Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape
Related Articles: Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape
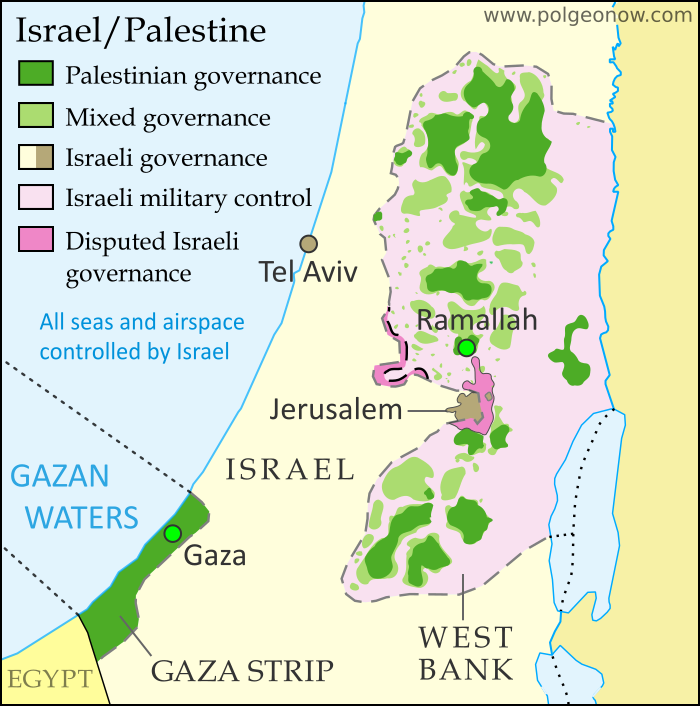
The Palestinian territories encompass a geographically diverse and politically charged region in the Middle East. Understanding the complexities of this area requires a nuanced approach that considers both historical context and contemporary realities. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Palestinian territories, highlighting their historical significance, current political landscape, and the ongoing struggle for self-determination.
Historical Context:
The Palestinian territories, encompassing the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and East Jerusalem, hold immense historical significance, deeply intertwined with the narratives of both Palestinians and Israelis. The region has been a crossroads of civilizations for millennia, witnessing the rise and fall of empires, from the ancient Canaanites to the Ottoman Empire.
The West Bank:
The West Bank, situated between Israel and Jordan, holds a significant place in Palestinian history and identity. It is home to ancient cities like Jericho, Nablus, and Hebron, each bearing witness to the rich tapestry of Palestinian culture and heritage. Following the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the West Bank was occupied by Jordan, while Israel gained control of East Jerusalem. In 1967, during the Six-Day War, Israel captured the entire West Bank, including East Jerusalem.
The Gaza Strip:
The Gaza Strip, a narrow coastal region bordering Egypt and Israel, holds a unique historical narrative. Following the 1948 war, it became a refuge for Palestinian refugees expelled from their homes in what is now Israel. The Gaza Strip has been under Israeli control since 1967 and has experienced multiple periods of armed conflict, leading to significant humanitarian challenges and political instability.
East Jerusalem:
East Jerusalem, a historically significant area encompassing the Old City and its surrounding neighborhoods, holds a central place in both Palestinian and Israeli narratives. It is home to sacred sites revered by Jews, Christians, and Muslims, making it a focal point of religious and political tension.
The Palestinian Authority:
In 1993, the Oslo Accords established the Palestinian Authority (PA), a self-governing body responsible for managing Palestinian affairs in the West Bank and Gaza Strip. The PA has limited autonomy, however, with Israel retaining significant control over security, borders, and access to resources.
The Ongoing Struggle for Self-Determination:
The Palestinian territories are a focal point of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, a decades-long struggle for self-determination and land rights. Palestinians seek the establishment of an independent state on the territories occupied by Israel since 1967, including East Jerusalem. However, the path to peace remains fraught with challenges, including the ongoing settlements in the West Bank, the blockade of Gaza, and the complex political landscape.
Understanding the Map:
The map of the Palestinian territories is a crucial tool for understanding the geopolitical complexities of the region. It showcases the physical boundaries between Israel, the West Bank, and Gaza, as well as the intricate network of settlements and checkpoints that impact daily life for Palestinians. The map also highlights the significance of East Jerusalem, a contested city with deep historical and religious significance for both Palestinians and Israelis.
Benefits of Mapping the Palestinian Territories:
Mapping the Palestinian territories serves several vital purposes:
- Visualizing the Conflict: Maps provide a visual representation of the contested land, helping to understand the complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the challenges faced by both sides.
- Understanding Palestinian Life: Maps showcase the daily realities of Palestinian life, including the impact of checkpoints, settlements, and limited access to resources.
- Promoting Dialogue and Understanding: Maps can facilitate dialogue and understanding by providing a shared visual framework for discussing the complexities of the region.
- Supporting Peacebuilding Efforts: Maps can be used to develop strategies for peacebuilding, including identifying areas of potential conflict and promoting equitable solutions.
FAQs about the Palestinian Territories:
1. What is the current status of the Palestinian territories?
The Palestinian territories remain under Israeli occupation, with the West Bank divided into Area A, Area B, and Area C. Area A is under Palestinian civil and security control, Area B is under joint Israeli-Palestinian control, and Area C is under full Israeli control. The Gaza Strip is under a blockade imposed by Israel, with Hamas controlling the territory.
2. What are the main challenges facing Palestinians in the territories?
Palestinians face numerous challenges, including:
- Limited self-governance: The PA has limited autonomy, with Israel retaining significant control over security, borders, and access to resources.
- Israeli settlements: The expansion of Israeli settlements in the West Bank continues to be a major source of tension and conflict.
- Blockade of Gaza: The ongoing blockade of Gaza has created a humanitarian crisis, with severe limitations on access to food, water, and medical care.
- Lack of economic opportunities: Palestinians face significant economic challenges, with limited access to employment opportunities and high levels of poverty.
3. What is the international community’s role in the Palestinian territories?
The international community plays a crucial role in the Palestinian territories, through:
- Providing humanitarian assistance: International organizations and governments provide financial and logistical support to Palestinians in need.
- Advocating for a two-state solution: The international community has consistently advocated for a two-state solution, with an independent Palestinian state alongside Israel.
- Monitoring human rights: International organizations monitor human rights violations in the territories and advocate for accountability.
Tips for Engaging with Maps of the Palestinian Territories:
- Consider the source: Maps can be biased, so it is essential to consider the source and the potential biases they may hold.
- Look for multiple perspectives: Engage with maps from different sources to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the region.
- Focus on the human impact: Maps can be used to understand the daily realities of Palestinians living under occupation.
- Use maps to promote dialogue: Maps can be a starting point for conversations about the conflict and potential solutions.
Conclusion:
The Palestinian territories are a complex and contested landscape with a rich history and a challenging present. Understanding the map of this region is crucial for comprehending the ongoing struggle for self-determination, the impact of occupation, and the challenges facing Palestinians. By engaging with maps in a thoughtful and critical manner, we can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of the region and contribute to efforts towards a peaceful and just resolution.
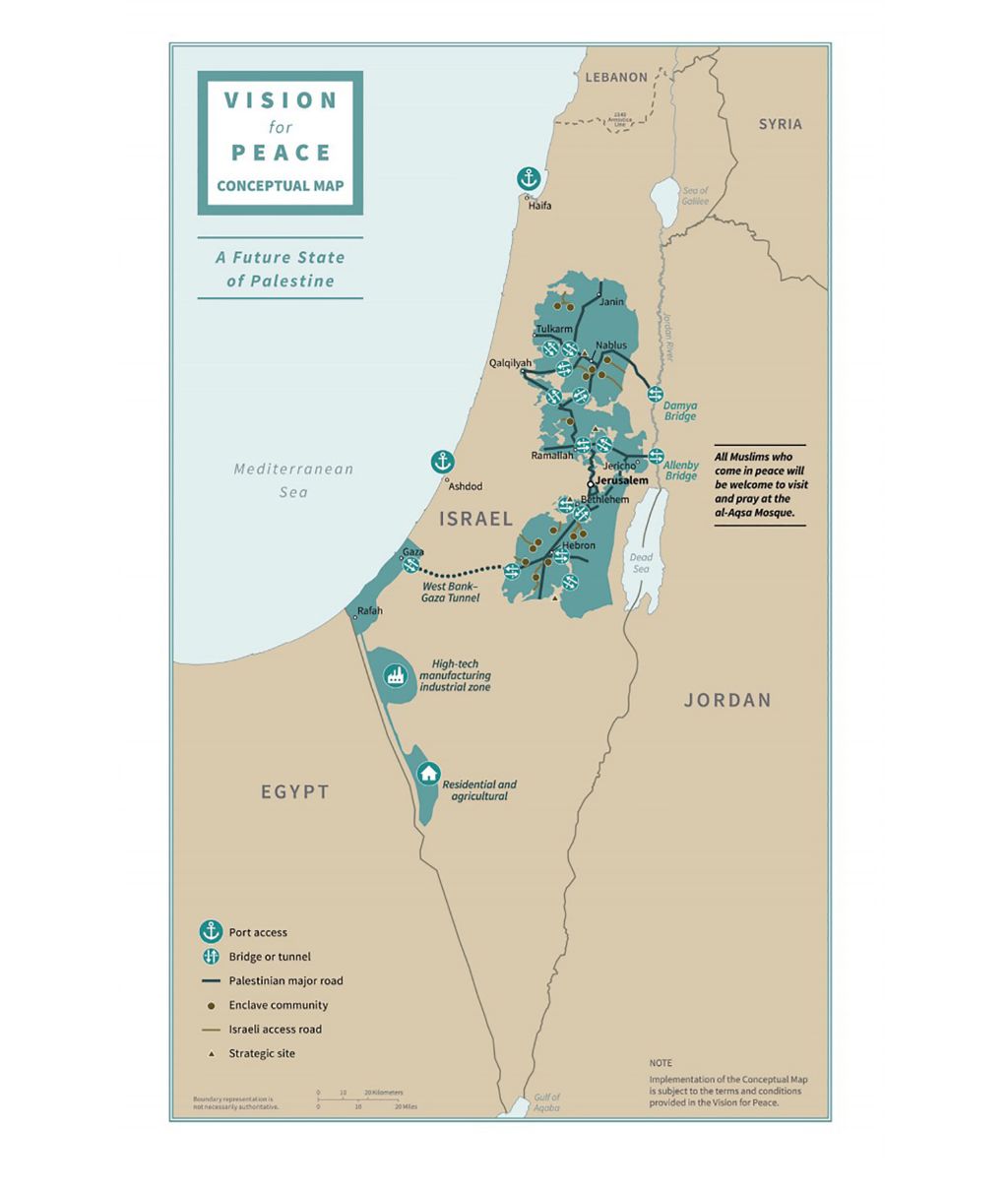





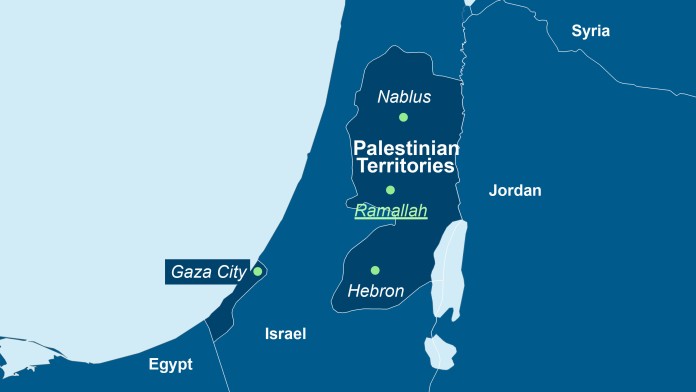
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!