Illuminating the Landscape: Understanding Light Maps of the United States
Related Articles: Illuminating the Landscape: Understanding Light Maps of the United States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Illuminating the Landscape: Understanding Light Maps of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Illuminating the Landscape: Understanding Light Maps of the United States
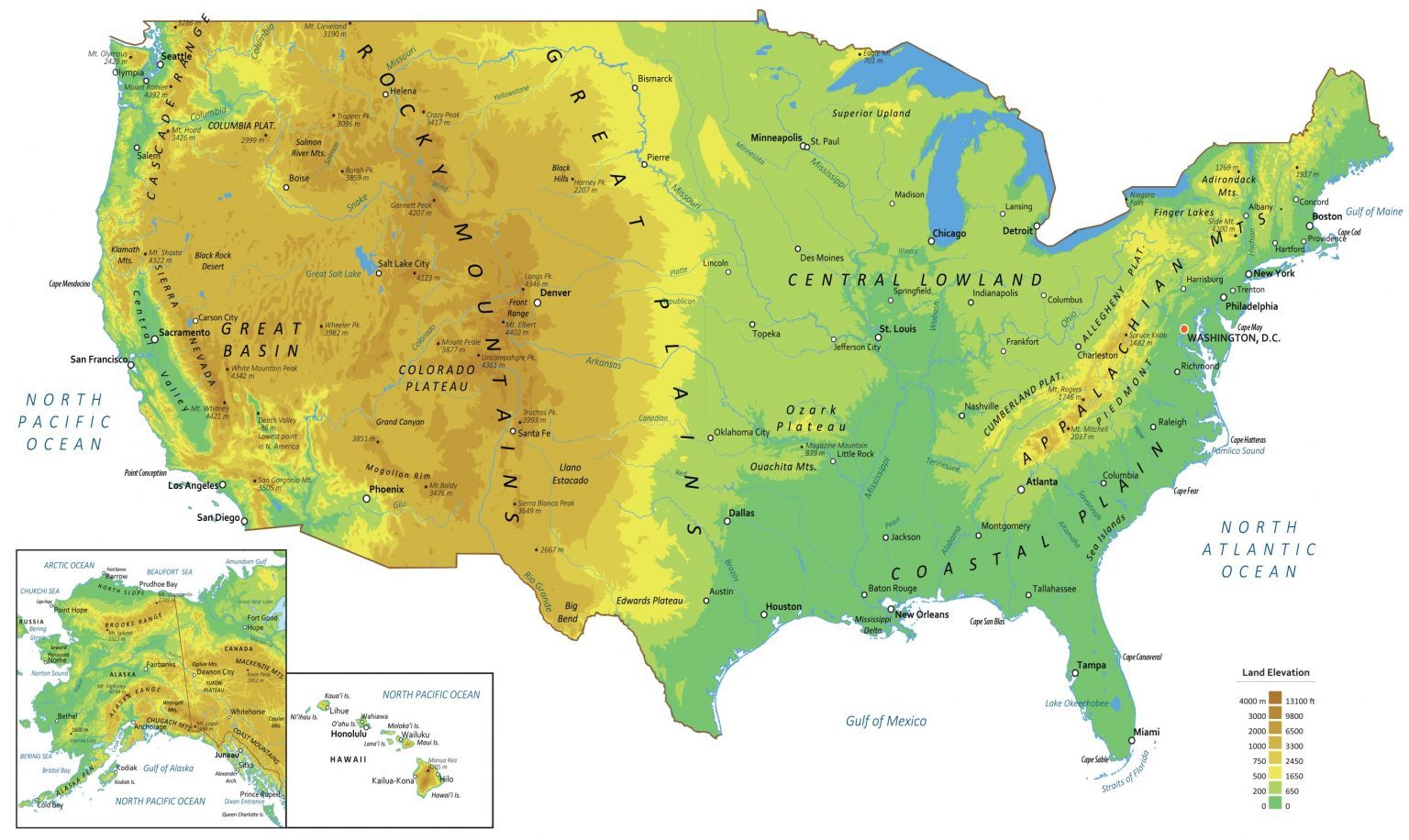
The United States, a vast and diverse nation, presents a complex tapestry of human activity, infrastructure, and natural landscapes. Visualizing this complexity can be challenging, but a powerful tool exists: the light map. Light maps, also known as nighttime light maps, offer a unique perspective on human settlement patterns, economic activity, and environmental change across the country.
Unveiling the Nighttime Glow:
Light maps are created by analyzing satellite imagery that captures the Earth’s surface at night. These images reveal the distribution of artificial light, primarily emanating from urban areas, infrastructure, and human settlements. The intensity of light serves as a proxy for population density, economic activity, and even energy consumption.
Benefits of Light Maps:
Light maps provide a wealth of information for various disciplines, including:
-
Urban Planning and Development: By identifying areas with high concentrations of light, urban planners can gain insights into population growth, infrastructure needs, and the potential for urban sprawl. Light maps can also be used to assess the effectiveness of urban renewal projects and the impact of new development on existing communities.
-
Economic Analysis: The correlation between light intensity and economic activity is well-established. Light maps can be used to track economic growth, identify areas with high economic potential, and monitor the impact of economic policies.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Light pollution is a growing concern, impacting wildlife and astronomical observation. Light maps can be used to identify areas with excessive light pollution, facilitating efforts to mitigate its impact. Furthermore, light maps can reveal changes in land use and deforestation patterns, contributing to environmental conservation efforts.
-
Disaster Response: In the wake of natural disasters, light maps can be used to assess the extent of damage, identify areas in need of immediate assistance, and guide relief efforts.
-
Security and Intelligence: Light maps have applications in national security, enabling analysts to track population movements, identify potential threats, and monitor critical infrastructure.
Applications Across Disciplines:
The versatility of light maps extends beyond traditional fields. Researchers in fields such as sociology, geography, and anthropology use light maps to study human behavior, migration patterns, and the impact of globalization on different communities.
Data Collection and Interpretation:
Light map data is collected by satellites equipped with specialized sensors that detect light emissions in various wavelengths. These data are then processed to create images that depict the spatial distribution of light. The interpretation of light maps requires careful consideration of factors such as:
- Light Source: Different types of light sources (e.g., incandescent bulbs, LED lights) emit different wavelengths and intensities, affecting the overall brightness of an area.
- Cloud Cover: Clouds can obscure light emissions, creating inaccuracies in light map data.
- Seasonal Variations: Light patterns can vary significantly across seasons due to factors like daylight hours and energy consumption.
Addressing Limitations:
While light maps provide valuable insights, it is important to acknowledge their limitations:
- Data Bias: Light maps primarily reflect artificial light sources, potentially overlooking areas with limited access to electricity or those relying on natural light.
- Privacy Concerns: Light maps can reveal sensitive information about individuals and their activities, raising concerns about privacy.
- Interpretation Challenges: Correlating light intensity with specific variables requires careful analysis and consideration of contextual factors.
FAQs Regarding Light Maps:
-
What is the resolution of light map data? The resolution of light map data varies depending on the satellite sensor used and the processing techniques applied. Higher resolution data provides more detailed information about light patterns, while lower resolution data offers a broader overview.
-
How often is light map data collected? Light map data is typically collected on a regular basis, often nightly or weekly, depending on the specific satellite mission.
-
Are light maps publicly available? Yes, many light map datasets are publicly available through organizations like NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
-
Can light maps be used to track individual movements? While light maps can reveal areas with high concentrations of light, they cannot be used to track individual movements. The resolution of most light map data is not sufficient for individual identification.
-
What are the ethical considerations associated with using light maps? As with any data source, it is crucial to use light maps responsibly and ethically, respecting privacy concerns and ensuring that the data is not used for discriminatory purposes.
Tips for Using Light Maps:
-
Consider the Data Source: Different organizations collect and process light map data using different methodologies. It is essential to understand the data source and its limitations before drawing conclusions.
-
Analyze Data in Context: Interpreting light map data requires considering contextual factors such as population density, economic activity, and local regulations.
-
Use Multiple Data Sources: Combining light map data with other sources of information, such as demographic data and socioeconomic indicators, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of a region.
-
Engage with Experts: Collaborating with experts in relevant fields, such as urban planning, environmental science, or social science, can enhance the interpretation and application of light map data.
Conclusion:
Light maps offer a powerful lens for understanding human activity, infrastructure, and environmental change across the United States. By illuminating the nighttime landscape, these maps provide insights into population dynamics, economic development, and environmental challenges. While it is essential to acknowledge their limitations and use them responsibly, light maps remain a valuable tool for researchers, policymakers, and citizens alike, contributing to a deeper understanding of the complexities of our nation.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Illuminating the Landscape: Understanding Light Maps of the United States. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
