A Comprehensive Guide to the Peninsular Malaysia Map
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to the Peninsular Malaysia Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to the Peninsular Malaysia Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to the Peninsular Malaysia Map
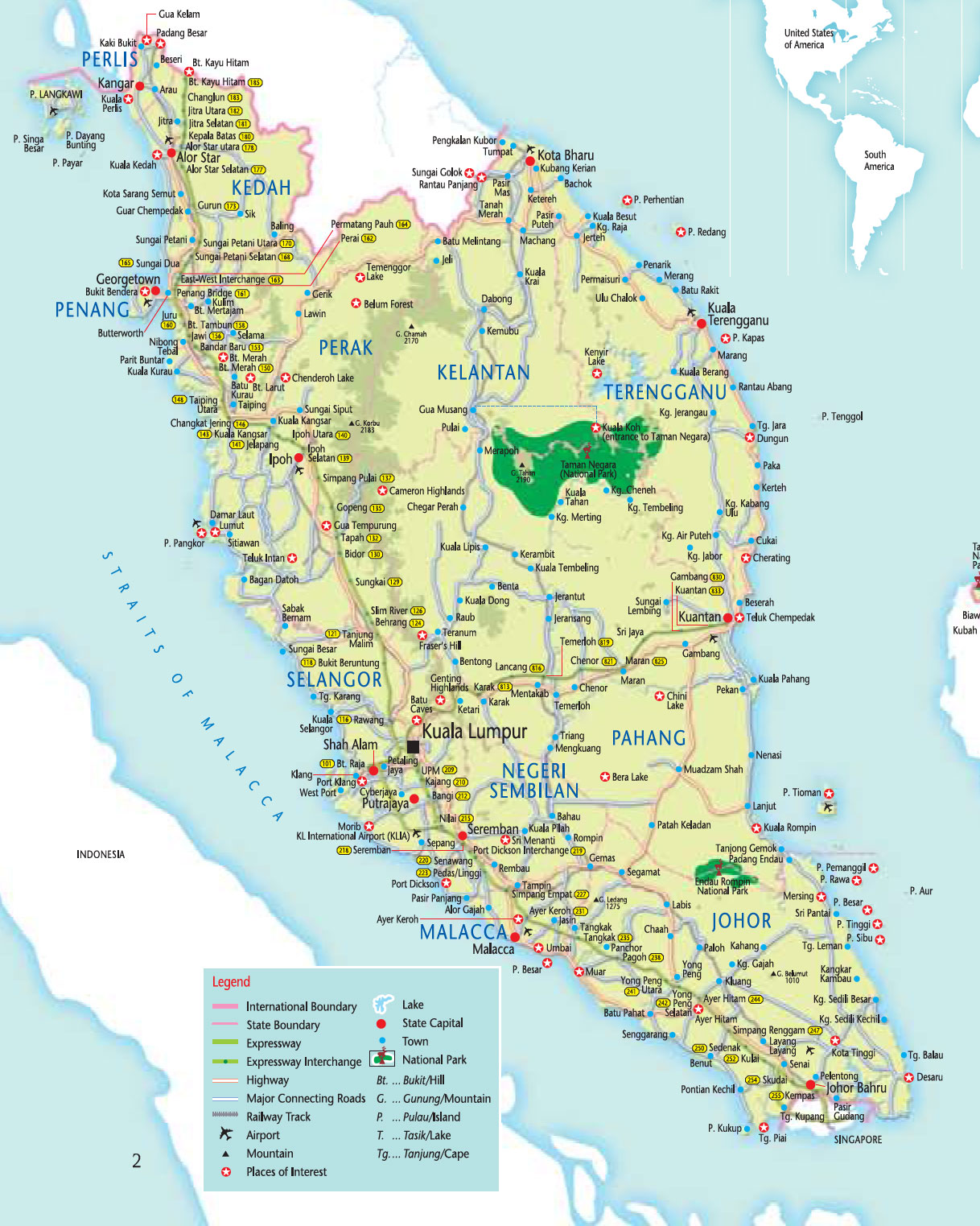
The Peninsular Malaysia map, a vital tool for understanding the geography and cultural tapestry of the nation, offers a visual representation of a diverse and vibrant landscape. This article delves into the map’s key features, exploring its historical significance, geographical complexities, and the cultural and economic importance of its various regions.
Geographical Overview
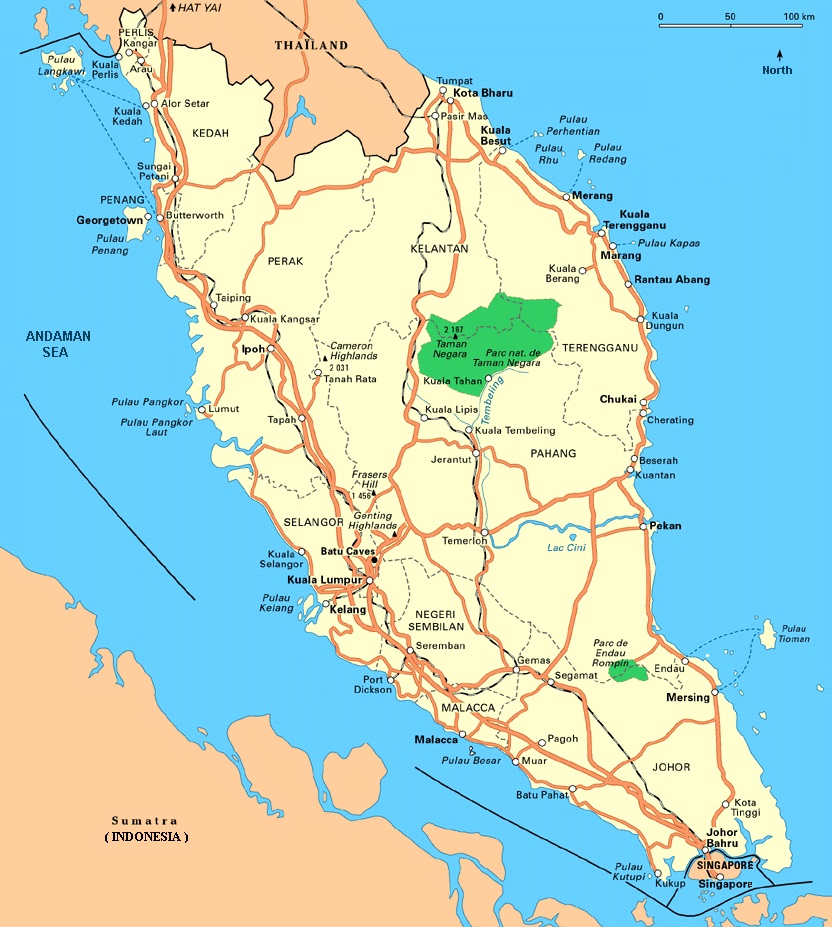
Peninsular Malaysia, officially known as West Malaysia, occupies the southern portion of the Malay Peninsula. This elongated landmass, bordered by the Straits of Malacca to the west and the South China Sea to the east, is a crucial geographic link between mainland Southeast Asia and the Indonesian archipelago. The peninsula is roughly 740 kilometers long and 320 kilometers wide, encompassing a total area of 131,588 square kilometers.
Major Geographical Features
The Peninsular Malaysia map reveals a landscape characterized by distinct geographical features:
- The Central Highlands: This mountainous region, running down the center of the peninsula, is dominated by the Titiwangsa Range, a significant watershed separating the western and eastern coastlines. The highest peak, Gunung Tahan, reaches an elevation of 2,187 meters.
- The Coastal Plains: Both the western and eastern coastlines feature extensive plains, formed by alluvial deposits and ideal for agriculture. These plains are dotted with major cities, including Kuala Lumpur, Johor Bahru, and Penang.
- River Systems: The peninsula is crisscrossed by numerous rivers, including the Perak, Pahang, and Kelantan rivers. These waterways play a crucial role in transportation, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation.
- Islands: The map highlights several islands off the coast, including Penang, Langkawi, and Tioman. These islands are popular tourist destinations, renowned for their beaches, natural beauty, and diverse ecosystems.
Historical Significance
The Peninsular Malaysia map reflects a rich and complex history. The peninsula has been a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange for centuries. Its strategic location along the Strait of Malacca, a vital sea route linking East and West, attracted traders from China, India, and the Middle East. This historical interaction is evident in the diverse cultural heritage of the region.
Cultural Diversity
The Peninsular Malaysia map reveals the country’s cultural richness, a mosaic of ethnicities and traditions. The Malay community, the largest ethnic group, has shaped the nation’s cultural identity. The map also highlights the presence of significant Chinese and Indian communities, contributing to the vibrant cultural tapestry of the peninsula.
Economic Importance
The Peninsular Malaysia map showcases the country’s economic prowess. The peninsula is a major economic hub, boasting diverse industries including agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and services. The map highlights key economic centers like Kuala Lumpur, the national capital and a center for finance and commerce, and Penang, a hub for technology and manufacturing.
Regional Divisions
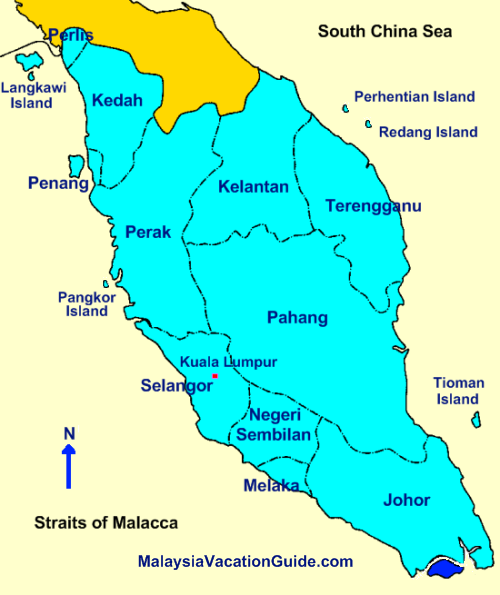
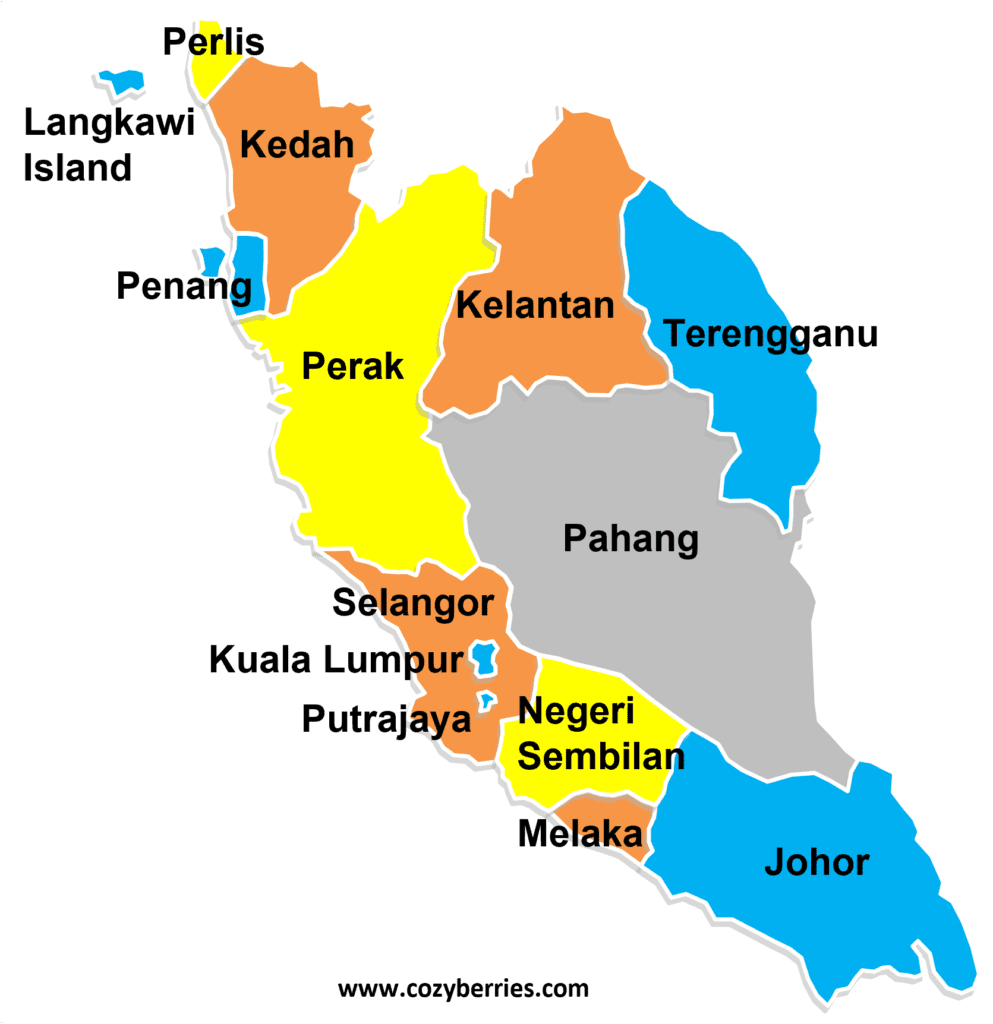
The Peninsular Malaysia map is divided into eleven states and two federal territories:
- States: Johor, Kedah, Kelantan, Melaka, Negeri Sembilan, Pahang, Perak, Perlis, Pulau Pinang, Sabah, Selangor, Terengganu.
- Federal Territories: Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya.
Each state and territory possesses unique cultural, economic, and geographical characteristics, contributing to the overall diversity of the peninsula.
FAQs about the Peninsular Malaysia Map
Q: What is the significance of the Strait of Malacca on the map?
A: The Strait of Malacca, depicted on the map as a narrow waterway separating the peninsula from Sumatra, holds immense historical and economic significance. It has been a vital trade route for centuries, connecting East and West, and remains a crucial channel for global shipping.
Q: What are the major cities highlighted on the Peninsular Malaysia map?
A: The map prominently features major cities like Kuala Lumpur, the national capital, Johor Bahru, the largest city in Johor, and Penang, a popular tourist destination. These cities are important centers for commerce, industry, and culture.
Q: What are some of the key geographical features that impact the peninsula’s climate and ecosystems?
A: The central highlands, the coastal plains, and the river systems play a significant role in shaping the peninsula’s climate and ecosystems. The highlands influence rainfall patterns, while the coastal plains provide fertile land for agriculture. The rivers contribute to the biodiversity of the region.
Q: What are the major industries represented on the Peninsular Malaysia map?
A: The map showcases the peninsula’s diverse industries, including agriculture, particularly palm oil and rubber, manufacturing, tourism, and services. These sectors contribute significantly to the national economy.
Tips for Understanding the Peninsular Malaysia Map
- Study the geographical features: Pay attention to the central highlands, coastal plains, and river systems. These features significantly impact the peninsula’s climate, ecosystems, and human settlements.
- Locate the major cities: Identify key urban centers like Kuala Lumpur, Johor Bahru, and Penang. These cities play crucial roles in the economy, culture, and politics of the peninsula.
- Explore the cultural diversity: The map reflects the diverse ethnicities and traditions that make up the peninsula’s cultural mosaic. Learn about the Malay, Chinese, and Indian communities and their contributions to the nation.
- Consider the historical context: The map reveals the peninsula’s strategic location and its role as a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange. Understanding this historical context provides valuable insights into the present-day landscape.
Conclusion
The Peninsular Malaysia map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the nation’s rich history, diverse culture, and economic dynamism. By delving into its geographical features, cultural tapestry, and economic landscape, the map provides a comprehensive overview of this vital region. It highlights the peninsula’s strategic location, its natural beauty, and its importance as a key player in the global economy. The map is not merely a static image; it is a dynamic representation of a nation in constant evolution, a testament to the enduring spirit of its people.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to the Peninsular Malaysia Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!