Burma (Myanmar) on the World Map: A Land of Ancient Heritage and Modern Challenges
Related Articles: Burma (Myanmar) on the World Map: A Land of Ancient Heritage and Modern Challenges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Burma (Myanmar) on the World Map: A Land of Ancient Heritage and Modern Challenges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Burma (Myanmar) on the World Map: A Land of Ancient Heritage and Modern Challenges

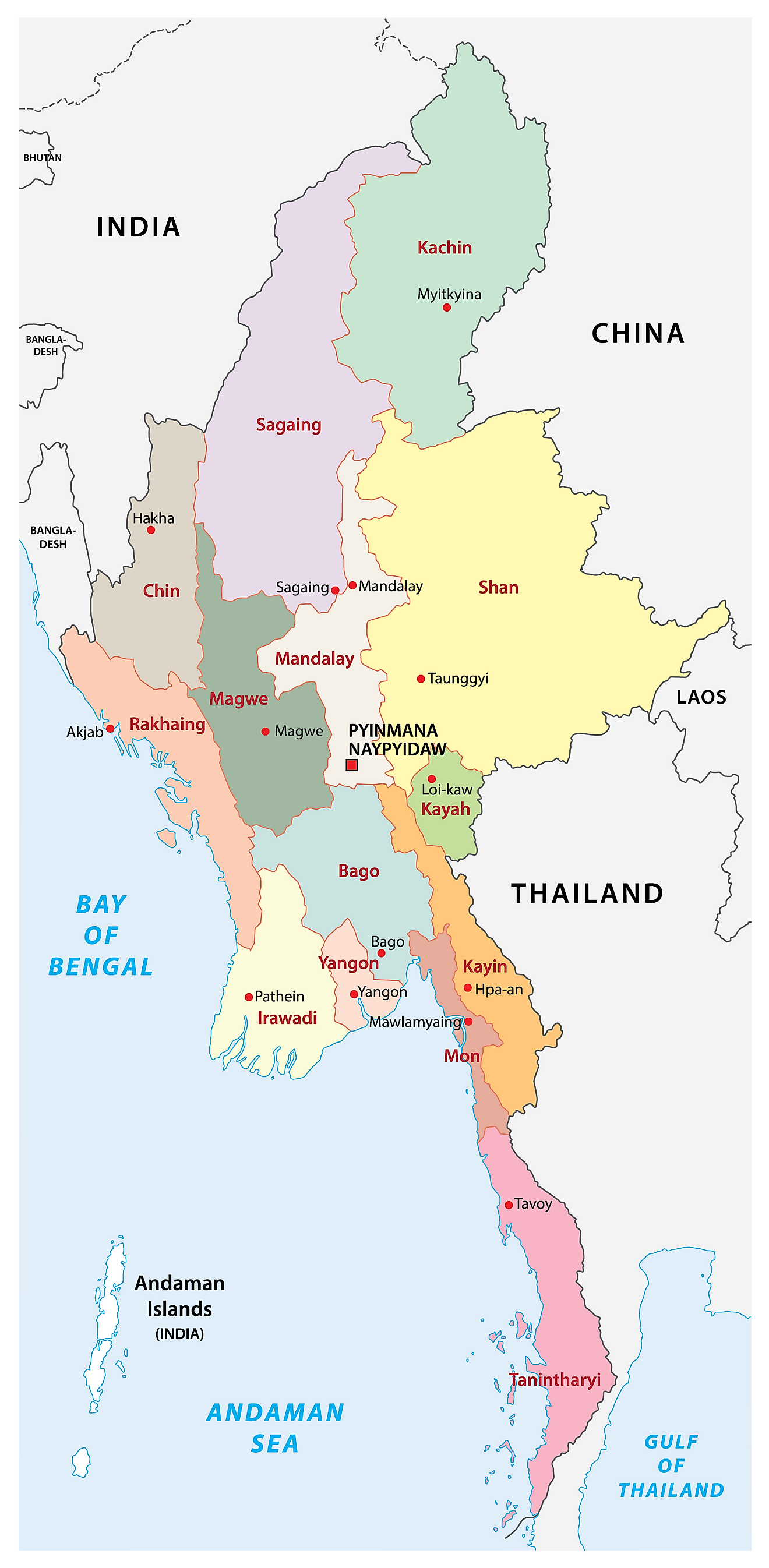
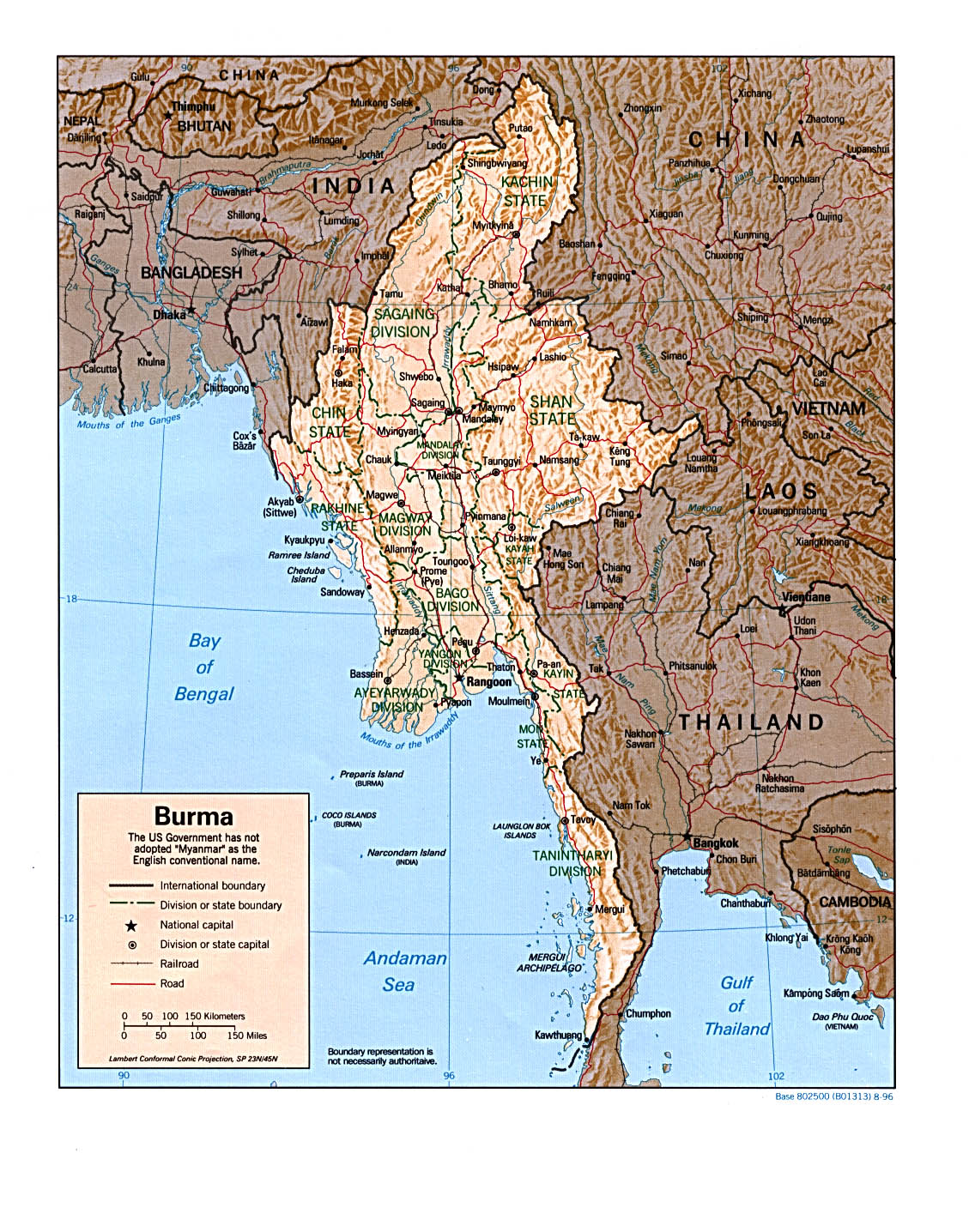
Burma, officially known as the Republic of the Union of Myanmar, occupies a strategically important position in Southeast Asia. Situated on the western edge of the Indochinese peninsula, it shares borders with India, Bangladesh, China, Laos, and Thailand. This geographically diverse nation encompasses a complex tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and histories, making it a captivating destination for travelers and scholars alike.
Geographic Significance:
Burma’s geographical location has historically influenced its political, economic, and cultural development. The country’s diverse terrain, ranging from the towering Himalayan foothills to the fertile Irrawaddy delta, has supported a variety of livelihoods, from agriculture to mining. The Irrawaddy River, flowing through the heart of Burma, has been a vital artery for trade and transportation since ancient times.
The nation’s proximity to major Asian powers has also played a significant role in its history. Burma’s strategic location has made it a target for both trade and conquest, with empires from India, China, and the West vying for influence over the region. This historical legacy continues to shape Burma’s present-day political landscape.
Cultural Tapestry:
Burma is home to a rich tapestry of ethnicities and cultures. The majority of the population is comprised of the Bamar people, who have a long and vibrant cultural tradition. However, over 135 distinct ethnic groups also inhabit the country, each with its own unique language, customs, and beliefs. This cultural diversity is reflected in the country’s vibrant arts, music, and literature.
Burma’s cultural heritage is deeply intertwined with its Buddhist faith. Buddhism arrived in the country over two thousand years ago and has profoundly shaped Burmese society. The country is home to numerous ancient temples and monasteries, which serve as important centers of religious life and cultural expression.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Burma has faced numerous challenges in recent decades. The country’s political history has been marked by periods of instability and conflict, culminating in the military junta’s rule from 1962 to 2011. This period saw widespread human rights abuses and economic stagnation.
In 2011, the military junta transitioned to a nominally civilian government, ushering in a period of political and economic reforms. However, the transition has been uneven, with ongoing challenges related to human rights, ethnic conflict, and economic development.
Despite these challenges, Burma possesses significant potential for growth and development. The country is rich in natural resources, including timber, gemstones, and natural gas. It also has a young and growing population, which presents a potential workforce for the future.
Burma on the World Stage:
Burma’s strategic location and growing economy have placed it increasingly on the world stage. The country has been actively seeking to reintegrate into the international community and has engaged in diplomatic efforts to address the challenges it faces.
Burma’s relationship with its neighbors is of paramount importance. The country is actively seeking to strengthen economic and political ties with China, India, and other regional powers. It is also participating in regional organizations such as ASEAN, seeking to promote cooperation and stability in the region.
FAQs:
-
Q: What is the official language of Burma?
- A: The official language of Burma is Burmese, a member of the Tibeto-Burman language family.
-
Q: What is the currency of Burma?
- A: The currency of Burma is the Burmese kyat (MMK).
-
Q: What is the capital of Burma?
- A: The capital of Burma is Naypyidaw, a planned city located in the country’s interior.
-
Q: What are some of the major tourist attractions in Burma?
- A: Burma offers a wide range of tourist attractions, including the ancient temples of Bagan, the Shwedagon Pagoda in Yangon, and the Inle Lake with its unique stilt villages.
-
Q: What are the major industries in Burma?
- A: Burma’s major industries include agriculture, mining, forestry, and tourism.
Tips for Visiting Burma:
- Respect local customs and traditions.
- Obtain a visa before traveling to Burma.
- Learn a few basic Burmese phrases.
- Be aware of the potential for political instability and conflict.
- Pack light and be prepared for hot and humid weather.
Conclusion:
Burma is a country of contrasts, a land of ancient heritage and modern challenges. Its strategic location, diverse cultures, and rich history make it a fascinating subject of study and a captivating destination for travelers. As Burma continues to navigate its path towards political and economic reform, it remains a nation with a bright future, poised to play an increasingly important role on the world stage.
-with-relief-roads-railroads-and-major-cities-1991.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Burma (Myanmar) on the World Map: A Land of Ancient Heritage and Modern Challenges. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!