Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression
Related Articles: Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression

The year 1939 marked a pivotal moment in European history, as Germany, under the leadership of Adolf Hitler, embarked on a path of aggressive expansionism. This period, known as the prelude to World War II, is vividly depicted on maps of the time, which reveal the extent of German territorial gains and the anxieties they generated across the continent.
Understanding the Map:
A map of Germany in 1939 presents a stark contrast to its pre-war borders. The nation, fueled by a potent mix of nationalist ideology and militaristic ambition, had aggressively annexed several territories, drastically altering the geopolitical landscape.
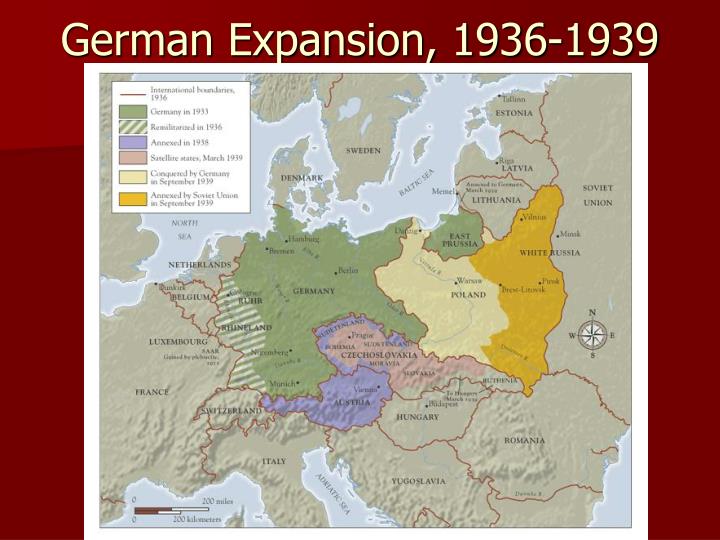
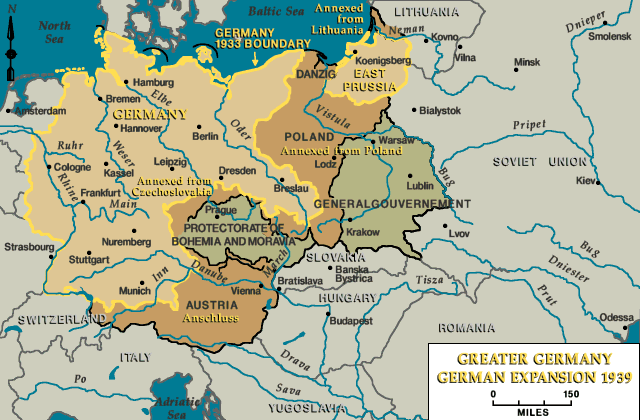
- The Sudetenland: This predominantly German-speaking region of Czechoslovakia was annexed in October 1938 following the Munich Agreement, a diplomatic agreement that appeased Nazi Germany at the expense of Czech sovereignty.
- Memel Territory: This Lithuanian region, populated by a significant German minority, was seized by Germany in March 1939, a move that further consolidated Germany’s control over the Baltic Sea.
- The Rest of Czechoslovakia: Following the Munich Agreement, Germany invaded and occupied the remaining parts of Czechoslovakia in March 1939, effectively dismantling the nation.
- The Free City of Danzig: This strategically important port city, situated on the Baltic Sea, was annexed by Germany in September 1939, sparking the outbreak of World War II.
- The Polish Corridor: This narrow strip of land, which separated East Prussia from the rest of Germany, was also annexed by Germany in September 1939, further solidifying Germany’s territorial gains.
The Significance of the Map:
The map of Germany in 1939 serves as a visual testament to the aggressive expansionism of Nazi Germany and its devastating consequences. It highlights the following crucial aspects:
- The Violation of International Law: Germany’s annexation of territories through force, particularly the invasion of Czechoslovakia and Poland, blatantly violated international law and the principles of self-determination.
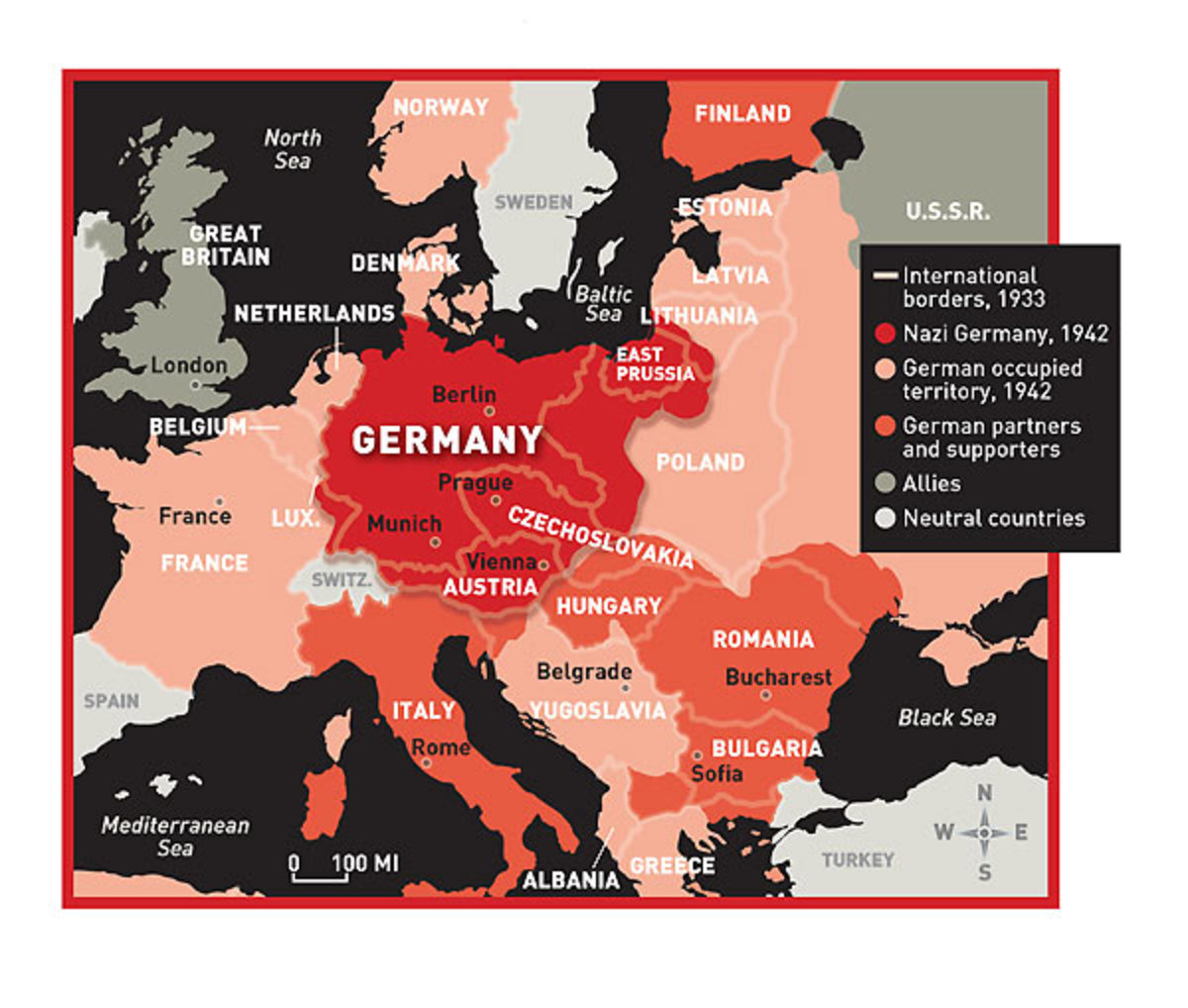
- The Expansion of Nazi Ideology: The map reflects the ambition of Nazi Germany to create a "Greater German Reich," a racially pure empire encompassing all Germanic-speaking territories.
- The Seeds of Conflict: The territorial gains of Germany in 1939 ignited widespread anxieties and fears among other European powers, ultimately leading to the outbreak of World War II.
- The Impact on European Borders: The map underscores the profound impact of German aggression on the political and geographical landscape of Europe, leading to a reshaping of borders and the displacement of millions of people.
- A Reminder of History’s Lessons: The map serves as a stark reminder of the dangers of unchecked nationalism, militarism, and the pursuit of dominance through force.
Analyzing the Map’s Impact:
The map of Germany in 1939 provides a crucial lens through which to analyze the complex geopolitical dynamics of the period. It reveals:
- The Failure of Appeasement: The map demonstrates the futility of appeasement as a strategy for preventing aggression. The Munich Agreement, which aimed to appease Hitler by conceding to his demands, ultimately emboldened him and fueled further aggression.
- The Rise of Totalitarianism: The map underscores the rise of totalitarian regimes in the 20th century, particularly Nazi Germany, and their propensity for expansionism and violence.
- The Importance of International Cooperation: The map highlights the importance of international cooperation and collective security mechanisms to prevent future conflicts.
FAQs about Germany in 1939:
1. What were the key events leading to the expansion of Germany in 1939?
The annexation of the Sudetenland, the seizure of Memel Territory, and the invasion of Czechoslovakia all served as stepping stones towards Germany’s larger ambitions. The Munich Agreement, which appeased Nazi Germany, emboldened Hitler and ultimately led to the invasion of Poland, triggering the outbreak of World War II.
2. What was the impact of German expansion on the people living in the annexed territories?
The annexation of territories by Germany brought with it significant hardship and suffering for the local populations. Many were subjected to persecution, displacement, and the suppression of their cultural identities. The Nazi regime implemented discriminatory policies aimed at eliminating any opposition and consolidating its control.
3. What were the international reactions to Germany’s expansion in 1939?
The international community responded to Germany’s aggression with a mix of condemnation and appeasement. While many nations condemned Germany’s actions, some, like Britain and France, initially pursued a policy of appeasement, hoping to avoid war. However, Germany’s continued expansion ultimately led to the declaration of war by Britain and France, marking the beginning of World War II.
4. How did the map of Germany in 1939 influence the course of World War II?
The map of Germany in 1939 played a crucial role in shaping the course of World War II. The annexation of territories, particularly Poland, provided Germany with valuable resources and strategic advantages. The expansion also fueled the anxieties and fears of other European powers, contributing to the formation of alliances and the outbreak of war.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Germany in 1939:
- Focus on the key territories: Pay close attention to the annexed territories, such as the Sudetenland, Memel Territory, Czechoslovakia, and Poland. These areas represent the extent of Germany’s territorial gains and the scale of its ambition.
- Consider the political context: The map should be understood within the broader political context of the time, including the rise of Nazi Germany, the ideology of National Socialism, and the failure of appeasement.
- Analyze the impact on different groups: Examine the map’s impact on different groups, including Germans, Czechs, Poles, and other nationalities. Consider the different perspectives and experiences of these groups during this turbulent period.
- Connect the map to historical events: Use the map as a tool to understand the key events leading up to World War II, such as the Munich Agreement, the invasion of Poland, and the outbreak of war.
- Reflect on the lessons of history: The map serves as a reminder of the dangers of unchecked nationalism, militarism, and the pursuit of dominance through force. It highlights the importance of international cooperation and collective security mechanisms to prevent future conflicts.
Conclusion:
The map of Germany in 1939 serves as a powerful reminder of the devastating consequences of unchecked aggression and the importance of upholding international law and human rights. It highlights the dangers of nationalist ideologies, the fragility of peace, and the need for a strong international order based on cooperation and mutual respect. By studying this map and understanding its historical context, we can learn valuable lessons about the importance of diplomacy, the dangers of appeasement, and the need for a united front against aggression.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Germany in 1939: A Map of Expansion and Aggression. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!