A Journey Through Time: Exploring Historical Maps of Europe
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring Historical Maps of Europe
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring Historical Maps of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Time: Exploring Historical Maps of Europe
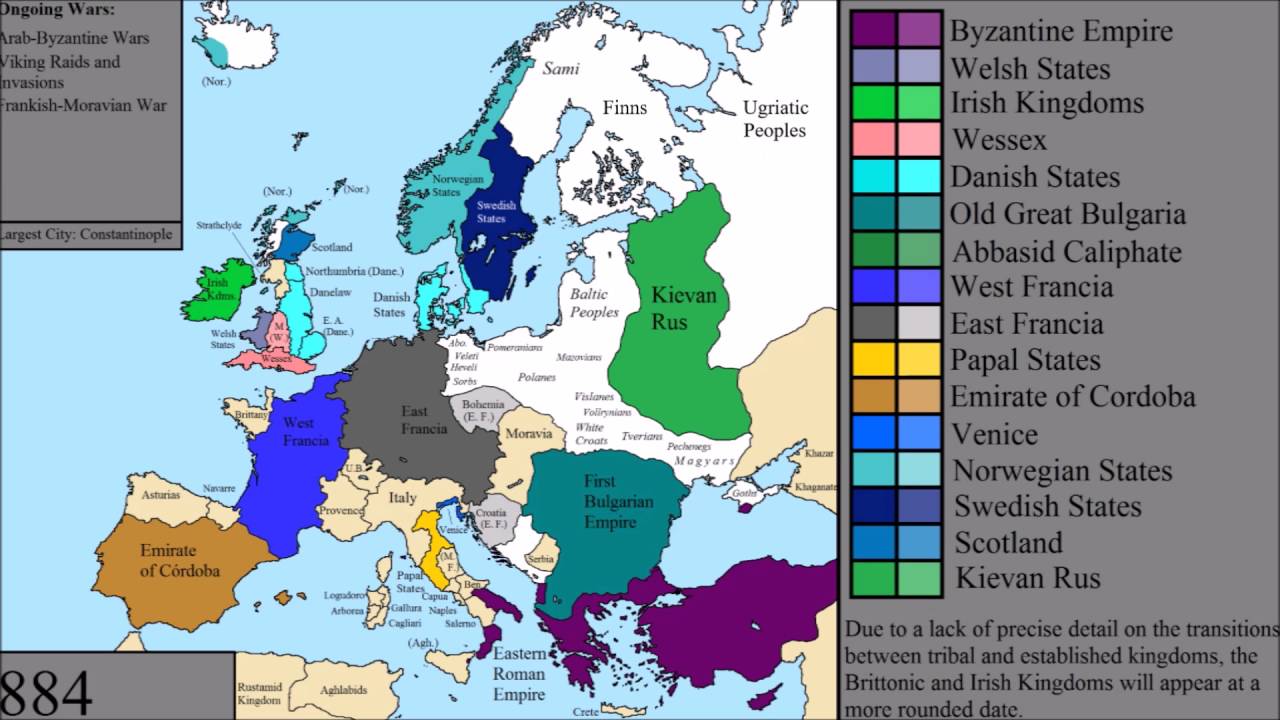
The ever-changing tapestry of Europe, a continent teeming with diverse cultures, languages, and political entities, is best understood through the lens of its historical maps. These cartographic records, spanning centuries, offer a fascinating window into the past, revealing the ebb and flow of borders, the rise and fall of empires, and the intricate dance of power that has shaped the continent’s identity.
Understanding the Evolution of Boundaries:
Historical maps are essential tools for comprehending the dynamic nature of European borders. They demonstrate how these lines, often drawn with ink and ambition, have shifted over time, reflecting political alliances, military conquests, and cultural exchanges. The fragmentation of the Roman Empire, for instance, is vividly portrayed in maps from the 4th and 5th centuries, showcasing the emergence of smaller kingdoms and the gradual loss of centralized control. Similarly, the expansion of the Ottoman Empire in the 16th and 17th centuries can be traced on maps, revealing its westward advance and the subsequent impact on European power dynamics.
Unveiling the Rise and Fall of Empires:
Beyond merely depicting territorial changes, historical maps provide invaluable insights into the rise and fall of empires. They highlight the vastness of Charlemagne’s Carolingian Empire in the 8th century, showcasing its dominance over much of Western Europe. Conversely, maps from the 18th and 19th centuries illustrate the decline of the Holy Roman Empire, a complex web of states and principalities struggling to maintain unity in the face of growing nationalism. These maps serve as visual reminders of the cyclical nature of power, demonstrating how empires, once seemingly invincible, can crumble under the weight of internal strife, external pressures, and the relentless march of time.
Illuminating Cultural and Economic Exchange:
Historical maps also shed light on the intricate network of cultural and economic exchange that has characterized Europe throughout history. Trade routes, depicted on maps from the Middle Ages onward, reveal the vibrant flow of goods, ideas, and people across the continent. The Silk Road, connecting Europe to the East, is a prime example, showcasing the vast distances traversed and the diverse cultures involved in this ancient trade network. Similarly, maps depicting the Hanseatic League, a powerful medieval trading alliance, highlight the interconnectedness of European cities and the economic power they wielded.
Visualizing Conflict and Cooperation:
Historical maps are particularly valuable in understanding the complex interplay of conflict and cooperation that has shaped Europe. They graphically depict the major battlefields of wars, from the Thirty Years’ War to the Napoleonic Wars, offering a visual understanding of the scale and impact of these conflicts. Conversely, maps detailing the formation of alliances, such as the Concert of Europe in the 19th century, demonstrate the efforts towards maintaining peace and stability. These maps serve as reminders that Europe’s history is not solely defined by war, but also by periods of diplomacy and collaboration, highlighting the continent’s capacity for both conflict and cooperation.
Understanding the Impact of Technological Advancements:
The evolution of cartographic techniques itself is a testament to the progress of science and technology. Early maps, often based on imprecise measurements and limited knowledge, gradually became more accurate and detailed with the advent of new tools and methods. The development of the printing press in the 15th century revolutionized mapmaking, enabling wider dissemination and access to cartographic information. This technological advancement facilitated the exchange of knowledge and ideas, contributing to the growth of scientific understanding and exploration.
Frequently Asked Questions about Historical Maps of Europe:
1. What is the earliest known map of Europe?
The earliest known map of Europe is the "Tabula Peutingeriana," a 12th-century copy of a Roman road map dating back to the 4th century. This map, despite its inaccuracies, provides a glimpse into Roman cartographic techniques and the understanding of geography at that time.
2. How did the invention of the printing press impact mapmaking?
The invention of the printing press in the 15th century revolutionized mapmaking by enabling mass production and wider dissemination of cartographic information. This facilitated the exchange of knowledge and ideas, contributing to the growth of scientific understanding and exploration.
3. What are some of the most significant historical maps of Europe?
Some of the most significant historical maps of Europe include:
- The Tabula Peutingeriana (4th century): An early Roman road map providing a glimpse into Roman cartographic techniques.
- The Hereford Mappa Mundi (13th century): A medieval world map depicting Europe as the center of the universe.
- The Mercator Projection (16th century): A revolutionary map projection that accurately depicts the shape of the Earth.
- The Atlas of France (17th century): A detailed and accurate map of France, showcasing the advancements in cartographic techniques.
- The Map of the French Empire (18th century): A map depicting the vastness of Napoleon’s empire at its peak.
4. How can historical maps be used in modern research?
Historical maps are invaluable tools for modern research in various fields, including:
- History: To study past events, political boundaries, and cultural exchanges.
- Geography: To understand the evolution of landscapes and the impact of human activity.
- Archaeology: To locate and interpret archaeological sites.
- Environmental Studies: To analyze historical patterns of land use and environmental change.
Tips for Using Historical Maps:
- Consider the context: Understand the time period, the creator’s perspective, and the intended audience of the map.
- Look for symbols and legends: Decipher the symbols and legends used on the map to understand its meaning.
- Compare with other maps: Compare different maps from different time periods to trace the evolution of borders, cities, and other features.
- Use digital tools: Utilize online databases and mapping software to access and analyze historical maps.
- Engage in critical thinking: Consider the limitations of historical maps, such as inaccuracies and biases.
Conclusion:
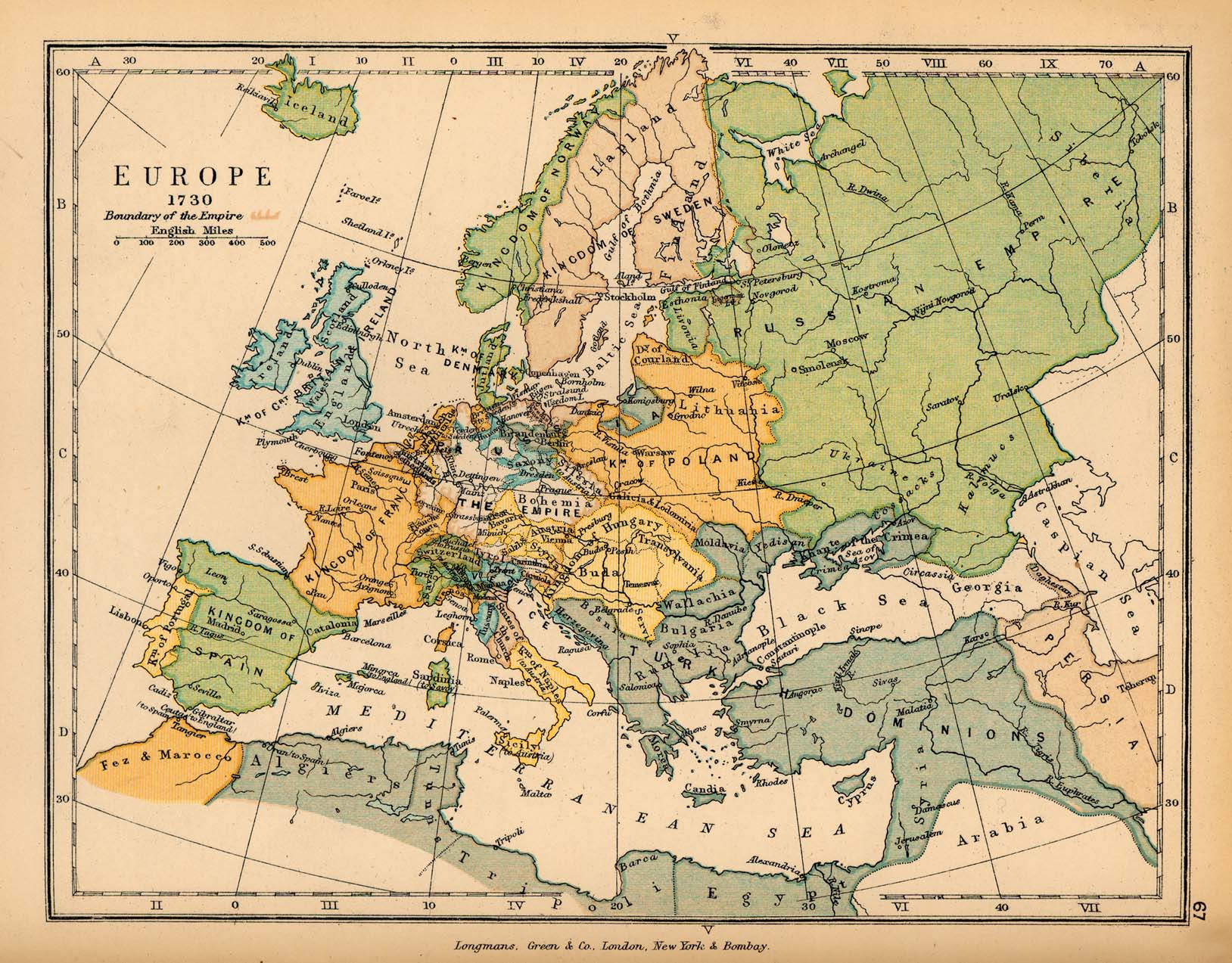
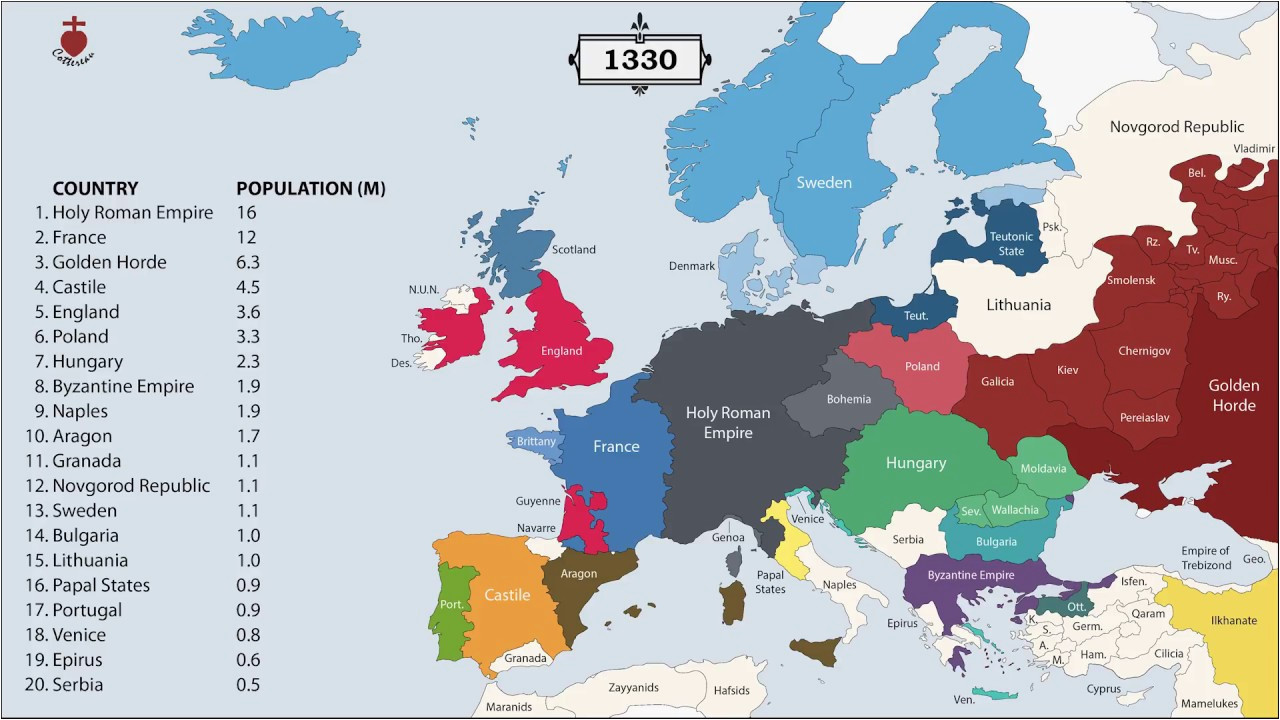
Historical maps of Europe are not mere static representations of the past; they are dynamic narratives that unfold the continent’s rich and complex history. They offer a visual understanding of the evolution of boundaries, the rise and fall of empires, the intricate web of cultural and economic exchange, and the interplay of conflict and cooperation. By studying these maps, we gain invaluable insights into the forces that have shaped Europe and continue to influence its present and future. Their enduring legacy lies not just in their ability to document the past, but also in their power to inspire further exploration and understanding of the dynamic forces that continue to shape the continent.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring Historical Maps of Europe. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!