Mapping the Threat: Understanding the Lyme Disease Landscape
Related Articles: Mapping the Threat: Understanding the Lyme Disease Landscape
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Threat: Understanding the Lyme Disease Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Threat: Understanding the Lyme Disease Landscape

Lyme disease, a debilitating illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, poses a significant public health concern. Its transmission through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks (also known as deer ticks) necessitates a nuanced understanding of geographic distribution and risk areas. This is where Lyme disease maps come into play, offering a critical tool for both public health officials and individuals to navigate the complexities of this disease.
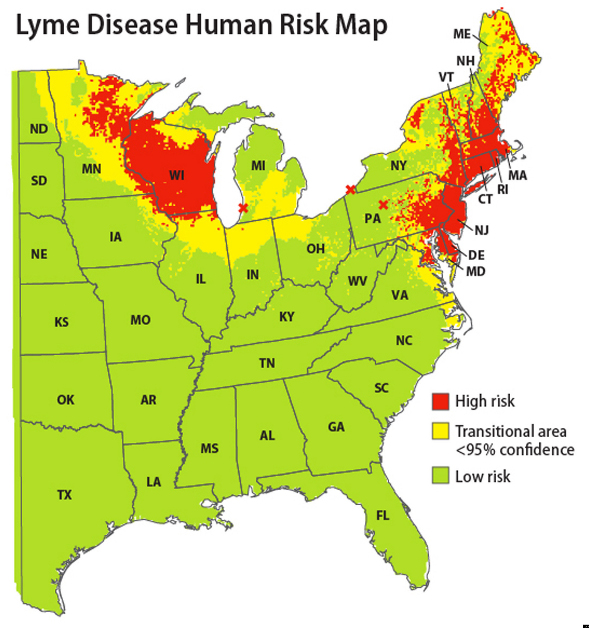
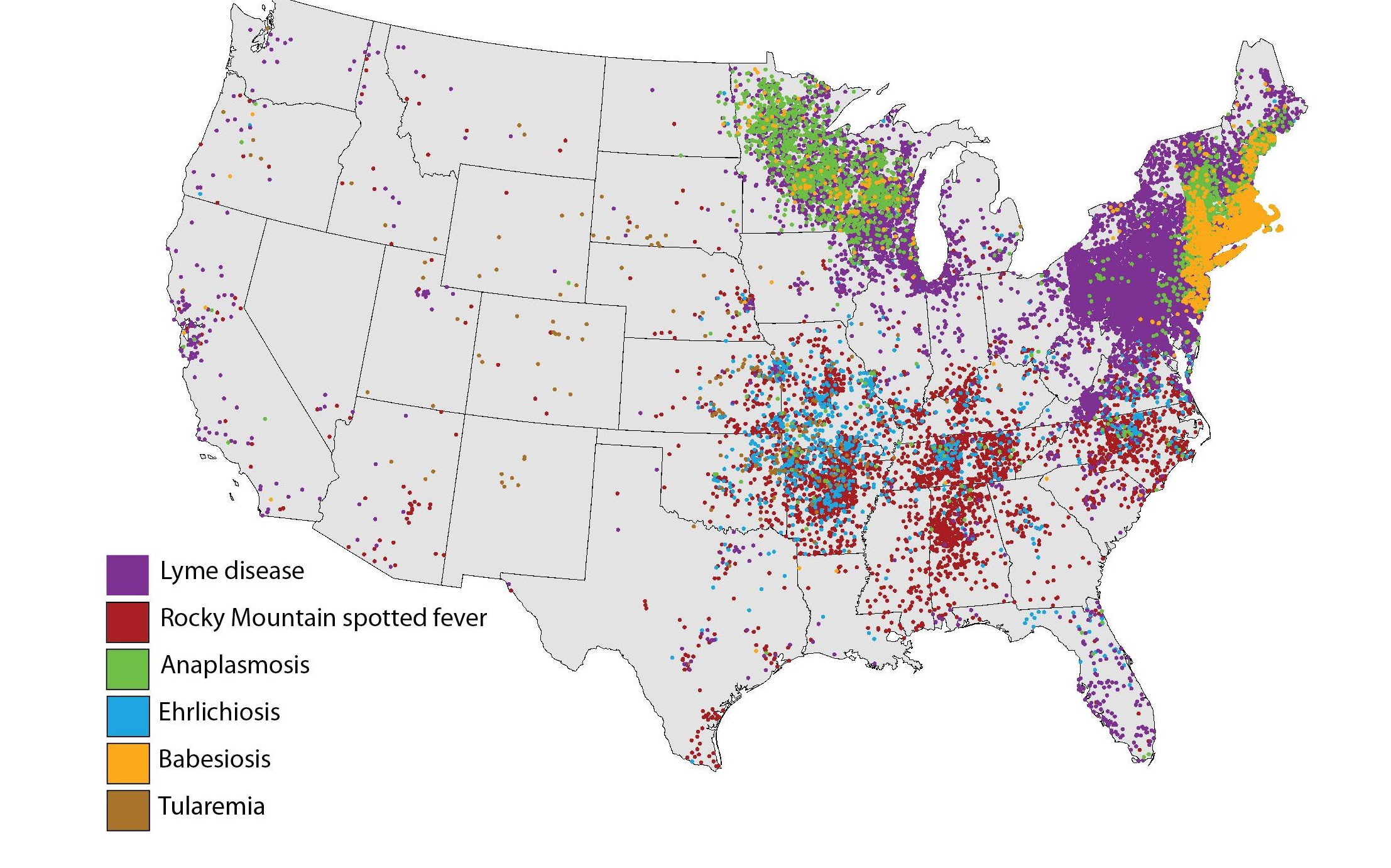
Decoding the Lyme Disease Map: A Visual Guide to Risk
Lyme disease maps are visual representations of the geographic distribution of Lyme disease and its associated risk factors. These maps can be categorized into two main types:
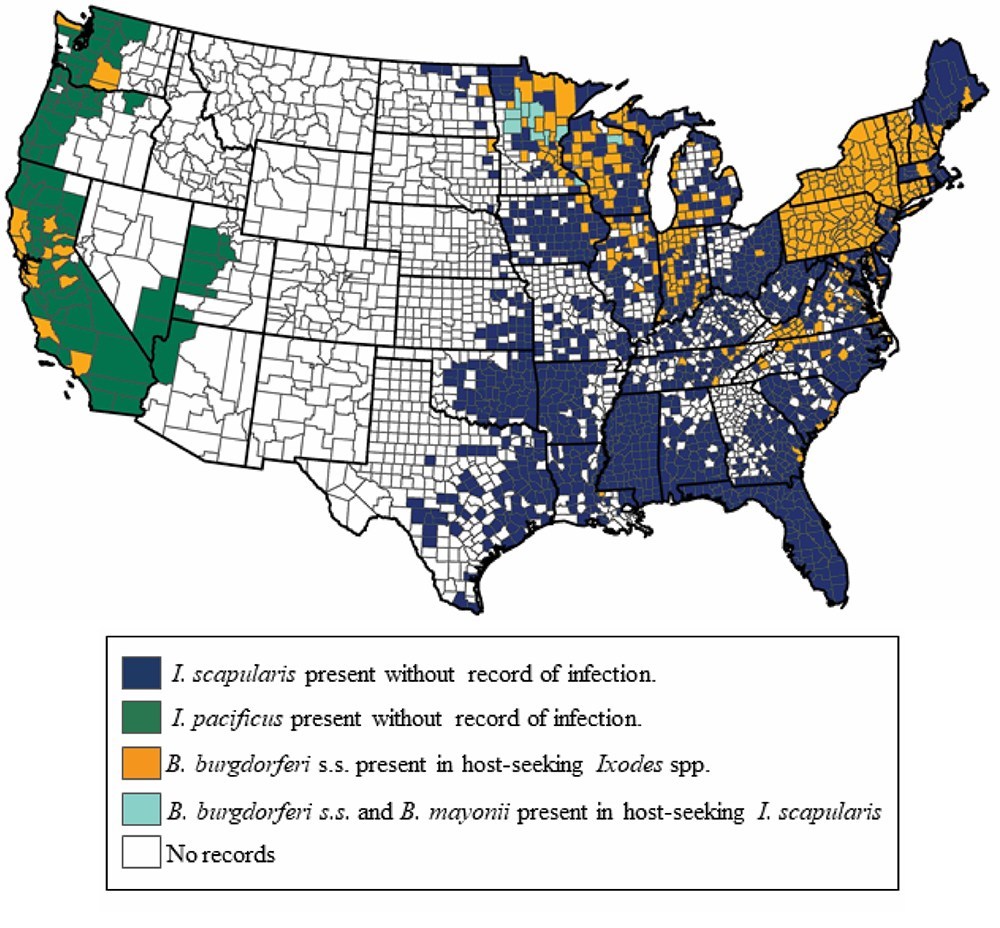
1. Tick Distribution Maps: These maps depict the geographic range of blacklegged ticks, the primary vector for Lyme disease. They highlight areas where ticks are known to be present, providing an initial indication of potential risk.
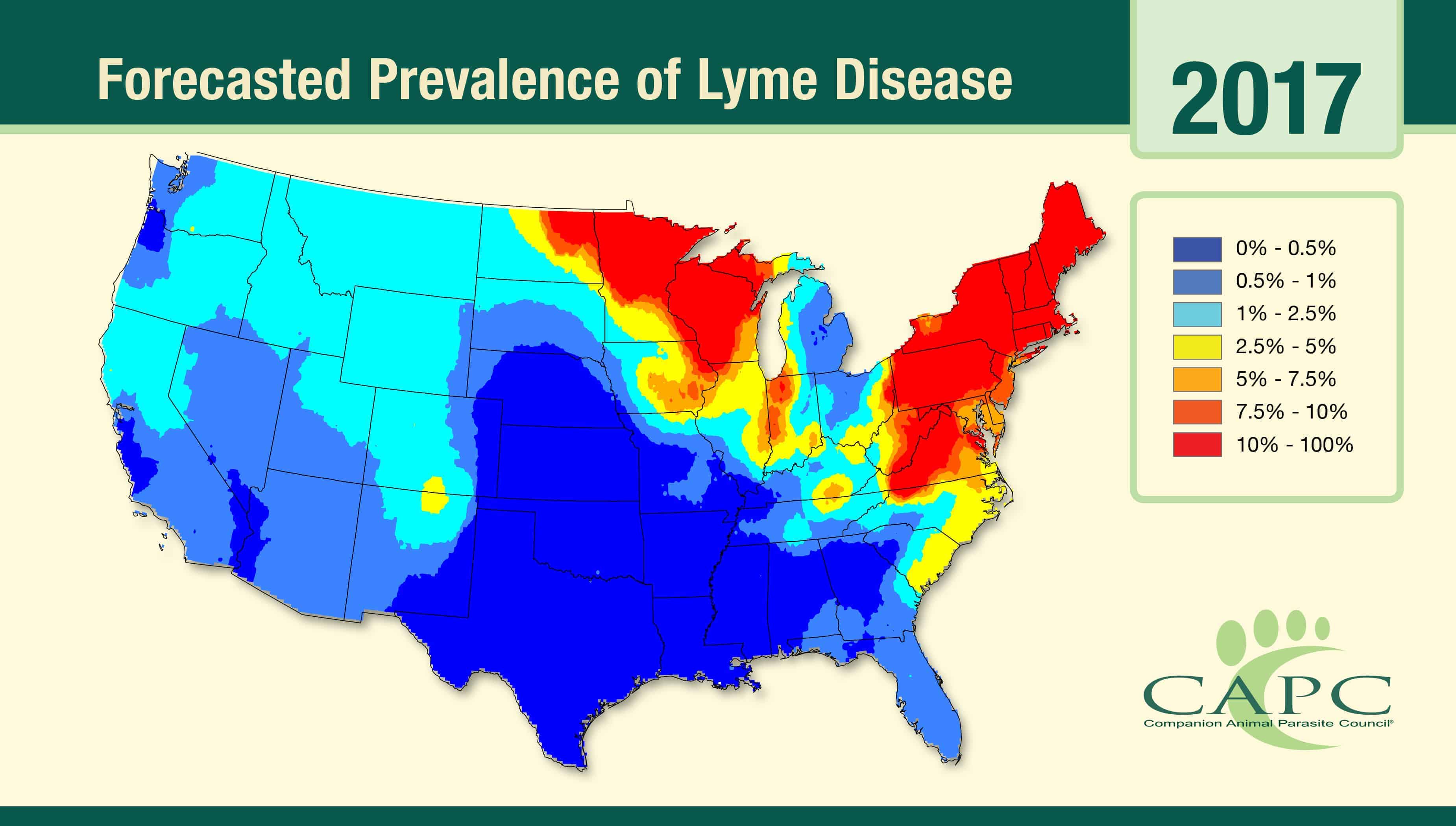
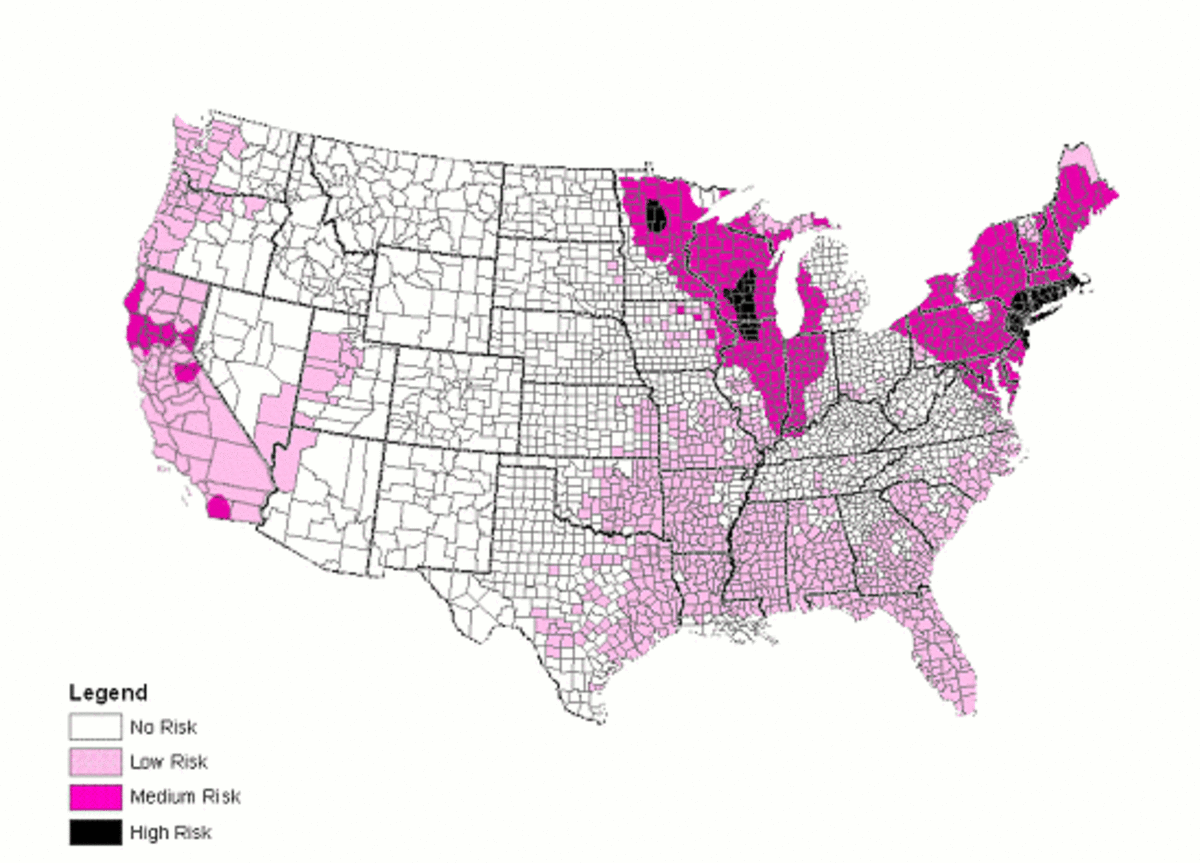
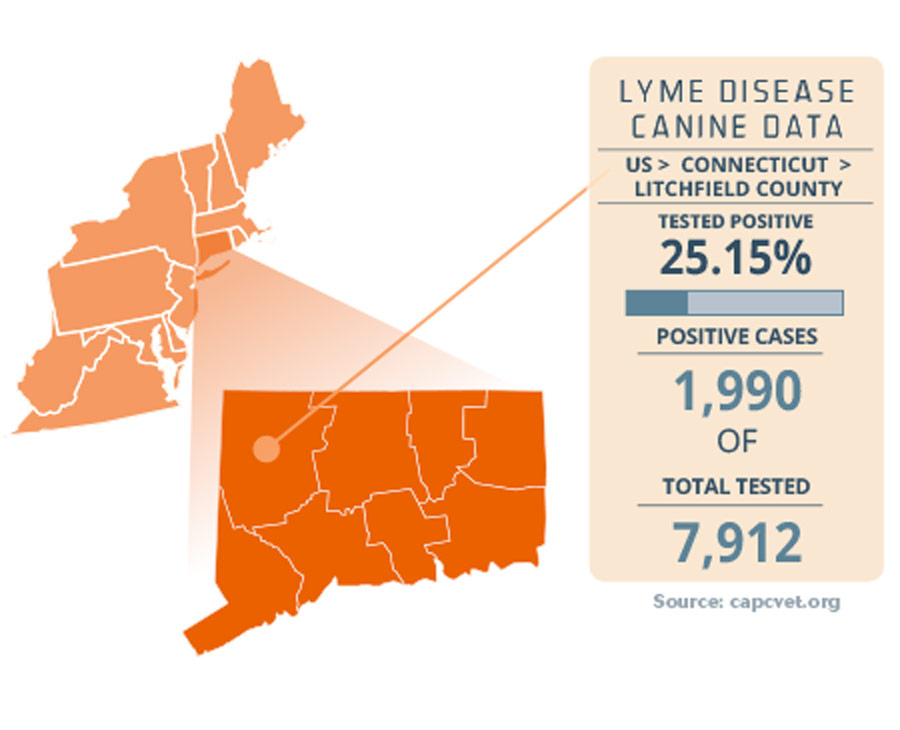
2. Lyme Disease Incidence Maps: These maps illustrate the incidence of Lyme disease in different geographic areas. They typically depict the number of reported Lyme disease cases per unit area, offering a direct visualization of disease prevalence.
Interpreting the Data: Understanding the Risk Landscape
Lyme disease maps are not simply static representations of tick populations or case numbers. They offer valuable insights into the following:
- Geographic Risk Zones: Maps clearly delineate areas with higher Lyme disease prevalence, enabling individuals to identify potential risk zones within their region.
- Seasonal Trends: Lyme disease activity often peaks during specific seasons, typically during spring and summer. Maps can incorporate this seasonal variation, providing a more dynamic understanding of risk throughout the year.
- Environmental Factors: Lyme disease prevalence is influenced by various environmental factors, including forest cover, humidity, and the presence of tick hosts like deer. Maps can incorporate these factors, offering a more comprehensive view of risk.
- Public Health Response: Lyme disease maps are crucial for public health officials in guiding prevention strategies, allocating resources, and monitoring disease trends.
Beyond the Map: A Multifaceted Approach to Lyme Disease Management
While Lyme disease maps are essential tools for understanding the geographic distribution of the disease, they are not the sole solution for prevention and management. A multifaceted approach is required, encompassing:
- Tick Awareness and Prevention: Educating the public about tick behavior, prevention measures, and early detection is crucial. This includes wearing protective clothing, using insect repellent, and conducting tick checks after outdoor activities.
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment: Prompt diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics are essential for successful Lyme disease management. Early intervention minimizes the risk of long-term complications.
- Tick Control Measures: Public health officials implement measures to reduce tick populations, such as habitat modification, tick-resistant landscaping, and targeted pesticide applications.
- Research and Development: Ongoing research is crucial to develop new diagnostic tools, treatment options, and preventative measures to combat Lyme disease effectively.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Lyme Disease Maps
1. How accurate are Lyme disease maps?
The accuracy of Lyme disease maps depends on the data used and the methodology employed. Maps based on reported cases can be influenced by factors like reporting bias and underreporting. However, maps incorporating ecological data and tick surveillance efforts provide a more robust representation of risk.
2. Can Lyme disease maps predict individual risk?
While Lyme disease maps provide valuable information about regional risk, they cannot predict individual risk. Factors like personal exposure to ticks, tick bite frequency, and individual immune response influence individual susceptibility to Lyme disease.
3. Are Lyme disease maps available for all regions?
Lyme disease maps are available for various regions, including the United States, Europe, and Canada. The availability and accuracy of maps can vary depending on the region and the data available.
4. How often are Lyme disease maps updated?
Lyme disease maps are updated periodically based on new data and research findings. The frequency of updates varies depending on the mapping organization and the specific map.
5. What are the limitations of Lyme disease maps?
Lyme disease maps are valuable tools but have limitations. They may not capture all risk factors, and their accuracy depends on data quality and reporting completeness. Moreover, maps are static representations of a dynamic system, and risk can change over time.
Tips for Using Lyme Disease Maps Effectively:
- Consult multiple sources: Compare maps from different organizations to gain a more comprehensive understanding of risk.
- Consider local factors: Factor in local environmental conditions, tick activity patterns, and personal risk factors when interpreting maps.
- Stay informed: Regularly check for updates and changes to Lyme disease maps and public health guidelines.
- Take preventative measures: Regardless of your location, prioritize tick prevention measures to minimize your risk of Lyme disease.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for Public Health and Individual Awareness
Lyme disease maps offer a valuable tool for understanding the geographic distribution and risk of Lyme disease. They empower both public health officials and individuals to make informed decisions about prevention, early detection, and management. By utilizing these maps in conjunction with other public health strategies, we can work towards mitigating the impact of Lyme disease and protecting communities from its debilitating effects.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Threat: Understanding the Lyme Disease Landscape. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!