A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the African Biomes Map
Related Articles: A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the African Biomes Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the African Biomes Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the African Biomes Map
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/4247569/Africa_comp.jpg)
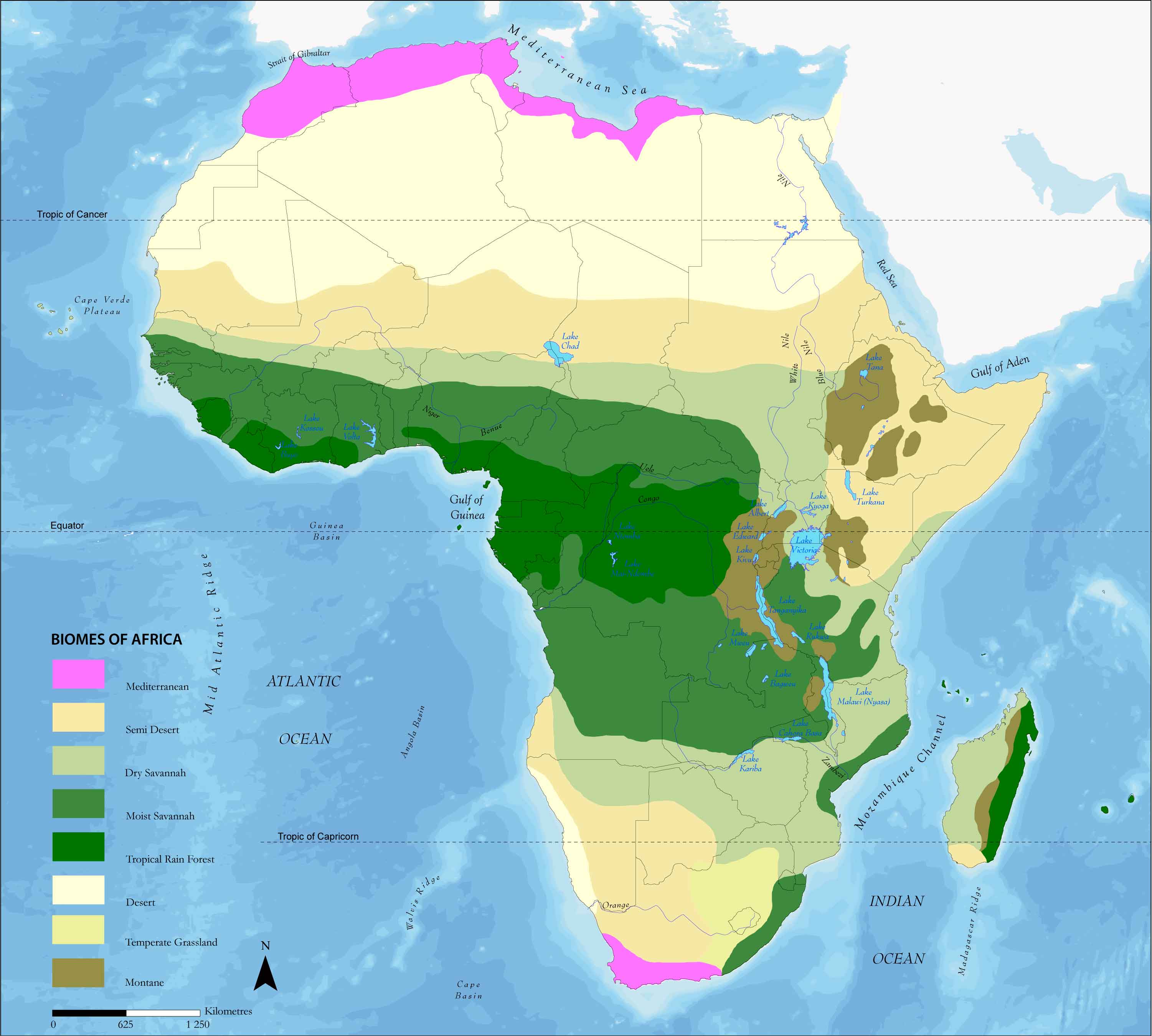
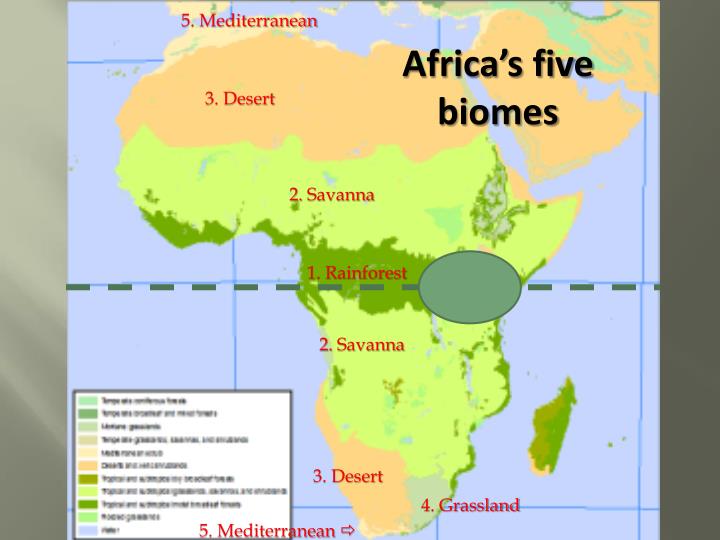
Africa, the second-largest continent, boasts a stunning array of landscapes and ecosystems, a testament to its vast size and diverse geological history. This rich tapestry of life is best understood through the lens of biomes, distinct ecological communities characterized by their dominant vegetation, climate, and wildlife. The African biomes map, a visual representation of these biomes, serves as a crucial tool for understanding the continent’s biodiversity, ecological processes, and the challenges faced by its ecosystems.
Delving into the African Biomes Map: A Visual Guide to Africa’s Ecology
The African biomes map reveals a fascinating mosaic of distinct ecosystems, each with its unique characteristics and adaptations.
1. Tropical Rainforests: Where Life Thrives in Abundance
Found primarily in Central and West Africa, the tropical rainforests are characterized by high rainfall, consistently warm temperatures, and dense, multi-layered vegetation. These forests are home to an extraordinary diversity of life, including iconic species like gorillas, chimpanzees, okapis, and a vast array of birds, reptiles, and insects. The dense canopy creates a humid and shadowy environment, supporting a unique ecosystem with intricate food webs.
2. Savannas: The Vast Grasslands with Scattered Trees
Dominating the landscape of East and Southern Africa, savannas are characterized by grasslands interspersed with trees, often acacia or baobab. The savanna biome experiences a distinct wet and dry season, with the dry season marked by frequent fires. This biome is home to iconic African wildlife, including elephants, lions, zebras, giraffes, and a diverse range of herbivores and predators.
3. Deserts: Harsh Environments with Remarkable Adaptations
The Sahara Desert, the world’s largest hot desert, dominates North Africa, while the Namib and Kalahari deserts occupy the southwest and south, respectively. These arid regions experience extreme temperatures, limited rainfall, and sparse vegetation. Despite the challenging conditions, deserts support a surprising diversity of life, including desert foxes, camels, scorpions, and a variety of hardy plants.
4. Mediterranean Woodlands and Shrublands: A Blend of Temperate and Arid Influences
Located along the northern and southern coasts of Africa, these biomes experience mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. They are characterized by evergreen forests and shrublands, often dominated by olive, oak, and pine trees. The Mediterranean biome supports a unique mix of flora and fauna, including fynbos in South Africa, a diverse ecosystem known for its unique floral diversity.
5. Montane Grasslands and Forests: Elevational Biodiversity
The higher elevations of Africa, particularly in the Ethiopian Highlands and the Eastern Rift Valley, support montane grasslands and forests. These biomes experience cooler temperatures, higher rainfall, and unique plant and animal communities adapted to these conditions. The Ethiopian Highlands, for example, are home to the endangered Ethiopian wolf and the endemic Gelada baboon.
6. Wetlands: Vital Habitats for Aquatic Life and Biodiversity
Africa’s wetlands, including swamps, marshes, and floodplains, are critical habitats for a wide range of aquatic life. These biomes are often characterized by high levels of biodiversity, supporting diverse fish populations, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. The Okavango Delta in Botswana and the Sudd in South Sudan are examples of significant wetland ecosystems in Africa.
The Importance of the African Biomes Map: A Tool for Conservation and Understanding
The African biomes map plays a crucial role in understanding the continent’s ecological dynamics and guiding conservation efforts.
1. Conservation and Management:
The map provides a framework for identifying and prioritizing areas of high biodiversity and ecological significance. It helps focus conservation efforts on areas most vulnerable to habitat loss, degradation, and climate change. Understanding the specific threats faced by each biome allows for tailored conservation strategies, ensuring the long-term survival of its unique flora and fauna.
2. Understanding Ecosystem Services:
The map highlights the crucial role of each biome in providing essential ecosystem services, such as clean water, air purification, pollination, and carbon sequestration. By understanding the interconnectedness of different biomes, we can better manage these services and mitigate the impacts of human activities on the environment.
3. Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation:
The map provides insights into the vulnerability of different biomes to climate change. Understanding the potential impacts of climate change on each biome, such as changes in precipitation patterns, temperature fluctuations, and increased frequency of extreme events, allows for the development of adaptation strategies to protect vulnerable ecosystems and communities.
4. Sustainable Development and Resource Management:
The map helps guide sustainable development practices by providing information on the ecological carrying capacity of different biomes. Understanding the limits of resource use and the potential impacts of human activities on the environment allows for informed decision-making and promotes sustainable resource management.
5. Education and Awareness:
The African biomes map serves as an educational tool, raising awareness about the continent’s incredible biodiversity and the importance of conservation. By visually illustrating the diverse ecosystems and their unique features, the map fosters appreciation for the natural world and encourages responsible environmental stewardship.
FAQs about the African Biomes Map:
Q1: What are the factors that determine the distribution of different biomes in Africa?
A: The distribution of biomes in Africa is primarily influenced by:
- Climate: Rainfall patterns, temperature variations, and the presence of distinct wet and dry seasons play a significant role in shaping biomes.
- Altitude: Elevational changes influence temperature, rainfall, and vegetation patterns, creating distinct montane biomes.
- Soil Type: Soil composition and nutrient availability influence plant communities and overall ecosystem structure.
- Human Activities: Deforestation, land use changes, and agricultural practices have altered the distribution of biomes over time.
Q2: How does climate change impact the African biomes?
A: Climate change poses significant threats to African biomes, with potential consequences including:
- Shifting Precipitation Patterns: Changes in rainfall distribution can lead to droughts in some areas and increased flooding in others, impacting vegetation and wildlife.
- Temperature Increases: Rising temperatures can lead to heat stress, changes in plant growth cycles, and shifts in species distribution.
- Sea Level Rise: Coastal biomes are vulnerable to sea level rise, leading to habitat loss and saltwater intrusion.
- Increased Frequency and Severity of Extreme Events: More frequent and intense droughts, floods, and storms can disrupt ecosystems and threaten biodiversity.
Q3: What are some examples of conservation efforts aimed at protecting African biomes?
A: Numerous conservation initiatives are underway to protect African biomes, including:
- National Parks and Protected Areas: Establishing protected areas helps safeguard critical habitats and biodiversity.
- Community Conservation: Involving local communities in conservation efforts helps ensure sustainable resource management and community ownership of conservation initiatives.
- Reforestation and Habitat Restoration: Restoring degraded ecosystems through reforestation and habitat restoration projects helps mitigate the impacts of deforestation and land degradation.
- Species Conservation Programs: Targeted conservation efforts focus on protecting endangered or threatened species and their habitats.
- International Collaboration: Collaboration between countries and international organizations is essential for addressing transboundary conservation challenges and promoting sustainable development.
Tips for Using the African Biomes Map:
- Explore the map in detail: Pay attention to the distribution of different biomes and their unique characteristics.
- Identify areas of high biodiversity and ecological significance: Focus on these areas for conservation efforts.
- Consider the impacts of human activities on different biomes: Analyze how land use changes, agriculture, and resource extraction affect each biome.
- Use the map to guide sustainable development practices: Ensure that development projects minimize environmental impacts and promote biodiversity conservation.
- Share the map with others: Educate others about the importance of African biomes and the need for conservation.
Conclusion:
The African biomes map is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s diverse ecosystems and their vital role in maintaining global biodiversity and ecosystem services. It provides a framework for guiding conservation efforts, promoting sustainable development, and mitigating the impacts of climate change. By appreciating the intricate web of life that unfolds across Africa’s biomes, we can foster a deeper understanding of the continent’s ecological richness and inspire responsible stewardship for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Landscapes: Understanding the African Biomes Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!