Area Map Measurement: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Space
Related Articles: Area Map Measurement: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Space
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Area Map Measurement: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Space. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Area Map Measurement: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Space

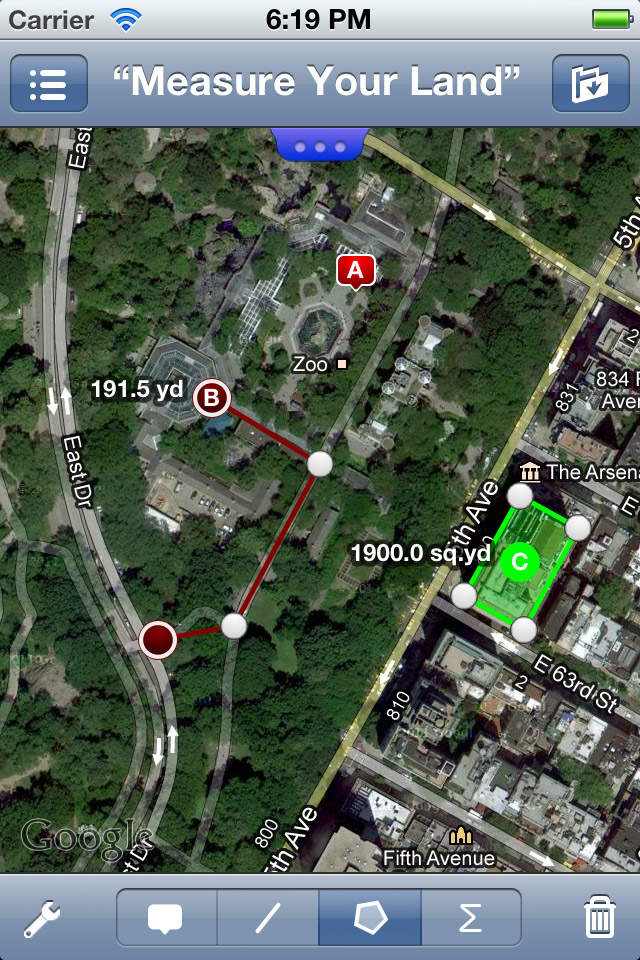
Area measurement, often referred to as area map measurement, plays a pivotal role in various fields, from urban planning and environmental management to real estate and construction. It involves determining the size of a defined space, whether it’s a room, a building, a plot of land, or a sprawling forest. This seemingly simple process holds immense value, providing crucial insights into the spatial dimensions of our world.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Area measurement relies on the basic concept of calculating the amount of surface enclosed within a defined boundary. The standard unit for measuring area is the square unit, such as square meters (m²), square feet (ft²), or square kilometers (km²). The choice of unit depends on the scale and purpose of the measurement.
Methods of Area Measurement
Various methods are employed to determine area, each suited for specific applications:
-
Manual Measurement: This involves using measuring tools like rulers, tapes, and protractors to directly measure the dimensions of a space. It’s suitable for smaller areas with simple shapes.
-
Planimetric Measurement: This method utilizes maps or plans to calculate area. It involves dividing the area into smaller, regular shapes like squares, rectangles, or triangles, and then calculating the area of each shape individually. The sum of these areas represents the total area.
-
Digital Measurement: This utilizes specialized software and tools to measure area on digital maps or images. It offers high precision and efficiency, particularly for complex shapes and large areas.
Applications of Area Measurement
The applications of area measurement are vast and far-reaching, impacting diverse sectors:
-
Real Estate: Area measurement is fundamental in determining the size of properties, calculating property taxes, and establishing market value.
-
Construction: Accurate area measurement is crucial for planning and executing construction projects. It informs material requirements, cost estimations, and the overall project design.
-
Urban Planning: Area measurement helps in zoning and land use planning, ensuring efficient allocation of resources and promoting sustainable urban development.
-
Environmental Management: Area measurement is essential for monitoring land cover changes, assessing deforestation rates, and managing natural resources effectively.
-
Agriculture: Area measurement plays a critical role in farm management, including land allocation, crop planning, and yield estimation.
-
Cartography: Area measurement is vital for map creation and analysis, providing valuable insights into geographic features and spatial relationships.
-
Disaster Management: Accurate area measurement helps in assessing the impact of natural disasters, planning rescue operations, and allocating resources efficiently.
Benefits of Area Measurement
The benefits of area measurement are numerous and contribute to improved decision-making, efficiency, and resource management:
-
Accurate Information: Area measurement provides precise and reliable data about the size of spaces, facilitating informed planning and resource allocation.
-
Efficient Resource Management: By understanding the area of a space, resources can be allocated effectively, minimizing waste and maximizing utilization.
-
Cost Optimization: Accurate area measurement helps in estimating project costs, reducing financial risks and ensuring efficient budget management.
-
Improved Decision-Making: Area measurement provides crucial data for informed decision-making, leading to better planning, resource allocation, and project outcomes.
-
Spatial Analysis: Area measurement facilitates spatial analysis, allowing for the identification of trends, patterns, and relationships within a defined space.
Challenges and Considerations
While area measurement offers significant benefits, it also presents challenges:
-
Accuracy: Obtaining accurate measurements requires precise tools, experienced personnel, and careful consideration of terrain variations.
-
Complexity: Measuring complex shapes or areas with irregular boundaries can be challenging and require specialized techniques.
-
Data Interpretation: Interpreting area measurement data requires a thorough understanding of the context and the limitations of the chosen method.
-
Technology Dependence: Digital area measurement relies heavily on technology, requiring access to software and equipment, which can be costly and require specialized skills.
FAQs on Area Measurement
Q: What are the common units used for area measurement?
A: The most common units for area measurement include square meters (m²), square feet (ft²), square kilometers (km²), and acres. The choice of unit depends on the scale and purpose of the measurement.
Q: What is the difference between area and perimeter?
A: Area refers to the amount of surface enclosed within a boundary, while perimeter refers to the total length of the boundary itself.
Q: How can I measure the area of an irregular shape?
A: Irregular shapes can be measured using planimetric methods, dividing the shape into smaller, regular shapes and calculating the area of each individually. Digital measurement tools can also be used for greater accuracy.
Q: What are the best practices for accurate area measurement?
A: Best practices include using calibrated tools, employing experienced personnel, considering terrain variations, and verifying measurements through multiple methods.
Tips for Effective Area Measurement
- Choose the Right Tools: Select tools appropriate for the size and complexity of the area being measured.
- Calibrate Instruments: Ensure that measuring tools are properly calibrated for accuracy.
- Consider Terrain Variations: Account for uneven terrain when measuring areas outdoors.
- Employ Multiple Methods: Utilize different methods for verifying measurements and enhancing accuracy.
- Document Measurements: Record measurements systematically, including dates, methods, and any relevant details.
Conclusion
Area measurement is a fundamental and versatile tool that provides invaluable insights into the spatial dimensions of our world. Its applications extend across diverse fields, contributing to informed decision-making, efficient resource management, and improved project outcomes. By understanding the principles of area measurement, its methods, and its benefits, individuals and organizations can leverage this powerful tool to optimize their operations and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient future.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Area Map Measurement: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Managing Space. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!