Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding California’s Earthquake Risk Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding California’s Earthquake Risk Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding California’s Earthquake Risk Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding California’s Earthquake Risk Map
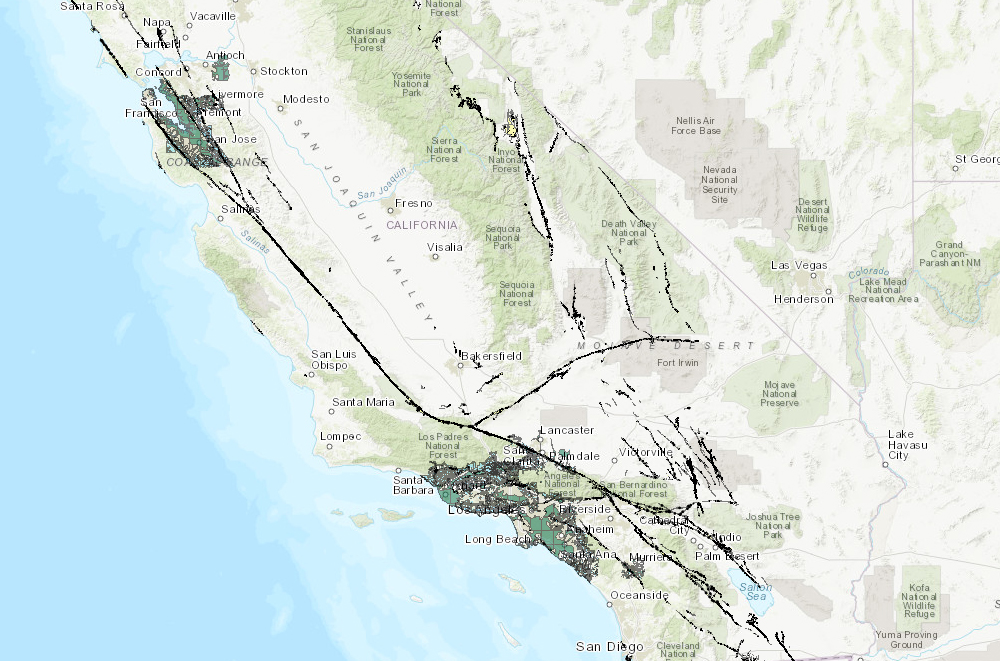
California is synonymous with earthquakes. The state sits atop the notorious San Andreas Fault, a geological scar stretching over 800 miles, marking the boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates. This constant geological dance generates seismic activity, making California a region perpetually susceptible to earthquakes. To better understand and prepare for these natural hazards, the California Geological Survey (CGS) has developed a comprehensive Earthquake Risk Map. This map, a vital tool for policymakers, emergency responders, and individuals alike, provides a visual representation of earthquake hazards across the state.
Deciphering the Map: A Visual Guide to Seismic Risks
The Earthquake Risk Map, available on the CGS website, is a complex and informative document. It uses a color-coded system to depict varying levels of earthquake risk, incorporating factors like:
- Fault Zones: The map clearly identifies major and minor fault lines, including the San Andreas Fault, which are prone to generating significant earthquakes.
- Ground Shaking Intensity: Using a scale known as the Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI) scale, the map indicates the potential intensity of ground shaking during an earthquake. Higher MMI values represent stronger shaking and greater potential for damage.
- Liquefaction Potential: Certain soils, when subjected to intense shaking, can lose their strength and behave like a liquid, a phenomenon known as liquefaction. The map identifies areas susceptible to liquefaction, highlighting the risk of foundation failure and structural damage.
- Landslides: Earthquakes can trigger landslides, particularly in areas with steep slopes and unstable soil. The map designates regions prone to landslides, emphasizing the need for mitigation measures.
- Tsunami Risk: Coastal areas are vulnerable to tsunamis, giant waves generated by earthquakes. The map outlines areas at risk of tsunami inundation, providing crucial information for evacuation planning.
Beyond the Colors: Understanding the Nuances of Earthquake Risk
The Earthquake Risk Map is more than just a visual representation of potential hazards. It serves as a vital tool for:
- Land Use Planning: The map helps guide decisions regarding land use, ensuring that development occurs in areas with lower earthquake risk. This minimizes the potential for damage and loss of life during seismic events.
- Infrastructure Design: Engineers use the map to design earthquake-resistant structures, bridges, and other infrastructure, making them more resilient to seismic forces.
- Emergency Response: The map assists emergency responders in prioritizing areas for search and rescue, medical aid, and disaster relief, ensuring efficient and effective response to earthquakes.
- Public Awareness: The map serves as a powerful educational tool, raising public awareness about earthquake risks and encouraging proactive measures to mitigate potential damage.
FAQs: Unveiling the Insights Behind the Map
1. How frequently are earthquakes expected in California?
California experiences an average of one earthquake with a magnitude of 6.0 or greater each year. However, the frequency and intensity of earthquakes vary depending on the specific location and the activity of the fault lines.
2. What is the significance of the San Andreas Fault?
The San Andreas Fault is the most significant fault in California, responsible for generating some of the state’s largest and most destructive earthquakes. It is a major boundary between the Pacific and North American tectonic plates, constantly moving and generating seismic activity.
3. How can I find my location on the Earthquake Risk Map?
The California Geological Survey website provides an interactive map tool that allows users to zoom in on specific locations and view the earthquake risk information for their area.
4. What steps can I take to prepare for an earthquake?
Preparing for an earthquake involves several steps, including:
- Secure your home: Secure heavy objects, install earthquake-resistant bracing for cabinets, and reinforce your home’s foundation.
- Create a family emergency plan: Develop a plan for communication and evacuation in the event of an earthquake.
- Prepare an emergency kit: Stock up on food, water, first-aid supplies, and other essentials that may be needed during a disaster.
- Stay informed: Subscribe to earthquake alerts and stay updated on the latest information from reliable sources.
Tips: Building Resilience in the Face of Earthquake Risk
- Understand your local risk: Familiarize yourself with the earthquake risk in your area by consulting the Earthquake Risk Map.
- Practice earthquake drills: Regularly practice earthquake drills with your family to ensure everyone knows what to do in the event of a seismic event.
- Secure your belongings: Secure valuable items, such as artwork and electronics, to prevent damage during an earthquake.
- Stay informed: Stay up-to-date on the latest earthquake research and safety recommendations from reputable sources.
Conclusion: A Constant Reminder of the Earth’s Unpredictability
California’s Earthquake Risk Map is not just a tool for understanding potential hazards; it is a reminder of the dynamic nature of our planet. Earthquakes are a natural phenomenon, and while we cannot prevent them, we can prepare for them. By understanding the risks, taking proactive steps, and staying informed, we can build resilience and minimize the impact of earthquakes on our lives and communities. The map serves as a constant reminder of the importance of preparedness, encouraging us to embrace the challenges of living in a tectonically active region.

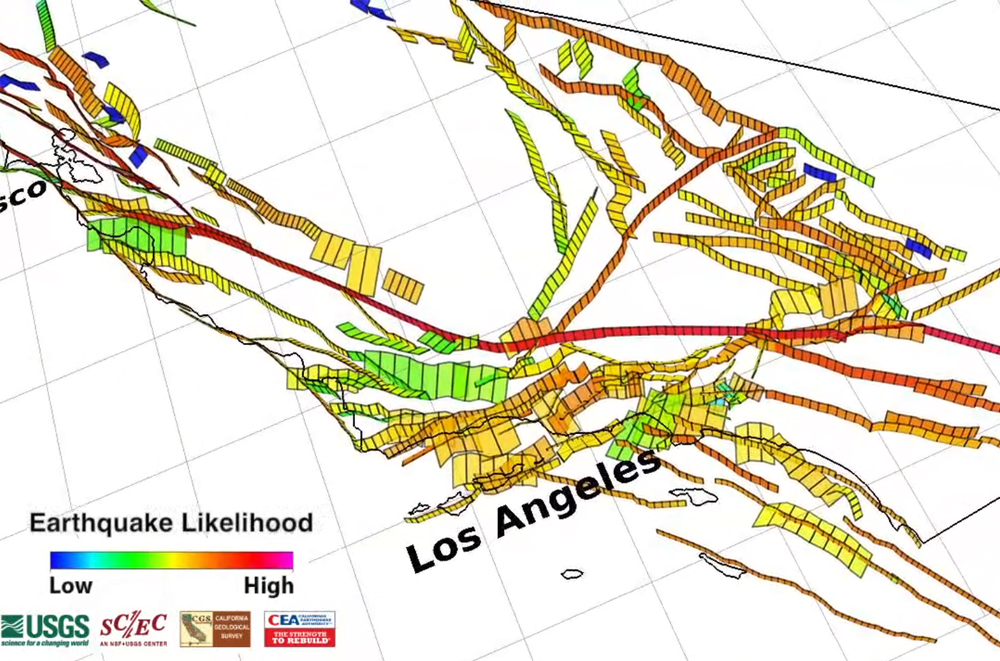



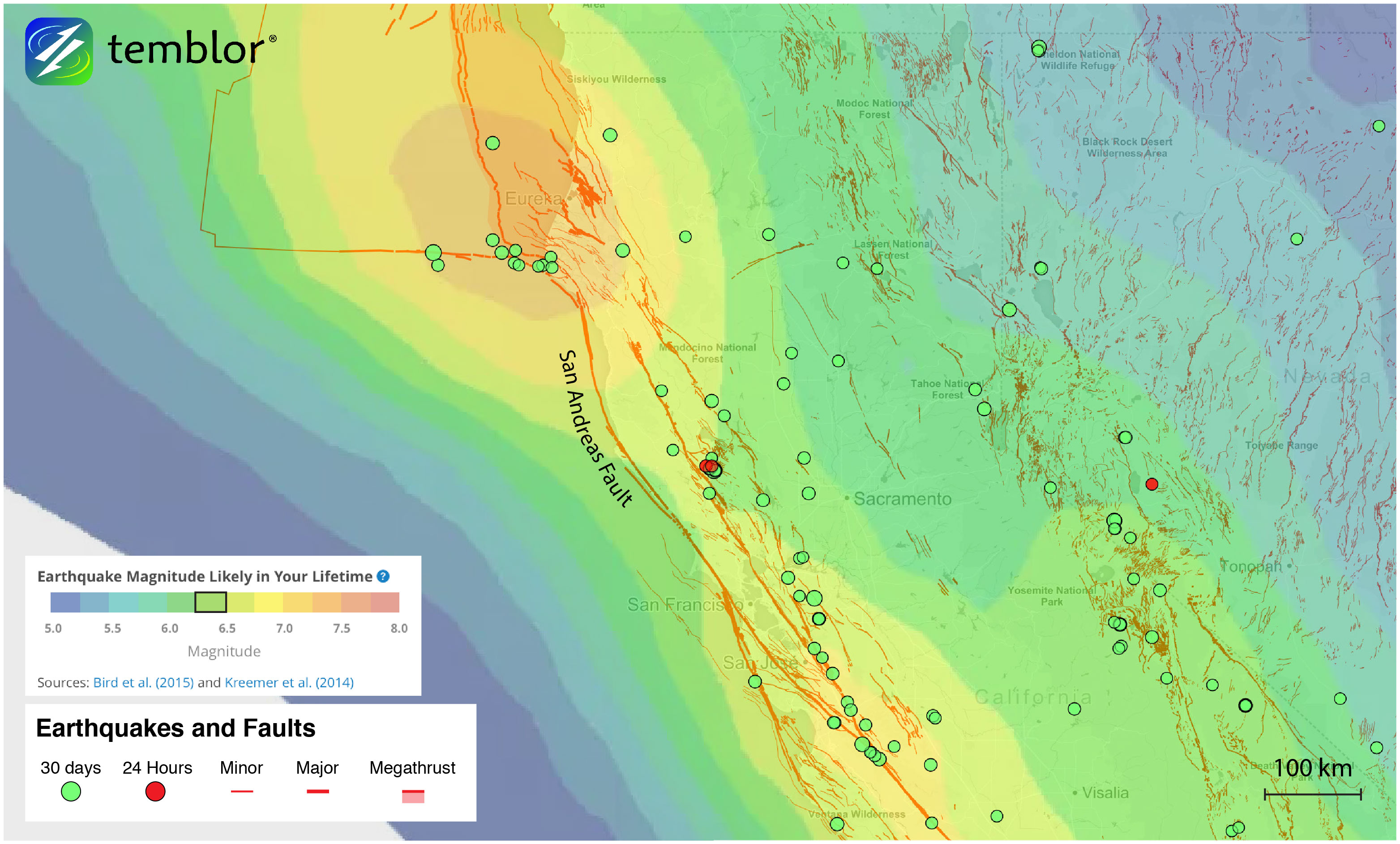


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Fault Lines: Understanding California’s Earthquake Risk Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!