Charting the Known World: A Look at 15th Century Maps of Europe
Related Articles: Charting the Known World: A Look at 15th Century Maps of Europe
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Known World: A Look at 15th Century Maps of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Known World: A Look at 15th Century Maps of Europe
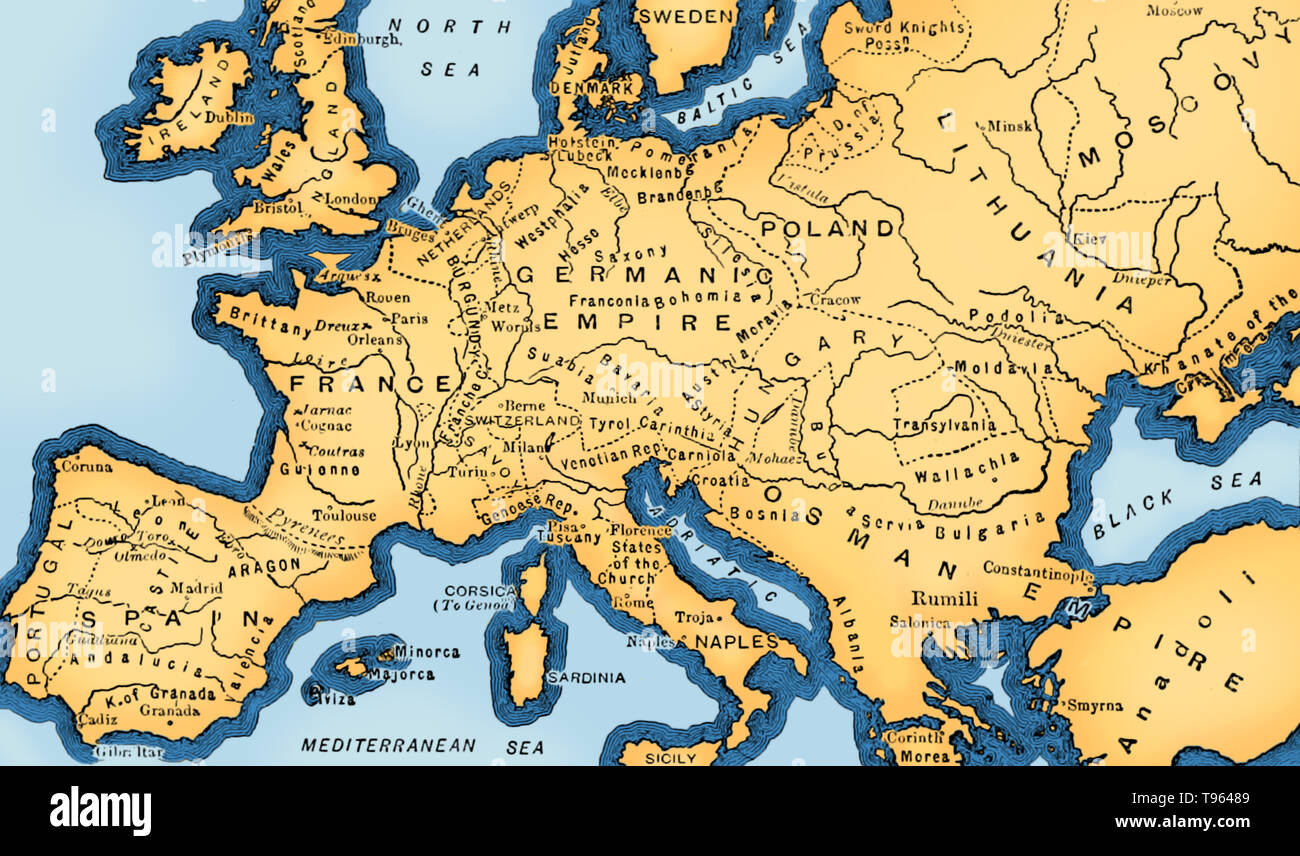
The 15th century witnessed a pivotal shift in the understanding of the world, fueled by the burgeoning Renaissance and the age of exploration. This period saw a surge in cartographic advancements, particularly in the mapping of Europe. These maps, though often imbued with inaccuracies and biases, were crucial tools for navigating the known world, fostering trade, and shaping the political and cultural landscape of Europe.
The Evolution of Cartography:
Prior to the 15th century, maps of Europe were largely based on ancient Greek and Roman sources, often incorporating mythical creatures and fantastical elements. However, the 15th century saw a move towards more accurate and detailed representations, driven by several key factors:
-
Renewed Interest in Classical Sources: The Renaissance witnessed a renewed interest in classical learning, including ancient cartographic works. Scholars like Ptolemy, whose "Geography" was rediscovered in the 15th century, provided a foundation for more accurate depictions of the world.
-
Advances in Navigation and Exploration: The development of new navigational instruments like the compass and astrolabe, coupled with the increasing voyages of exploration, provided cartographers with more precise data about distances, coastlines, and geographic features.
-
The Rise of Printing: The invention of the printing press in the mid-15th century facilitated the mass production and dissemination of maps, making them accessible to a wider audience. This contributed to the standardization of cartographic techniques and the spread of knowledge about the world.
Key Characteristics of 15th Century European Maps:
-
Emphasis on Accuracy: While still imperfect, 15th century maps exhibited a notable shift towards greater accuracy compared to their predecessors. They incorporated more detailed coastlines, rivers, and mountains, reflecting the increasing reliance on empirical observation and navigational data.
-
Use of Projections: The 15th century saw the introduction of new map projections, such as the Mercator projection, which enabled cartographers to represent the curved surface of the earth on a flat plane with greater accuracy.
-
Emphasis on Cities and Towns: 15th century maps often focused on urban centers, highlighting their importance in trade and political power. They frequently featured city plans and depicted important buildings and landmarks.
-
Inclusion of Symbolic Elements: While striving for accuracy, maps of this period often incorporated symbolic elements, such as heraldic emblems, religious icons, and mythological creatures. These elements reflected the prevailing cultural and religious beliefs of the time.
The Importance of 15th Century European Maps:
-
Navigation and Exploration: Maps served as essential tools for navigating the seas and exploring new lands. They provided sailors with information about coastlines, currents, and potential dangers, enabling safer and more efficient journeys.
-
Trade and Commerce: Maps facilitated trade by providing merchants with information about routes, ports, and markets. They helped establish trade networks and facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas across Europe.
-
Political and Military Strategy: Maps played a crucial role in military planning and strategy. They provided information about terrain, fortifications, and enemy movements, enabling commanders to make informed decisions.
-
Cultural and Intellectual Exchange: The dissemination of maps contributed to the exchange of knowledge and ideas across Europe. They helped people visualize the world and understand their place within it.
FAQs about 15th Century Maps of Europe:
Q: What were the most common types of maps in the 15th century?
A: The most common types of maps in the 15th century were portolan charts, which were detailed navigational maps focusing on coastlines and ports, and world maps, which depicted the known world based on the latest geographical knowledge.
Q: Who were some of the most prominent cartographers of the 15th century?
A: Prominent cartographers of the 15th century included Fra Mauro, who created a large-scale world map in 1459, and Johannes Schöner, known for his celestial globes and maps of the Americas.
Q: How accurate were 15th century maps?
A: While more accurate than earlier maps, 15th century maps still contained inaccuracies, particularly regarding the size and shape of continents and oceans. These inaccuracies were due to limitations in surveying techniques and the lack of complete geographical knowledge.
Q: What impact did the printing press have on the development of maps?
A: The printing press revolutionized the production and dissemination of maps. It allowed for the mass production of maps, making them more accessible to a wider audience and contributing to the standardization of cartographic techniques.
Tips for Studying 15th Century Maps of Europe:
-
Pay attention to the scale and projection: Understanding the scale and projection of a map is essential for interpreting its information accurately.
-
Look for symbols and legends: Maps often use symbols and legends to represent different features, such as cities, rivers, and mountains.
-
Consider the context: Maps are products of their time and reflect the cultural, political, and religious beliefs of the period.
-
Compare and contrast different maps: Comparing and contrasting different maps from the same period can provide insights into the evolution of cartographic knowledge and techniques.
Conclusion:
The 15th century witnessed a significant transformation in the understanding and representation of Europe. Maps of this period, while not perfect, played a crucial role in shaping the political, economic, and cultural landscape of the continent. They facilitated exploration, trade, and communication, and provided a framework for understanding the world. The legacy of 15th century maps continues to resonate today, reminding us of the enduring power of cartography in shaping our perception of the world.
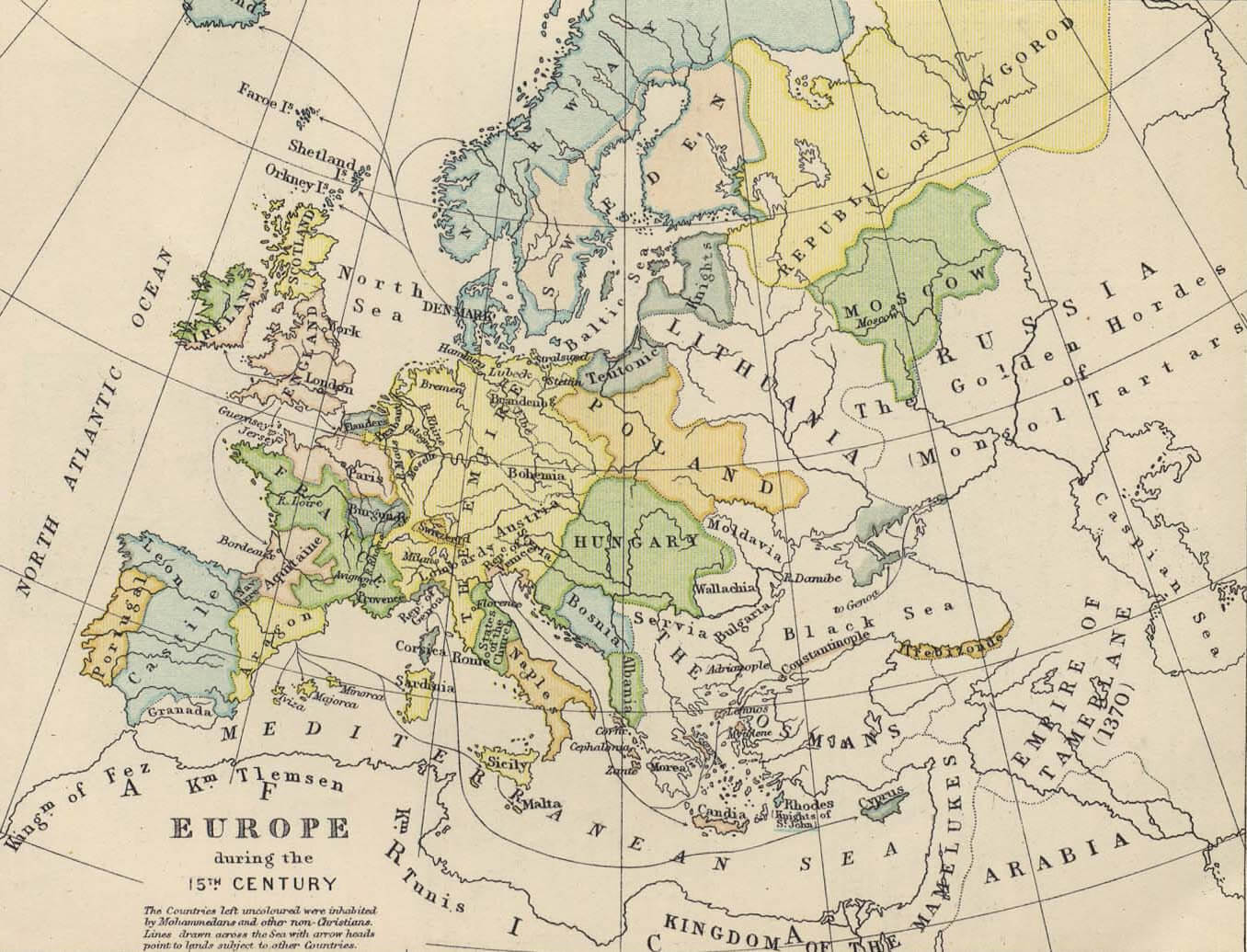


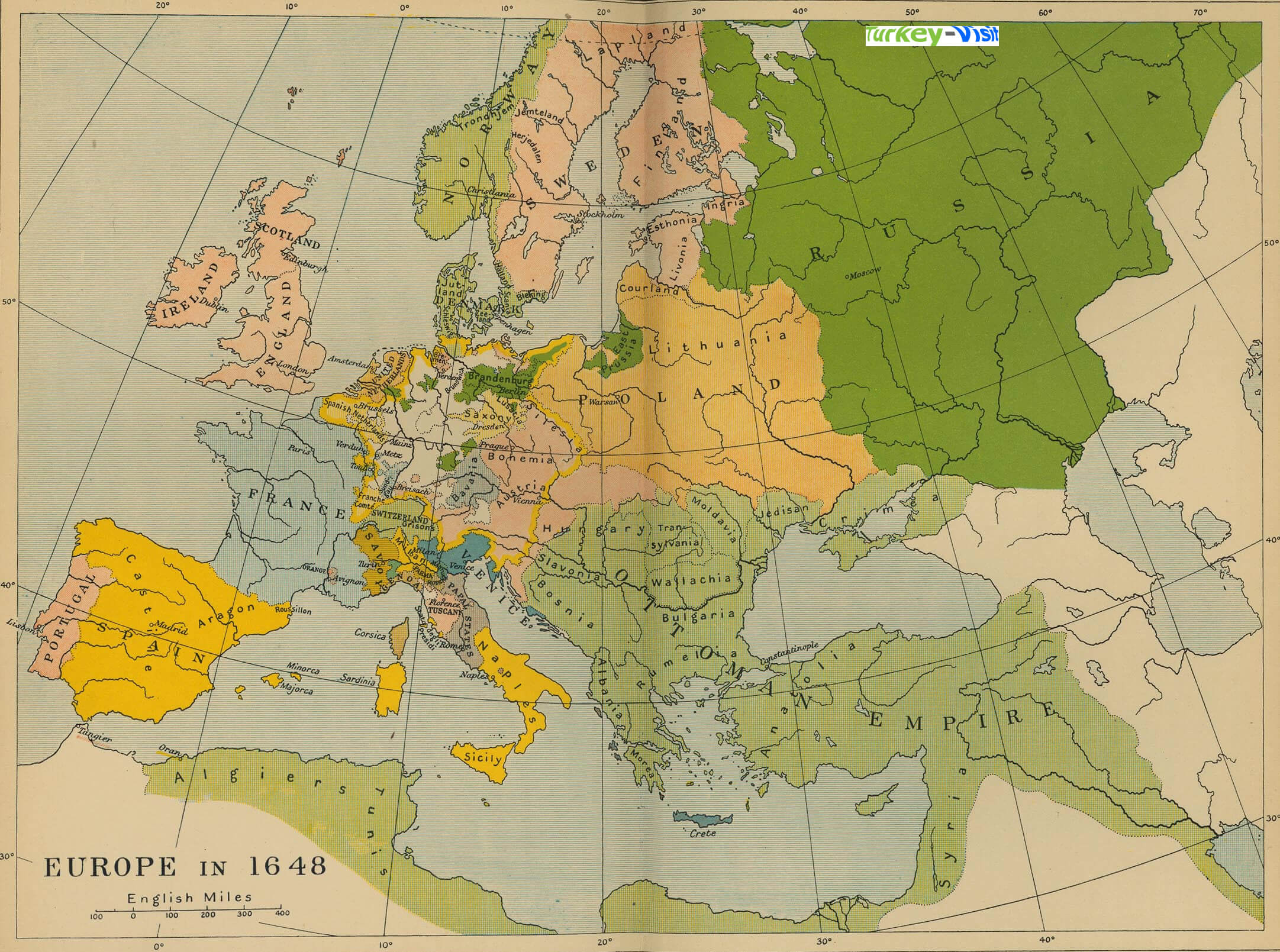
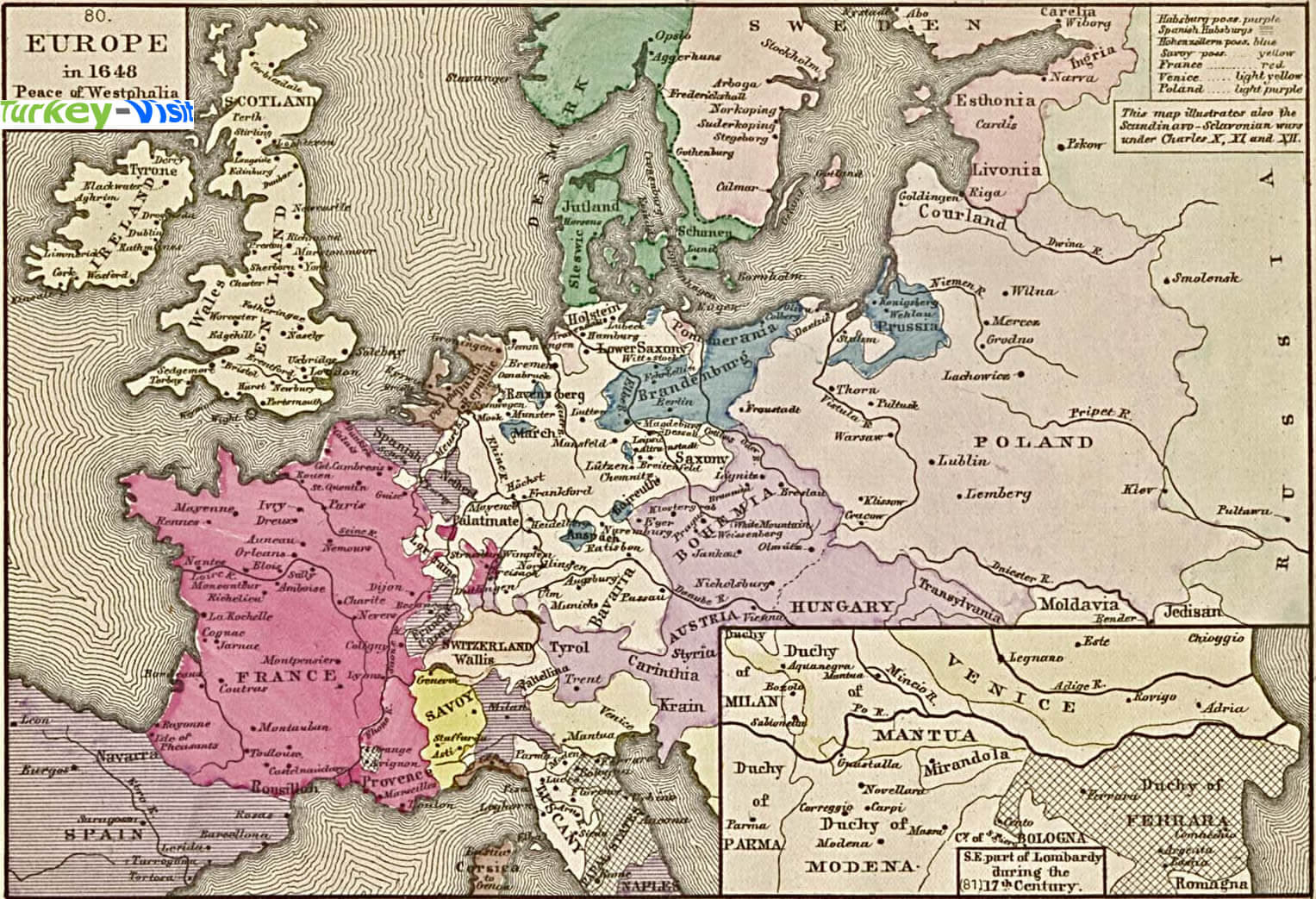
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Known World: A Look at 15th Century Maps of Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!