Navigating the Landscape of Trust: A Comprehensive Guide to the Trust Region Constraint (TRC) Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Trust: A Comprehensive Guide to the Trust Region Constraint (TRC) Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Trust: A Comprehensive Guide to the Trust Region Constraint (TRC) Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Trust: A Comprehensive Guide to the Trust Region Constraint (TRC) Map
The Trust Region Constraint (TRC) map, a powerful tool in the realm of optimization, offers a structured and efficient approach to navigating complex optimization problems. This map serves as a visual representation of the optimization process, highlighting key elements and providing a framework for understanding the algorithm’s progress.
Understanding the Fundamentals
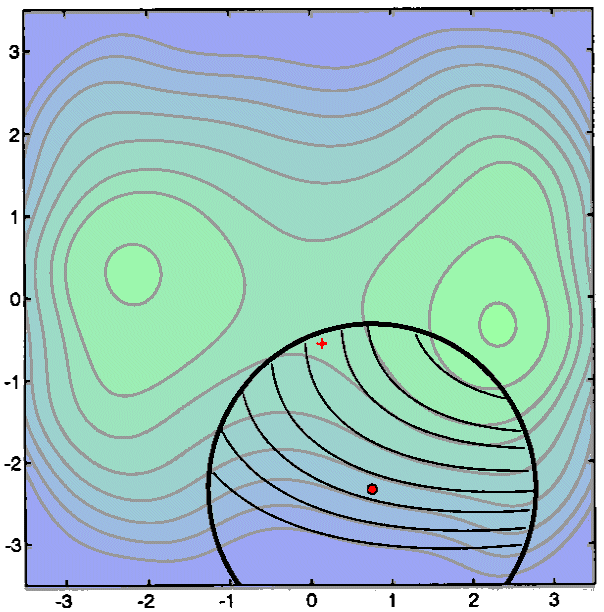
At its core, the TRC map visualizes the search for an optimal solution within a defined region of the problem space. This region, known as the "trust region," represents the area where the algorithm believes the objective function behaves predictably. The map then presents a series of iterations, each representing a step taken by the algorithm towards the optimal solution.
Key Components of the TRC Map
The TRC map comprises several crucial elements:
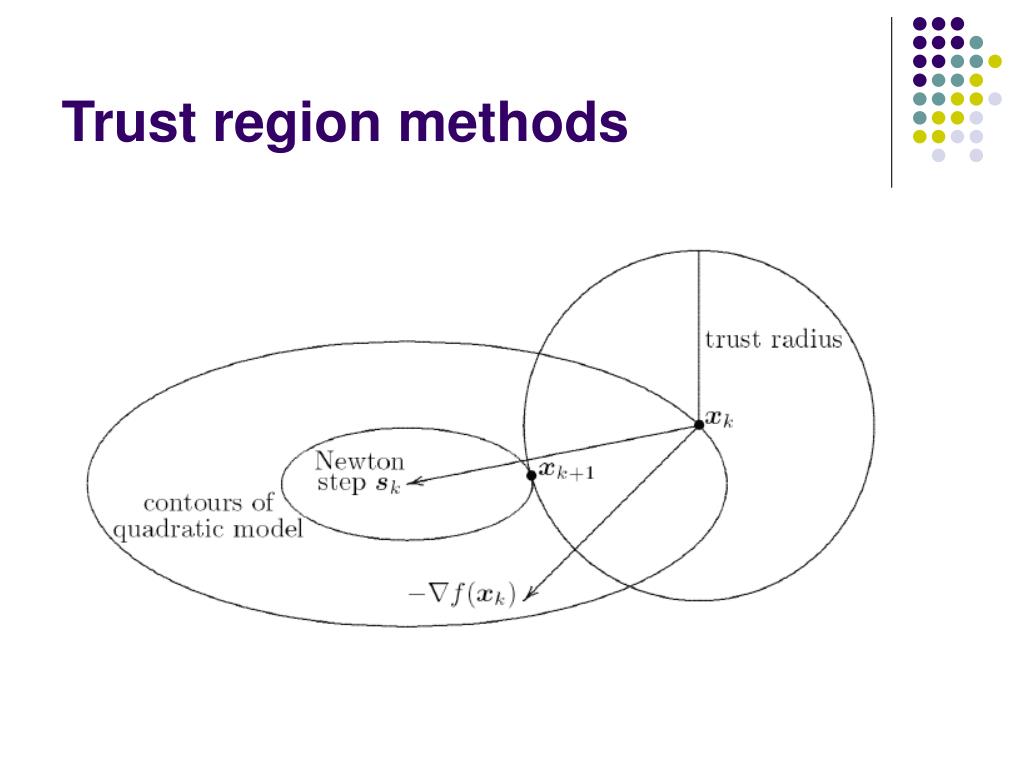
- Trust Region: This region is depicted as a circle or an ellipse on the map, encompassing the area where the algorithm expects a reliable approximation of the objective function.
- Current Solution: This point on the map represents the algorithm’s current best estimate of the optimal solution.
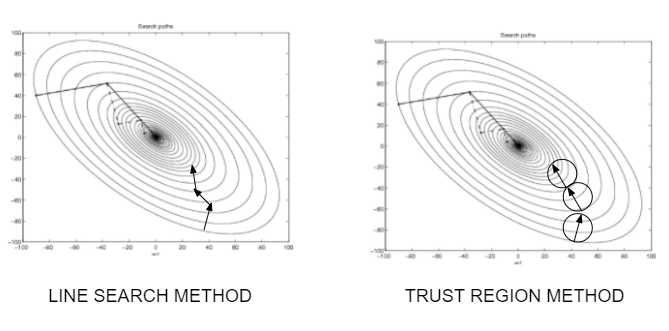
- Step Direction: Each iteration involves a step taken from the current solution in a specific direction, aimed at improving the objective function value. This direction is represented by an arrow on the map.
- Step Length: The length of the arrow indicates the magnitude of the step taken in the chosen direction.
- Objective Function Value: The map often includes contours or color gradients to represent the values of the objective function across the problem space.
Iterative Optimization Process
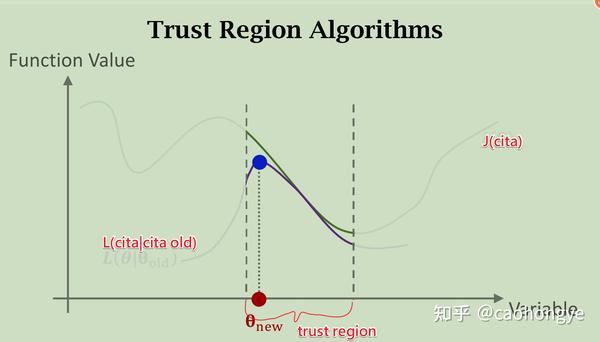
The TRC map visualizes the iterative nature of the optimization process. The algorithm starts with an initial solution and iteratively refines it by taking steps within the trust region. The size and shape of the trust region are dynamically adjusted based on the algorithm’s progress.
Benefits of the TRC Map
The TRC map offers several advantages:
- Visual Understanding: It provides a clear visual representation of the optimization process, allowing for a deeper understanding of the algorithm’s behavior.
- Problem Identification: The map can highlight potential issues like poor step directions or inefficient trust region sizes, enabling adjustments to improve the algorithm’s performance.
- Convergence Monitoring: The map allows for visualization of the algorithm’s convergence behavior, indicating whether it is approaching the optimal solution.
- Algorithm Comparison: By comparing TRC maps for different optimization algorithms, it becomes possible to evaluate their relative effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Beyond Visualization: Practical Applications
The TRC map’s application extends beyond visualization. It serves as a powerful tool for:
- Algorithm Design: The map aids in developing new optimization algorithms by providing insights into the interplay of step direction, step length, and trust region size.
- Parameter Tuning: The map helps in fine-tuning algorithm parameters, such as the initial trust region size and the step length control mechanism.
- Problem Analysis: The map provides a framework for analyzing the structure of the optimization problem, identifying potential difficulties and suggesting strategies for overcoming them.
FAQs Regarding the TRC Map
1. What are the limitations of the TRC map?
While the TRC map offers valuable insights, it has limitations. It primarily focuses on the local behavior of the objective function within the trust region. It may not capture the global landscape of the problem, potentially missing alternative optimal solutions.
2. How does the TRC map handle constraints?
Constraints are incorporated into the optimization problem by modifying the trust region shape or adding additional constraints to the step direction calculation. The map still provides a visual representation of the constrained optimization process.
3. How does the TRC map relate to other optimization methods?
The TRC map is a visualization tool that can be used with various optimization methods, including gradient descent, Newton’s method, and quasi-Newton methods. Its application is not limited to specific algorithms.
4. What are some examples of practical applications of the TRC map?
The TRC map finds applications in diverse fields, including:
- Machine Learning: Optimizing machine learning models, such as neural networks.
- Engineering: Designing optimal structures and systems.
- Finance: Portfolio optimization and risk management.
- Operations Research: Solving complex scheduling and logistics problems.
Tips for Utilizing the TRC Map Effectively
- Choose a Suitable Scale: Select an appropriate scale for the map to clearly visualize the relevant details of the optimization process.
- Use Color and Shape: Employ different colors and shapes to represent key elements, enhancing the map’s readability and clarity.
- Include Relevant Information: Incorporate essential information, such as objective function values, step lengths, and trust region sizes, to provide a comprehensive picture.
- Interpret the Results: Analyze the map to gain insights into the algorithm’s performance, identify potential issues, and guide further optimization efforts.
Conclusion
The TRC map offers a valuable tool for understanding, analyzing, and improving optimization algorithms. By providing a visual representation of the optimization process, it allows for a deeper understanding of the algorithm’s behavior, aiding in algorithm design, parameter tuning, and problem analysis. Its application extends across various fields, making it a powerful tool for tackling complex optimization challenges. As optimization techniques continue to evolve, the TRC map remains a valuable resource for navigating the landscape of trust and reaching optimal solutions.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Trust: A Comprehensive Guide to the Trust Region Constraint (TRC) Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!