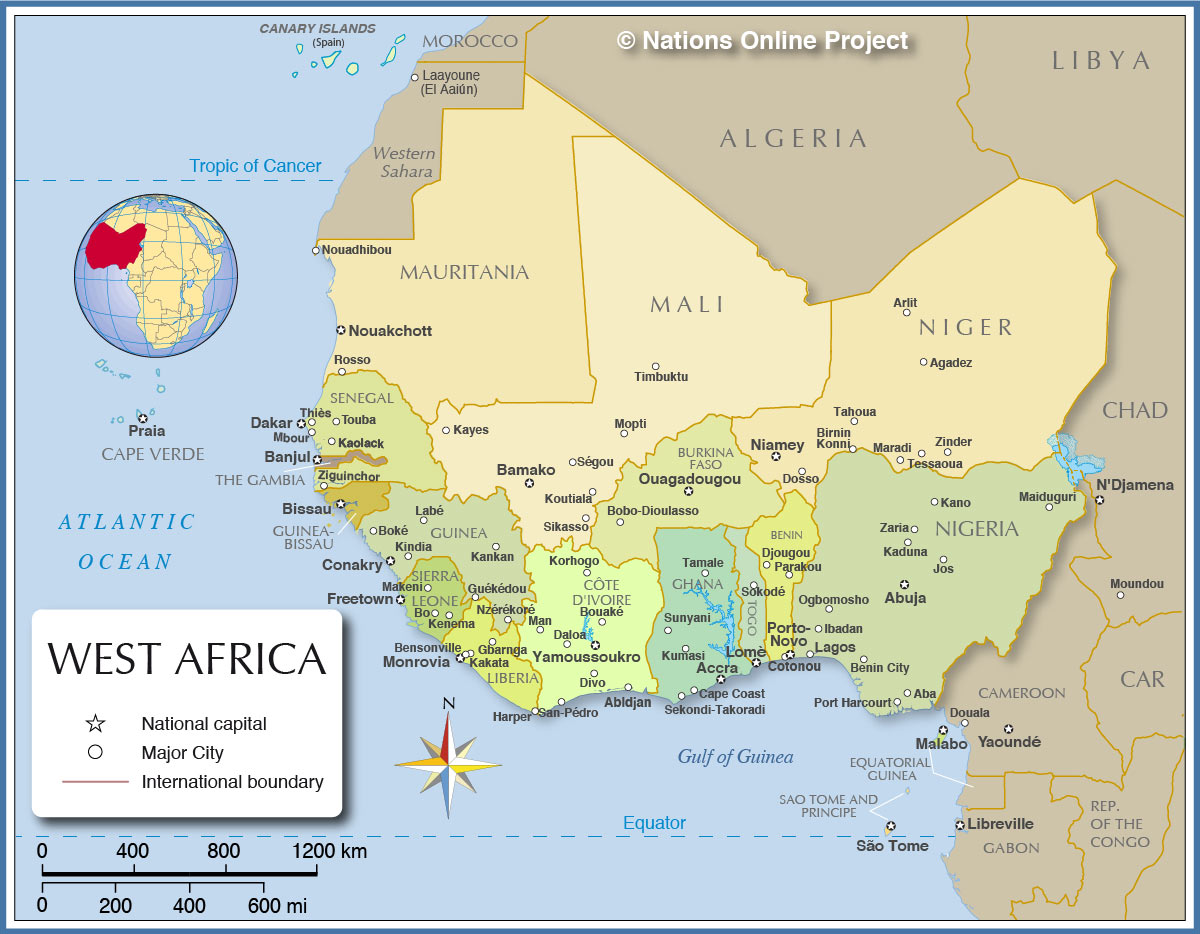
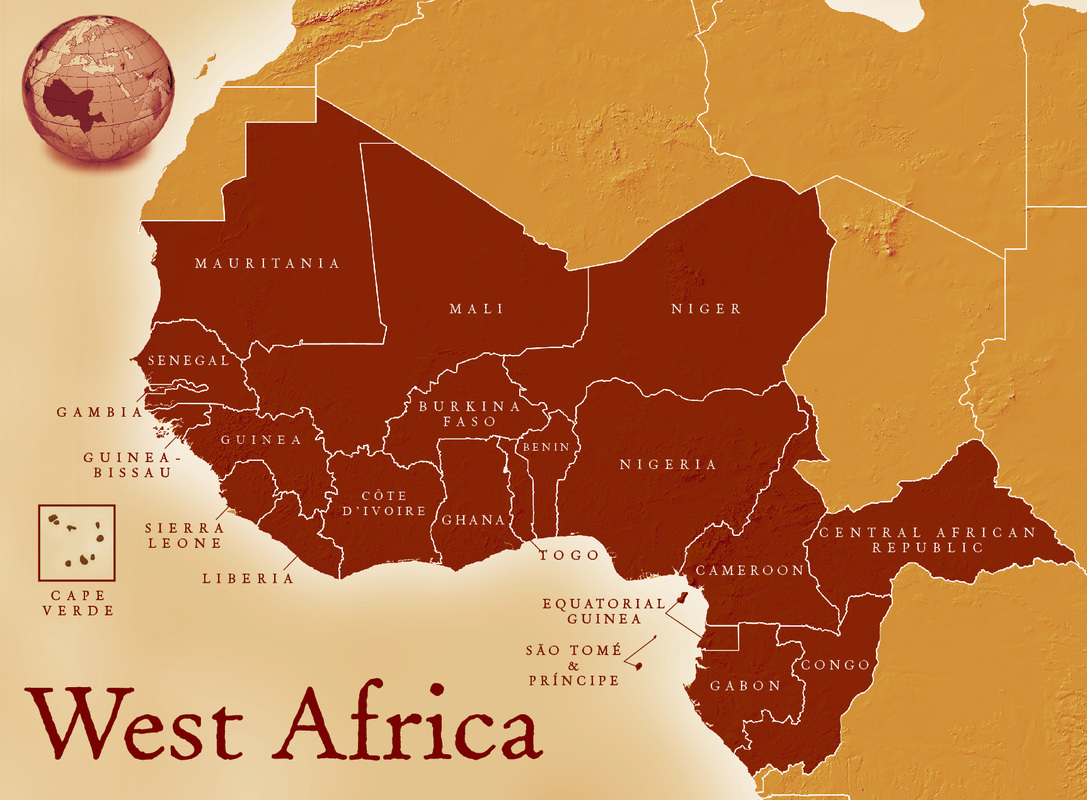
West Africa, a vibrant region on the westernmost edge of the African continent, is a tapestry of diverse cultures, landscapes, and histories. Understanding the geography of this region is crucial for appreciating its complexities and appreciating the interconnectedness of its people and ecosystems.
A Mosaic of Nations:
West Africa encompasses sixteen distinct countries, each with its unique character and contributions to the region’s rich heritage:
-
The Coastal Belt:
- Senegal: Known for its vibrant culture, stunning beaches, and the historic city of Saint-Louis.
- Gambia: The smallest country in mainland Africa, renowned for its riverine landscape and rich wildlife.
- Guinea-Bissau: Characterized by its diverse archipelago, mangrove forests, and historical ties to Portugal.
- Guinea: A nation rich in mineral resources, with a unique cultural heritage and breathtaking highlands.
- Sierra Leone: A country recovering from past conflict, with a growing economy and a rich tradition of music and dance.
- Liberia: Founded by freed American slaves, Liberia boasts beautiful beaches, diverse ecosystems, and a rich cultural heritage.
- Côte d’Ivoire: A nation known for its cocoa production, vibrant cities, and diverse cultural landscape.
- Ghana: A nation with a rich history, including the ancient Kingdom of Ghana, and a modern economy driven by cocoa and gold.
- Togo: A country with a diverse landscape, ranging from coastal plains to mountainous regions, and a vibrant cultural scene.
- Benin: Home to the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Ouidah, Benin boasts a rich cultural heritage and a growing economy.
- Nigeria: The most populous country in Africa, Nigeria is a major oil producer with a diverse cultural landscape and a thriving entertainment industry.
-
The Sahel Region:
- Mauritania: A vast country with a diverse landscape, including the Sahara Desert, the Atlantic Coast, and the Senegal River Valley.
- Mali: Known for its rich cultural heritage, including the Dogon cliff dwellings and the Timbuktu mosque.
- Burkina Faso: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, including the Mossi plateau and the Pendjari National Park.
- Niger: A country with vast desert landscapes, a rich cultural heritage, and a growing economy based on uranium mining.
- Chad: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, including the Sahara Desert, the Lake Chad Basin, and the Tibesti Mountains.
Navigating the Map:
A map of West Africa provides a visual representation of the region’s diverse geography. The Atlantic Ocean forms the western boundary, while the Sahel region, a transitional zone between the Sahara Desert and the savanna, stretches across the northern part of the region.
The map highlights key geographical features:
- The Niger River: This major waterway flows through the region, providing a vital source of water for agriculture and transportation.
- The Volta River: This river system forms the Volta Basin, a major source of hydropower and a significant agricultural region.
- The Sahara Desert: The world’s largest hot desert, the Sahara extends into the northern reaches of West Africa, influencing the region’s climate and ecology.
- The Guinean Forests: These lush rainforests along the coast are home to a remarkable diversity of flora and fauna.
- The Fouta Djallon Highlands: These highlands in Guinea are a vital source of water for the region and play a significant role in regulating the climate.
Beyond the Boundaries:
The West African map is not merely a collection of geographical features. It represents a complex tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions.
- Linguistic Diversity: West Africa is home to hundreds of languages, reflecting the region’s long history of cultural exchange and migration.
- Cultural Tapestry: From the vibrant music and dance traditions of Senegal to the ancient rituals of the Dogon people in Mali, West Africa’s cultural diversity is a testament to its rich history and enduring traditions.
- Historical Connections: The region’s history is intertwined with the transatlantic slave trade, colonialism, and the struggle for independence. These historical events continue to shape the region’s present and future.
The Importance of the West African Map:
Understanding the geography of West Africa is essential for:
- Understanding the Region’s Challenges: Challenges such as poverty, climate change, and conflict are intricately linked to the region’s geography.
- Supporting Sustainable Development: Effective development strategies must consider the region’s unique geographical characteristics and the needs of its diverse communities.
- Preserving Cultural Heritage: The map highlights the importance of protecting the region’s diverse cultural heritage and promoting cultural understanding.
- Promoting Regional Integration: The map serves as a reminder of the shared challenges and opportunities facing West African nations, fostering regional cooperation and integration.
FAQs about West Africa:
1. What is the largest country in West Africa?
Nigeria, with a population of over 200 million, is the largest country in West Africa by both population and land area.
2. Which West African countries are landlocked?
Mali, Burkina Faso, Niger, and Chad are landlocked countries in West Africa.
3. What is the significance of the Niger River?
The Niger River is a vital source of water for agriculture, transportation, and drinking water for millions of people in West Africa. It also plays a significant role in the region’s cultural and economic life.
4. What are the major economic activities in West Africa?
Major economic activities in West Africa include agriculture, mining, oil and gas production, and tourism.
5. What are some of the challenges facing West Africa?
West Africa faces a number of challenges, including poverty, conflict, climate change, and environmental degradation.
Tips for Understanding the West African Map:
- Use a detailed map: A detailed map with clear labels and geographical features will provide a comprehensive understanding of the region.
- Study the physical features: Pay attention to the major rivers, mountains, deserts, and forests, as these features play a significant role in shaping the region’s landscape and influencing its climate.
- Explore the cultural landscape: Learn about the diverse cultures, languages, and traditions of the region.
- Consider the historical context: Understanding the region’s history, including colonialism and the transatlantic slave trade, is essential for appreciating its current state.
- Engage with local communities: If you have the opportunity, interact with people from different parts of West Africa to gain a deeper understanding of their perspectives and experiences.
Conclusion:
The map of West Africa is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s diverse geography, its rich cultural heritage, and the challenges it faces. By navigating the map and exploring its intricacies, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of this vibrant region and its importance in the global landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating West Africa: A Geographical and Cultural Journey. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!