A Journey Across Continents: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Americas
Related Articles: A Journey Across Continents: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Americas
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Across Continents: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Americas. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Across Continents: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Americas

The Americas, a vast and diverse landmass spanning from the Arctic Circle to the southern tip of South America, presents a captivating tapestry of physical features. Understanding its geography, from towering mountain ranges to sprawling plains, is crucial to appreciating the continent’s unique ecosystems, rich history, and diverse cultures. A comprehensive exploration of the Americas’ physical map reveals a complex interplay of geological forces, climate patterns, and human adaptation that has shaped the landscape and its inhabitants.
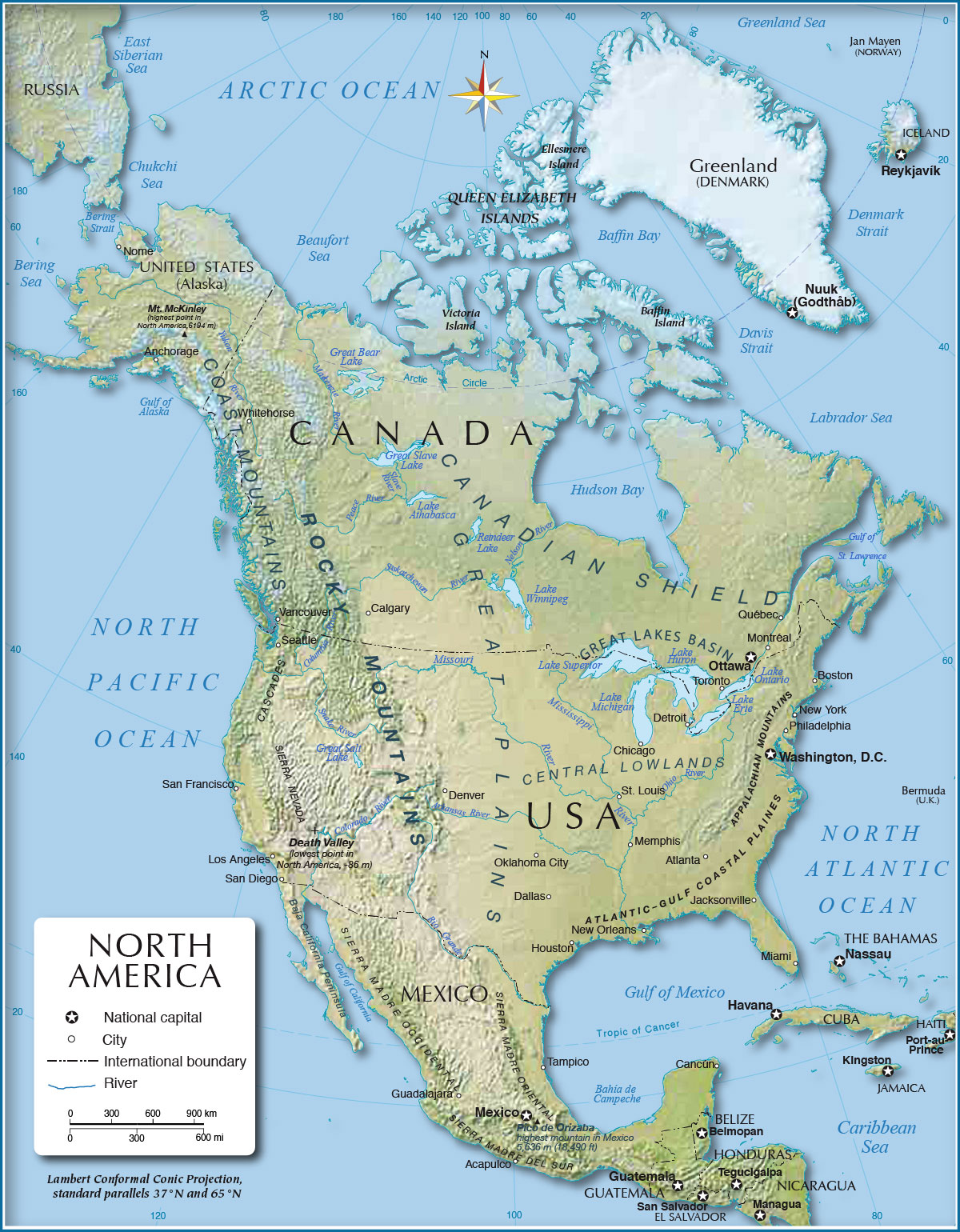
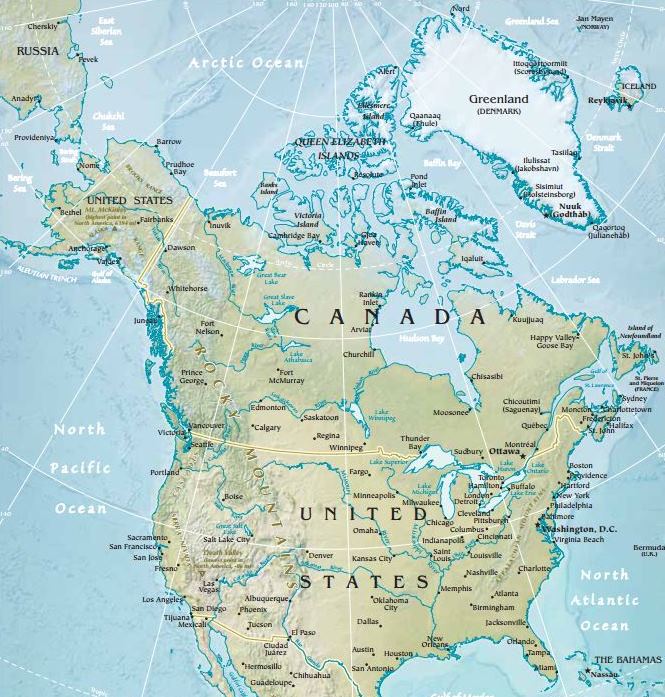
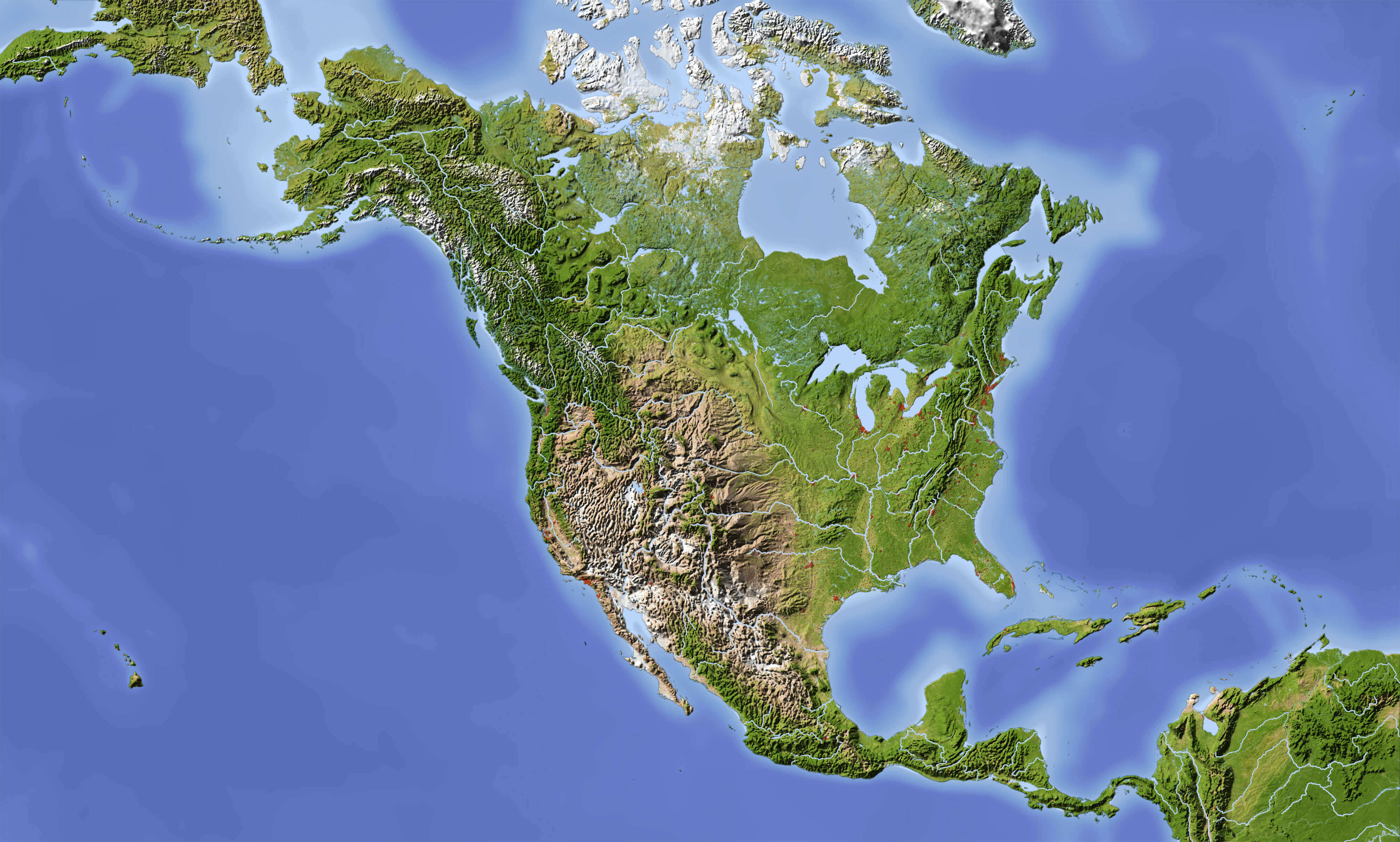
The North American Landscape: A Mosaic of Diverse Features
North America, the northernmost continent of the Americas, showcases a wide range of physical features. The continent’s western edge is dominated by the majestic Rocky Mountains, a vast mountain range that extends from the Canadian border to New Mexico. This iconic range, formed by tectonic plate collisions millions of years ago, boasts towering peaks, deep canyons, and fertile valleys.
East of the Rockies, the Great Plains, an expansive grassland stretching from the Canadian prairies to Texas, stretches across the heart of the continent. This fertile region, once home to vast bison herds, is now a major agricultural hub. Further east, the Appalachian Mountains, a much older mountain range, form a rugged backbone along the eastern seaboard.
The northernmost region of North America is characterized by the vast Canadian Shield, a Precambrian bedrock formation that covers much of Canada. This ancient landmass, dotted with lakes and forests, is known for its mineral wealth and abundant freshwater resources.
North America’s coastal regions are equally diverse. The Pacific Coast, stretching from Alaska to California, is marked by towering cliffs, deep fjords, and fertile valleys. The Atlantic Coast, on the other hand, is characterized by sandy beaches, barrier islands, and numerous estuaries.
Central America: A Bridge Between Continents
Central America, the narrow land bridge connecting North and South America, is a region of dramatic topography and volcanic activity. The Isthmus of Panama, a narrow strip of land separating the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, is a key feature of the region, playing a crucial role in the exchange of flora and fauna between the continents.
Volcanic activity is prevalent throughout Central America, giving rise to majestic volcanoes like Arenal in Costa Rica and Pacaya in Guatemala. These volcanoes, while posing potential hazards, also contribute to fertile soils and stunning landscapes.
South America: A Continent of Extremes
South America, the southernmost continent of the Americas, is renowned for its vast Amazon rainforest, towering Andes Mountains, and expansive grasslands.
The Amazon Rainforest, the world’s largest rainforest, covers much of the continent’s interior, providing a vital role in regulating global climate and harboring an incredible biodiversity.
The Andes Mountains, the longest mountain range in the world, run along the western edge of South America, forming a formidable barrier between the Pacific Ocean and the continent’s interior. The Andes, home to towering peaks like Aconcagua, the highest mountain outside of Asia, are a testament to the powerful forces of plate tectonics.
The Patagonian Steppe, a vast arid region in southern Argentina, is characterized by windswept grasslands and towering peaks. This region, known for its dramatic landscapes and unique wildlife, offers a glimpse into a harsh yet captivating environment.
The Importance of Understanding the Americas’ Physical Map
A thorough understanding of the Americas’ physical map is essential for several reasons:
- Resource Management: The continent’s diverse physical features influence the distribution of natural resources, such as water, minerals, and fertile land. Understanding these resources allows for their sustainable management and equitable distribution.
- Climate Change Adaptation: The Americas’ physical map provides insights into the continent’s vulnerability to climate change. Understanding the impact of rising sea levels, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events is crucial for developing effective adaptation strategies.
- Conservation Efforts: The Americas are home to a vast array of ecosystems, including rainforests, deserts, and grasslands. Understanding the physical features that shape these ecosystems is vital for effective conservation efforts.
- Infrastructure Development: The continent’s physical geography plays a critical role in infrastructure development, influencing the construction of roads, bridges, and other transportation networks. Understanding the terrain and climate conditions is essential for building resilient infrastructure.
- Cultural and Historical Understanding: The physical features of the Americas have shaped the continent’s history, culture, and identity. From the impact of the Andes Mountains on Inca civilization to the influence of the Amazon Rainforest on indigenous cultures, understanding the physical landscape provides a deeper appreciation of the continent’s rich heritage.
FAQs about the Americas’ Physical Map
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in the Americas?
A: The Americas are home to several prominent mountain ranges, including the Rocky Mountains in North America, the Appalachian Mountains in North America, and the Andes Mountains in South America.
Q: What are the major rivers in the Americas?
A: The Americas are traversed by numerous major rivers, including the Mississippi River in North America, the Amazon River in South America, and the Rio Grande in North America.
Q: What are the major climate zones in the Americas?
A: The Americas exhibit a wide range of climates, from the Arctic tundra in the north to the tropical rainforests in the south. Major climate zones include tundra, boreal forest, temperate forest, grassland, desert, and tropical rainforest.
Q: What are the major geological features that shape the Americas?
A: The Americas’ physical map is shaped by various geological features, including tectonic plate boundaries, volcanic activity, and erosion. These features have created the continent’s diverse landscapes, from towering mountains to vast plains.
Q: What are the major ecosystems in the Americas?
A: The Americas are home to a wide variety of ecosystems, including rainforests, deserts, grasslands, tundras, and boreal forests. Each ecosystem supports a unique biodiversity and plays a vital role in the continent’s ecological balance.
Tips for Exploring the Americas’ Physical Map
- Use a variety of resources: Utilize physical maps, atlases, online tools, and geographical databases to gain a comprehensive understanding of the Americas’ physical features.
- Focus on specific regions: Explore different regions of the Americas in detail, paying attention to their unique landscapes, climates, and ecosystems.
- Connect physical features to human activities: Analyze how the physical map influences human settlements, transportation networks, and economic activities.
- Consider historical and cultural contexts: Explore how the Americas’ physical features have shaped the continent’s history, culture, and identity.
- Engage in hands-on activities: Create models, draw maps, and participate in field trips to enhance your understanding of the Americas’ physical geography.
Conclusion
The Americas’ physical map is a testament to the dynamic forces that have shaped our planet. Its diverse landscapes, ranging from towering mountains to vast plains, provide a rich tapestry of natural beauty and ecological diversity. Understanding this map is crucial for appreciating the continent’s unique history, culture, and environmental challenges. By exploring the Americas’ physical features, we gain a deeper understanding of our planet’s interconnectedness and the importance of sustainable management for future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Across Continents: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Americas. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!